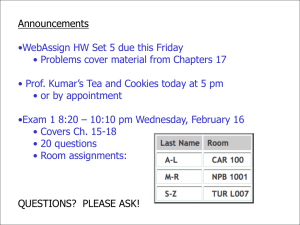
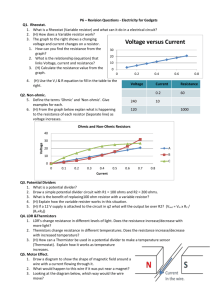
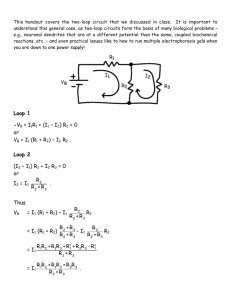
Elecrtonics_L1
D & T Design Lesson
MacPherson Secondary School
Technological Areas -
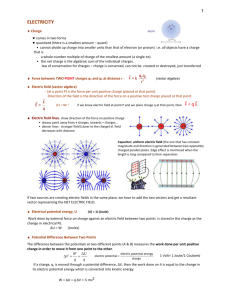
Electronics
Sec 3B
By: MdmLee Kah Gek
1
Technological Areas
Structures
Mechanisms
Electronics
2
Electronics Module
3
Objectives
1. Know basic electronics components and its function ( Res, var res, relay, transistor, temp sensor and light sensor)
2. Learn the electrical symbols.
3. Series and Parallel Circuits
4
Power Supply
• AC rating ( 230V, 110V, 415V)
• AC to DC power supply
• DC to DC power supply
• Batteries
5
Switches
• Samples of switches
6
1. Resistor (fixed and variable)
Resist electricity
Used to supply the correct voltage to the various components in an electric circuit.
Variable resistor
7
Task 1: Read the resistor value
• Write down the colour code
• Check the table
• State the resistor value
8
Series and Parallel connections
A
R
1
R
2
Three resistors in series.
Total Resistance AB is
R
T
R
1
R
2
R
3
R
3 B
R
1
P
R
2
Two resistors in parallel
Q
Total resistance PQ is
1
R
T
1
R
1
1
R
2
9
Exercise 1: Find the total resistance
Q1.
A
30 K Ω 6.67 K Ω
B 40 K Ω
P
Q2.
P
Total resistance
= R
1
+ R
2
= 30 K Ω + 6.67K Ω
= 36.67 k Ω
10 K Ω 30 K Ω
Q
60 K Ω
Q
1
R
1
R
1
1
R
2
1
R
1
40000
1
60000
R
1
24000
24000
24 K
20 K Ω 40 K
Total top series resistance
Ω
= 10 K Ω + 30 K Ω
= 40 K Ω
Total bottom series resistance
= 20 K Ω + 40 K Ω
= 60 K Ω 10
V
1
Voltage Divider
I
R
1
Va
R
2
Voltage can be stepped down from
9 V to 3 V and 6V.
Va
V
1
R
1
R
2
R
2
Or Va = IR
2
50K
By replacing the 10K resistor with a 50K variable resistor, we can vary the stepped down voltage.
11
Exercise 2: a) Device A has a voltage drop of 2 V across it and needs to draw a current of 4 mA. Suggest a suitable value for resistor R.
Voltage across resistor
Device
A = 3 – 2 V
3V
= 1 V
R
V=IR
1 = 0.004R
R = 250 Ω b) What is the circuit arrangement below called? If A and C are connected across a 6 V battery, calculate the voltage at B if the variable resistor is set to (i) 5 k Ω (ii) 40 k Ω
A
10 k
Voltage divider or potential divider
( i ) Vb
6
5
5
10
2 V
B
C
( ii ) Vb
6
40
40
10
4 .
8 V
12
2. Relay
Electrically operated switch
Coil of wire and a metal lever which changes the position of the switch.
Advantage - permits a low voltage
DC circuit to control a completely separate high-power circuit
13
3. Transistors
Transistors have many uses including switching, voltage/current regulation, and amplification
Two types NPN and PNP
14
4. Temperature Sensors (Thermistor)
Decreases as the temperature rises ( negative temperature coefficient or ntc thermistor)
Increase in resistance with temperature. ( positive temperature coefficient , or ptc thermistor)
15
5. Light Dependent Resistor
(LDR)
A LDR varies it resistance according to the amount of light falling on its surface.
Total darkness -1 MOhm
In bright light - a couple of kOhm.
16
Identify the electronics symbols
17