Balancing DFD
advertisement
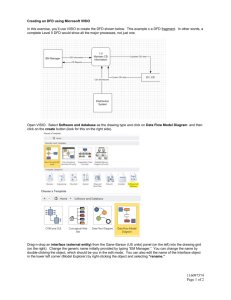
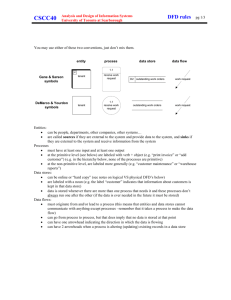
Data Flow Diagram(DFD) 4/13/2015 Introduction to DFD When it comes to conveying how information data flows through systems (and how that data is transformed in the process), data flow diagrams (DFDs) are the method of choice over technical descriptions for three principal reasons. 1. DFDs are easier to understand by technical and nontechnical audiences 2. DFDs can provide a high level system overview, complete with boundaries and connections to other systems 3. DFDs can provide a detailed representation of system components 4/13/2015 DFD Symbol Process Data store Source/Sink Data flow 4/13/2015 Some Rules for External Entities • External people, systems and data stores • Reside outside the system, but interact with system • Either a) receive info from system, b) trigger system into motion, or c) provide new information to system • e.g. Customers, managers • Not clerks or other staff who simply move data 4/13/2015 External Entity Some Rules for Data Stores • Internal to the system • Data at rest • Include in system if the system processes transform the data – Store, Add, Delete, Update • Every data store on DFD should correspond to an entity on an ERD • Data stores can come in many forms: – Hanging file folders – Computer-based files – Notebooks 4/13/2015 D1 Data Stores Some Rules for Data Flows • Data in motion, moving from one place to another in the system – From external entity (source) to system – From system to external entity (sink) – From internal symbol to internal symbol, but always either start or end at a process Data Flow 4/13/2015 Some Rules for Processes • Always internal to system • Law of conservation of data: #1: Data stays at rest unless moved by a process. #2: Processes cannot consume or create data – Must have at least 1 input data flow – Must have at least 1 output data flow – Should have sufficient inputs to create outputs 4/13/2015 0. Processes Data Flow Diagram Types Data Flow Diagram is of two types: • 1. Physical Data Flow Diagram: Physical data flow diagrams are implementation-dependent and show the actual devices, department, people, etc., involved in the current system. • 2. Logical or Conceptual Data Flow Diagram: Logical data flow diagram represents business functions or processes. It describes the system independently of how it is actually implemented, and focuses rather on how an activity is accomplished. 4/13/2015 Physical Data Flow Diagram • Describes about “How a system works”. • Describes the flow of physical data components between physical operations in a system. CUSTOMER ORDER Reject 1 Ordering Processing Clerk Customer Order 4/13/2015 2 Enter into computer file 3 Run LOCATE program Delivery node Logical Data Flow Diagram • Describes about “What a system does”. • Describes the flow of logical data components between logical operations in a system. Reject 1 Receive customer order Customer order 4/13/2015 2 Find Locations of parts 3 Arrange delivery Delivery order Asynchronous operation (a) Asynchronous operation • The two processes are connected through a data store. Hence, the operations of the two bubbles are independent. 4/13/2015 Synchronous operation Synchronous operation • The above two processes are directly connected by a data flow. This means that the ‘validate-number’ process can start only after the ‘read-number’ process had supplied data to it. 4/13/2015 Data Flow Diagramming Rules • Specific rules to DFD is as follows – – – – 4/13/2015 Context Diagram (or Level-0 DFD) Level-1 and lower decompositions Numbering of the processes Balancing across levels Context Diagram of College Database System User Want to view records about students/fac ulty Show the specified records Add a record The specified record is added issue the specified book for the user if available College Database System 0 The specified record is deleted Administrator 4/13/2015 Want to issue books Delete a record Level-1 DFD College Database System User Wants to view Records about students/ faculties Shows the specified record Wants to view records about books/want to issue books Educational Dept 0.1 add or delete student records Add or delete the specified data to database Administrator 4/13/2015 Shows records/issue Wants to the specified view records book if available Library 0.2 Shows records as specified Accounts section 0.3 Level-2 DFD College Database System User Ask to Give records Give records as specified Give records as specified Student 0.1.1 Ask to add or delete record Add or delete record as specified Administrator 4/13/2015 Ask to Give records Faculty 0.1.2 Balancing DFD • The data that flow into or out of a bubble must match the data flow at the next level of DFD. 4/13/2015 Balancing DFD An example showing balanced decomposition In the next level, bubble 0.1 is decomposed. (a) Level 1 DFD In the level 1 of the DFD, data items d1 and d3 flow out of the bubble 0.1 and the data item d2 flows into the bubble 0.1. 4/13/2015 Balancing DFD continued…. (b) Level 2 DFD The decomposition is balanced, as d1 and d3 flow out of the level 2 diagram and d2 flows in. 4/13/2015 What is a Good DFD? • DFDs have a number of features which can be used to ensure that they are self explanatory, complete and unambiguous. The features are: • • • The absence of flowchart structures Conservation of data and Good naming convention 4/13/2015 A good DFD should • • • • Have no data flows that split up into a number of other data flows Have no crossing lines Not include flowchart loops of control statements and Not include data flows that act as signals to activate processes 4/13/2015 Advantages of DFD • DFD is a graphical text used for requirement analysis. • DFD depicts information software without explicit representation of procedural logic • DFD also depicts real time systems with the help of some extended notations 4/13/2015