Slow Twitch and Fast Twitch Muscle Fibres
advertisement

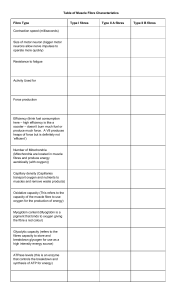
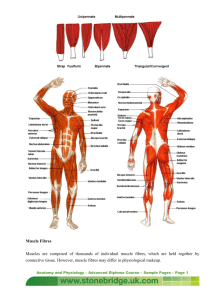
Slow Twitch and Fast Twitch Muscle Fibres Did you eat white meat or dark meat over the holidays? Slow-Twitch Most active during: long-distance running, swimming, and cycling Red or dark in colour Generate and relax tension slowly; able to maintain a lower level of tension for long durations Low levels of myosin ATPase and glycolytic enzymes High levels of oxidative enzymes Fast-Twitch Ideal for: short sprints, power lifting, and explosive jumping Pale in colour Ability to tense and relax quickly; generate large amounts of tension with low endurance levels High levels of myosin ATPase and glycolytic enzymes Fast vs. Slow Approximate Distribution of Muscle Fibre Types for Different Sports The Importance of Myoglobin • The difference in _____________________ is determined by the amount of ____________ used in energy production • Myoglobin: ____________________________ Myoglobin • Slow fibres vs. Fast fibres – Slow twitch fibres are __________ in myoglobin – Fast Twitch Fibres have ______________ amounts of myoglobin 3 Fibre Types Type I or Slow-Oxidative (SO) Type IIA or Fast-Oxidative Glycolytic (FOG) Type IIB of Fast-Glycolytic (FG) Why the Split of Type II Fibres? • Studies have shown that there is evidence for changing the type ________to Type ______ muscle fibres with endurance training • THERE IS NO WAY ANY TYPE ___ MUSCLE FIBRES CAN BECOME TYPE ____ • In other words a fast twitch muscle can _________become a slow twitch muscle Characteristics of Different Muscle Fibre Types So how are the fibres distributed? • How a muscle works is determined by its fibre type and vice versa • TWO categories for basic muscle functions: – Tonic – Phasic Tonic Muscles • These are used on a daily basis for • High concentration of _________ twitch fibres (Type I) • Great for endurance activities • Core and back muscles: constantly contracted Phasic Muscle • Higher percentage of ________ twitch fibres • Example: Biceps have a lower amount of Type I fibres and a higher amount of type II because they are used for explosive movement (lifts) So how do you find where these fibres are? • The only true way is to do a _____________to find the percentage of each type of fibre. • Muscle biopsy: tissue sample using a needle to take a small amount from the muscle belly Athletic Performance • Elite athletes may have __________% of a specific fibre type in their body Why does Kenya keep winning in long distance? • You are going to read a short article on page 91 • Answer the following questions – What has been found regarding the Kenyan’s muscle fibre type? – What social factors have played a large role in Kenyan runners?