LANs & WANs Requirements and Internet
NETWORKS
LANs & WANs Requirements and
Advantages & Disadvantages of the Internet
Learning Objectives
Discuss the hardware and software requirements for LANs and WANs to function.
Identify the advantages and disadvantages of using the Internet.
Structure Diagram
COMMUNICATIONS
MAIN MEMORY ROM
INPUT DEVICES OUTPUT DEVICES PROCESSOR
AUXILIARY
STORAGE
Communications
Sending and receiving data to and from other computers.
Communications software
Necessary to allow computers to communicate.
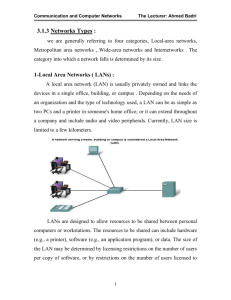
Network Components for a LAN
Network Cards & Cables
N etwork I nterface C ards
( NIC s)
Allows communication between computers in a LAN.
Cable
Connects the computers together.
Repeater
Amplifies the signals between two LANs that are too far apart.
Is not intelligent and simply amplifies all signals whether they are intended for computers on the other segment or not.
LAN 1
Repeater
LAN 2
Hubs
Hub
Hubs
Is not intelligent as all signals received by a hub are retransmitted down every other cable connected to it enabling a physical star network.
Multi-port repeaters.
Bridges
Amplifies the signals between two LANs that are too far apart.
Is intelligent as it only amplifies signals which are intended for computers on another LAN.
Intelligent Repeater
LAN 1
Bridge
LAN 2
Note: Networks with combined typologies (like the one below) are called Tree or Hybrid networks.
Stations Server Stations Server
Switch
Backbone
Switch
Switch
Switch
Stations
Server
Stations
Server
Switch
A switch is intelligent as signals received by a switch are only sent to the intended recipient computer (not down all cables) .
Intelligent hub
Like a bridge but can link many LANs.
It allows many terminals all to use the same communications line (backbone – fast medium e.g. optical fibre) between network segments at different times.
If all stations want to access the main network, the switch has no affect on the speed of this link and it may be necessary to upgrade the link to the main network.
WANs (
W
ide
A
rea
N
etworks)
Networks with computers that cover a large geographical area.
e.g. large companies with offices or factories in widely separated areas, like Microsoft, IBM, Ford, AT&T, etc.
The internet is also an example of a WAN.
Will usually use some form of long range telecommunication e.g. telephone wires, satellite links etc…
Network Components for a WAN
Routers
LAN Router
Public network
Router LAN
Routers
Connect LANs & WANs together.
e.g. connect a LAN to the internet using one IP address.
Directs signals down different routes according to their desired destinations.
Analogue Data
Analogue devices such as:
Clocks
Thermometers
Phones
Speakers
Represent variables by an analogous quantity or variations
(modulations) :
Time is represented by the angle of the hands.
Temperature is represented by the height of a column.
Sound waves on a normal phone line or from speakers.
Digital Data
Computers work with data in a digital form.
Streams of 0's and 1's
Need for conversion
If computers are to receive or send analogue data (sensors, speakers, phone lines, etc…).
There must be conversion between analogue and the digital data computers use.
Devices which do this are called:
ADC
s
(
A
nalogue to
D
igital
C
onverters)
Modem
Modem:
A hardware device that allows computers or other digital devices e.g. faxes to communicate using telephone lines.
Converts analogue phone signals to digital data which the computer can understand.
Converts digital data to analogue phone signals so they can be transmitted through the phone line
Firewalls & Proxy servers
Firewall
Software to protect LAN from unwanted access.
Proxy server to allow one Internet connection for whole network.
This allows more control over the internet access of the workstations on the LAN as it acts as an intermediary server.
Internet
The Internet is worldwide and intended to be accessed by anybody.
A global network connecting millions of computers.
More than 100 countries are linked into exchanges of data, news and opinions.
Advantages
Convenience:
accessible at home, work, or through a wireless device
Easy to contact other people no matter where they are.
Access to other cultures
Access to a vast amount of information
Can be used Night or Day - it never stops
Can be used to learn (or teach)
Makes it possible to Telework
Possible to buy and sell things online
Advantages
Can present their work more neatly
Pupils can share ideas
Less waste of paper
Disadvantages
Must have a home computer
Transmission of viruses
Must have Internet / Modem
Must remember passwords / usernames
Pupils can copy off others
Disadvantages
Undesirable sites may be accessed
Have to pay for internet access
May receive unsolicited e-mails from undesirable characters
Health reasons
Demand on equipment
Can waste time exploring unreliable sites
Can get distracted playing games
Plenary
What are the hardware and software requirements for LANs and WANs?
LANs & WANS
Communications Software
Cable
Server
Network Card
WANs
Communications Software
Server
Modem
Plenary
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using the Internet?
Advantages
Allows communication.
Pupils can share ideas.
Large amounts of educational material.
Allows students to access information to help with studies and to enjoy their learning.
Allows student to learn at own speed / at own times.
Disadvantages
Many sites do not give accurate information.
Many sites give access to inappropriate material
(downloading music / ordering drugs / watching pornography).
Health and Safety problems.
Sites available to buy coursework / helps to cheat in examinations.
May allow hacker into your system / viruses prevalent.
Disadvantages
Undesirable sites may be accessed
Have to pay for internet access
May receive unsolicited e-mails from undesirable characters
Health reasons
Demand on equipment
Can waste time exploring unreliable sites
Can get distracted playing games