Modals - AuthorAID
advertisement

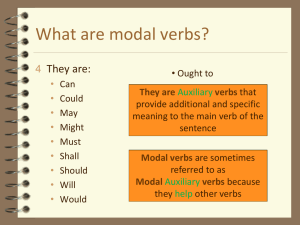
ESL Short Subject Modals Intensive Course in Research Writing Texas A&M University July 11-15, 2011 Susan E. Aiello, DVM, ELS susan@words-world.net WordsWorld Consulting www.words-world.net Modals Auxiliaries that add a specific meaning to a verb Most common: can, could, may, might, must, should Others: ought to/have to, had better, have to, will, would, would rather, would like Modals Show the difference between facts, inferences, and possibilities Modal errors can considerably affect reader’s ability to understand meaning Common Problems Wrong modal chosen to express intended meaning Modal verb phrase incorrectly formed Time reference of modal verb phrase is incorrect Formation of Modal Verb Phrases Present time modal + base form What does he usually do for exercise? He might exercise at the gym, but I’m not sure that he definitely does. (time = present habitual) modal + be + present participle What is he doing right now? He might be exercising at the gym. (time = right now) Formation of Modal Verb Phrases Future time modal + base form What is he going to do tomorrow night? He might exercise at the gym. (time = future) Formation of Modal Verb Phrases Past time modal + have + past participle What did he do last night? He might have exercised at the gym. (time = past) modal + have + been + present participle What was he doing when you called last night? He might have been exercising at the gym. (time = past with an emphasis on duration) Formation of Modal Verb Phrases ought to and have to The modals ought to and have to in the present and in the past have a preposition to in the modal verb phrase. The other modals do not. We ought to/have to study before the test. (present) We ought to have studied more than we did. (past) We had to study hard before the test. (past) versus We should study before the test. We should have studied hard before the test. Functions of Modals CAN to show ability I can run 2 miles. to suggest a possibility or to give an option Students can pre-enroll for certain courses. to ask for or to give permission Can I call you? You can leave when your work is done. to show impossibility It cannot be Jim standing over there. He went away for the weekend. Functions of Modals COULD to show past ability I could run 12 miles when I was in college. to ask a polite question Could I call you? to show possibility Why isn’t Mary here? She could be busy. to show impossibility He could not be here at work. He is out of town. Functions of Modals COULD to suggest a possibility or to give an option You could try going to Dr. Davis to see if he can help. show a past opportunity that was not realized I could have asked for help with the project, but I wanted to do it myself. Functions of Modals MAY to ask for or to give permission (formal) May I call you? You may leave when your work is done. to show possibility The instructor may come to class late today. Functions of Modals MIGHT to show possibility The instructor might come to class late today. Functions of Modals SHOULD to show advisability You should try that new restaurant downtown. to show advisability after the fact We should have tried that new restaurant downtown. But we did not. to show obligation I should renew my driver’s license. It expires next month. to show an obligation that was not carried out I should have renewed my driver’s license. But I forgot to do so. Functions of Modals SHOULD to show expectation You should receive my letter in two days. to show an expectation that was not realized You should have received my letter two days ago. But you did not. Functions of Modals HAD BETTER to show advisability We had better leave. It is getting late. Functions of Modals MUST to show probability or to make a logical assumption Jan must be out this evening. She does not answer her telephone. to show necessity I must call my parents tonight. I have not talked to them in a long time. to show prohibition You must not smoke in the building at any time. Functions of Modals HAVE TO to show necessity Mike has to make up the chemistry lab he missed. to show lack of necessity I am glad that I do not have to cook tonight. Functions of Modals WILL to indicate future time I will leave for the airport early on Saturday. to make a promise or to show willingness The federal government will provide assistance to the flood victims. to state a general truth The new car they have developed will run on either gasoline or ethanol. to ask a polite question Mike, will you help me lift these boxes? (Note: time = now) Functions of Modals WOULD to ask a polite question Would you please call me later tonight? to indicate a repeated action in the past When I lived in Detroit, I would wash my car every weekend. to indicate future time in a sentence that is in the past Mark promised that he would help me learn the new software. Functions of Modals WOULD RATHER to show a preference I would rather work late every night than come in on Saturday. Functions of Modals WOULD LIKE to express a desire I would like to go to music school. To express a desire that was not realized I would have liked to have gone to music school. But I did not. Functions of Modals Use modals to adjust the degree of certainty Assertion of fact Assertion showing capability Prediction showing certainty Prediction showing probability Prediction showing possibility none can will should may, might, could Example: Aspirin reduces (the) pain. Functions of Modals Use modals to adjust the degree of obligation Assertion of fact Requirement Strong recommendation/advice Opportunity or option Suggestion none must should can could, might Example: Researchers use the library...