Strategies for Academic Success
advertisement

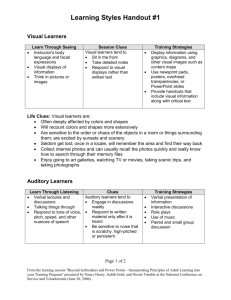
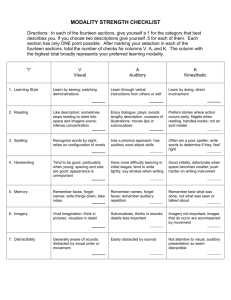
Strategies for Academic Success Jackie Rautio Grand Valley State University How do you define Success as a Student? Successful students: Have Good Study Habits Understands themselves as learners Are persistent Learn from their mistakes Are willing to ask for help Find an internal/personal reason to learn material Set goals and put the necessary time and effort toward them. Different types of learning styles: Visual – learn best by seeing and visualizing Auditory – learn best by hearing Kinesthetic – learn best by doing Reading & Writing –often associated with visual learning Mixed Modality Learning Style 1. learn with a little of all styles – no strong preference, or can easily adjust to the situation 2. Need to use all 4 types of styles Visual learners Keen sense of visual media and art Remember information presented in pictures or diagrams Strong visualization skills. They can look up and ‘see’ the information Make ‘movies in their minds’ of the information they are reading Pay close attention to the body language of others (facial expressions, eyes, stance, etc.) Study tips for visual learners Avoid visual distractions in study environment Use colors often when studying Note – the brain remembers Red the longest. Draw maps, charts, diagrams Use bright colored ‘sticky notes’ Post where you will see them often. Create flash cards with colored pens Turn your notes into mind maps Watch the teacher Draw pictures and symbols Look at diagrams and pictures in textbooks Use whiteboards Example of mind-mapping Characteristics of auditory learners Accurately remember details of important information from conversations or lectures Have strong language skills and a well-developed vocabulary Often have an interest in music as they can hear tones, rhythms and individual notes Auditory Avoid auditory distractions Talk about what you are learning Study in groups Repeat material out loud when studying Read textbooks out loud Use rhymes and songs to learn Make auditory tapes of important information Use flashcards – recite the answers out loud Ask questions Characteristics of kinesthetic learners Work well with their hands Are often well coordinated and have a good sense of timing Learn by movement Often wiggle/tap feet or move their legs when seated Tactile/Kinesthetic Study Tips Walk around or pace when memorizing Find a safe/non distracting “fidget” tool Try studying when laying on your back or stomach or in a comfortable chair Study with music Use your favorite color to highlight Make games out of learning material Use flashcards actively Vary your activities Write/type lists or information over and over Use whiteboards and markers Short intense study periods Characteristics of read/write learners Like lists and words and often use “To Do” lists Remember information that is displayed as words Like reading and writing Read/Write Study Tips Take notes as you read Rewrite ideas into other words Use dictionaries and make flashcards to remember vocabulary Write things out again and again Re-read things (silently) Write out the steps for solving problems Multi-Modal Some multi-modal learners choose a single mode to suit the occasion or situation. There are others who are not satisfied until they have had input (or output) in all of their preferred modes. They take longer to gather information from each mode and, as a result, they often have a deeper and broader understanding. Test taking Strategies 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Be Prepared – there is no substitute Study material over several days. Take a deep breath before the test and think positively. Read the test over before starting, pay attention to how many points each section is worth. Answer the questions you know first and then go back to the ones you don’t know. Test Taking Strategies cont 6. Read each question all the way through before answering. 7. For multiple choice questions: 1. 2. 3. Try to answer the questions yourself before you look at the answers. First eliminate the obviously wrong answers and then make your choice from the remaining ones. Read the question with the answer in it to see if it makes sense. Test-taking strategies cont 8. True/False questions: make sure both parts of the statement are true and related. 9. Short answer/essay: 1. 2. 3. Jot notes as soon as you get the test to keep focused and remember. Just write the key points Make sure you answer the question. Test Taking Strategies cont. 10. Don’t panic if you draw a blank, try to relax and recall what you know about the subject. 11. If you have time, review the test before turning it in to make sure you have answered all the questions. 12. Keep things in perspective. Some thoughts about test anxiety Some anxiety is okay – it helps motivate us to do our best. When anxiety gets in the way: What is the stressor? Fear of failing Parental disapproval Self-pressure Lack of preparation Difficulty of material Remember that your grade on a test is not a measure of your worth as a person. It is a measure of your performance in one class on one day. General Study Strategies Find a study environment that works best for you. Schedule regular study time and keep it. Study in short blocks of time and take breaks Study the most difficult subject first Look at the rubric before, during and after the project Keep track of your grades and progress. Learn from your mistakes on tests and assignments. Edit all papers for grammar and spelling. Ask for support from your friends and family. Reward yourself for work well done! Thank you!