Money Supply in India
advertisement

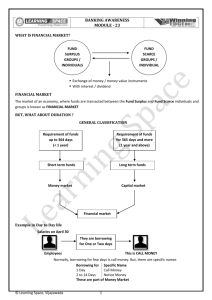
Money Supply in India Monetary policy refer to steps taken by RBI to regulate cost and supply of money in order to achieve certain socio Economic objective like price stabilization full employment, exchange regulation and increased economic growth There is no unique measure to money aggregate Money Supply M : M1 + M2 + M3 + M4 M1 It consist of • Currency notes and coins with public ( excluding cash in hand of all banks) • Demand deposit ( excluding inter bank deposit) • Deposit held with RBI ( excluding IMF,PF, guarantee fund & adhoc liabilities N A RROW MONEY M2 • M1 PLUS • Saving deposit with post office saving bank M3 • M1 PLUS • Time deposit of commercial bank & cooperative • bank ( excluding inter bank deposit) It includes net bank credit to government +bank credit to commercial sector + net foreign exchange assets + government currency liability to the public BROAD MONEY M4 • M3 PLUS • Total deposit with post office organization The growth in money supply must be higher then the growth in the real national Income This stems for two reasons (i) As income grows ,the demand for money as one of the component of saving tends to increase (ii) An increase in money supply is also necessitated by gradual reduction of the non-mentioned sector of the economy. In our country, the rate of increase in money supply has been far excess of the rate of growth in real national income Money stock measure ( Rs crores) M1 1990-91 2001-02 92,890 4,21,200 Post office saving 4,210 bank deposit 5,040 M2 4,26,240 97,100 Time deposit with 1,72,940 banks 10,75,930 M3 2,65,830 14,97,130 Total post office deposit 14,680 25,970 M4 2,80,510 15,23,100 Money Market MM is “ Centre for dealings, mainly of a short term character, in monetary assets; it meets the short term requirement of the borrowers and provides liquidity or cash to the lenders. It is a place where short term surplus investible funds at the disposal of the financial and other institution and individual are bid by borrowers, again comprising institutions and individual and also by government Function of Money Market • It provides various kind of credit instrument to augment the money supply • It helps to minimise the gluts and stringencies in money market due to seasonal variations in the flow of and demand of funds • It helps in quick transfer of funds Operation in Money Market • Call (overnight) money • Notice money • Commercial Bills • Treasury Bills • Certificate of Deposit • Commercial Paper Features of Investment methods in Money Market MM instruments Minimum Amount per transaction Period Secured /Unsecured Liquidity Participant 182 days treasury bill 0.25 1-182 days Secured Easy Open to all Commercial bills 0.50 1-90 days Secured Reasonable Sh. Com. Banks,coop. Banks, MF etc Certificate of 0.25 deposit (CD) 46-365 days Secured Moderate Open to all Commercial Papers 0.25 90-180 days Unsecured Moderate Open to all Call Money 1 1 day Unsecured Easy Sh. Com. Banks,coop. Banks, MF etc Notice Money 0.50 2-14 days Unsecured Easy Sh. Com. Banks,coop. Banks, MF Call/Notice Money • All categories of bank and financial institution are allowed to participate in call/notice market. The fund are lent for one day or from Saturday to Monday or for a period up to 14 days. Both the borrower and lender have current account with the RBI. It is also used by banks to maintain CRR/SLR level to avoid punitive measure by the RBI Commercial Bills One ways the bank extend credit to their customer is by discounting their commercial bills. Such credit bill finance is repayable on maturity of the bill. The eligibility criteria prescribed by RBI for rediscounting a bill stipulates interalia that the bill should fall withi 90 days from date of discounting. The bill discounting rate is dictated by the market force & there is less volatility in interest rate in this then call market. 182 Days Treasury Bills This is a short term government debt securities introduced in November 1986. The treasury bill is issued on auction by RBI. It is issued at a discount and on maturity the face value is paid to the holder. Every fortnight ,RBI invites bids for sale of 182 days treasury bills Certificate of Deposit RBI introduced CD in 1989. CD is a front ended negotiable instrument, issued at a discount and face value is payable at maturity by the issuing bank. The CD are short-term deposit instrument for a period ranging from three month to one year. The discount rate for the issue of CD are market driven. Commercial Paper The RBI introduced a scheme of CP in January 1990. CP is a short term negotiable money market Instrument and is issued by companies in the form of a usance promissory note, redeemable at par to the holder on maturity. The period of CP is 15 days to 365 days from date of issue and is issued at a discount. Role of DFHI Established in 1988,it was established by RBI jointly with PSU banks and all-India Financial Institution to deal in short term monery market instruments. DFHI has branches in Delhi, Calcutta, Chennai, Ahemdabad and Bangalore. DFHI also provides ‘ repos ’ facility ( buy-back and sell-back) to banks, selected financial institution and PSU’s upto a period of 14 days at predetermined interest rate.