Project Management Training Outline
advertisement

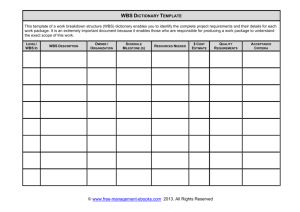
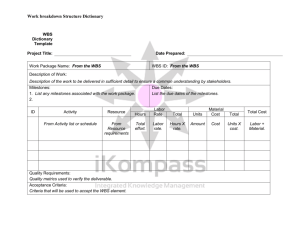
Project Management … an overview Rodney Grubb, PE, PMP, PEM February 28, 2013 Rev 11 4/13/2015 1 Rodney Grubb, PE, PMP, PEM Chairman, ASEM Professional Development & Continuing Education President RMX Technologies, LLC rgrubb@rmxt.co www.rmxtechnologies.net 4/13/2015 2 Today? – 45 minutes Why do we care? Project Management as a Process Some supporting activities – Communication, Earned Value, Risk 4/13/2015 3 Session Guidance Enjoy and learn something useful Focus on communication, EV management and risk Cheer or Boooo … just don’t ignore CWE PM is a Professional Discipline Accepted Body of Knowledge College Degrees Extensive Lessons Learned Professional Society – PMI Certification Program (s), PMP and others Consistent Vocabulary 4/13/2015 5 Why Project Management? Why Plan? In case something happens to the Lead person. To obtain management / team buy-in. – This is what I am going to do. – This is what it will take. – This is how long and how much. As a simulation of the project – don’t forget something. Resources are limited – use them wisely. The tools are good even for small PROJECTS – just use the graded approach. 4/13/2015 6 Why Plan – consequences? 4/13/2015 7 Why is there interest in Project Management? Resources Are Limited Jobs Are Regularly Underestimated Missed Schedules Are Common Staff / Support Downtime is a Wasted Resource – Time Lost Cannot Be Recovered To Get the Most For the $$ Invested – Value Project Management Can Improve the Way We Do Business – Plan, Do, Check, Act Provides a consistent vocabulary and way to do business 4/13/2015 8 What Is A Project? Single set of objectives Finite life span Organized team effort Recognized project manager Impose unique set of requirements on organization Authorized by top management A PROJECT SHOULD BE VIEWED AS A SINGLE ENTITY! Project or Operations? Another way to define a project – by comparison. Scope: Owner to builder: “I said the LEARNING TOWER of PISA.” 10 A Project Management Process Project Objectives – Value SOW – Alignment with Customer – What are the deliverables? – What is in and what is out of scope? WBS – To the Action Level Schedule – Built on WBS Estimate – Resource Loaded Schedule Approval – Know the Decision Maker GO! – Now Manage All Changes (PMBOK shows the process) 4/13/2015 11 Home improvement projects – issues? (risk, scope, objective, cost) 4/13/2015 12 Do you see project issues? Quality, risk, schedule, objective, scope 4/13/2015 13 Project Planning Overview Have you heard: “Scope, Schedule, or Budget: pick two” 4/13/2015 14 Scope Project Triple Constraint Cost/Budget Time/Schedule Plan begins with scope Write scope statement in clear and narrow terms. Provide statement of processes, internal entities, systems, customers, and outside entities that will /will not be part of project. Cross-reference scope statement, project objectives and project deliverables for consistency. Mark Twain – “I am sorry I did not have time to write you a short letter.” 4/13/2015 - 16 Then we must manage scope Scope Creep is the Leading Cause of Project Failure Soooooo … it is really important that we document the scope and then manage changes Booooooooo!! 4/13/2015 - 17 Managing Teams is key to PM Success If Teams are so important to Successful Projects … what does a good team look like? Sports? Business? Professional Organizations? I know it when I see it … 4/13/2015 18 Do you see any team issues?? http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=L 7pXIC49R3c Team Examples Think about the best team you have been a part of. Why was it the best? Research says that the most effective teams have common attributes … what are they? 4/13/2015 20 Any of these attributes? Challenging Work Clear Objectives Over Communication Involvement in planning Team input Shared effort “Good” leader – Attributes? 21 “In the Beginning” …Does your organization charter teams / projects? Why is it important? – Management buy-in – Team Understanding – Definition of Objectives and plan Do you have electronic Project Information? How are project teams chartered in your organization? You can control this process ... Even if the organization does not require it. 4/13/2015 22 WBS Process – The Action List WBS is Work Breakdown Structure – The Preparation is a Process THINK Task List or Action Items Action list to complete the Scope Good Info in Your Book Hierarchy – manageable pieces ALL Of the Work Action Level At the Bottom There is Rarely “ONE Correct WBS” 4/13/2015 23 Intro to Schedules The schedule is the heart of the plan Tie it to the WBS – Action Level – Know who is responsible and involve them in scheduling Understand Dependencies – Predecessors and Successors Define your milestones Use scheduling tools Critical Path Concept – Critical Chain 4/13/2015 24 Once we are underway there are execution processes Measuring Progress (cost and schedule variance) Earned Value Concept Communication Human Resources Risk Management Monitoring Progress Track Against the Plan Communicate the Objectives Regularly Change Management is key – Recognize, document and agree Report Progress – EARNED VALUE is about THE WORK ACCOMPLISEHED not the MONEY SPENT or TIME PASSED. Understand Variance Document what we learn and USE IT for planning, estimating, and risks and problems 4/13/2015 26 Communication is critical to successful project plan & execution Push communication – don’t wait … be proactive – Use your process so something doesn’t get missed – Five times rule – say it, write it, e-mail it … Pull the string … if you feel uneasy then ask the question. “Seek first to understand then to be understood” – Covey Are you listening … or waiting your turn to talk? 4/13/2015 27 COMMUNICATIONS – Succinct? Why? The Six-Word Novel – Hemmingway "For sale: baby shoes, never worn.“ "Epitaph: He shouldn't have fed it.“ “machine. Unexpectedly, I’d invented a time “ "Will this do (lazy writer asked)?“ “He read his obituary with confusion.” "Oh, that? It's nothing. Not contagious." 4/13/2015 28 Again … Communication Consider a Communications (Management) Plan Use Your Computer or PDA to Remind You … Then Call or Visit Vary Communication Format Regularly with the Customer With Team Members – 5 TIMES Rule? With Management 4/13/2015 29 Actual PM Quotes COMMUNICATIONS "We know that communication is a problem, but the company is not going to discuss it with the employees.“ "E-mail is not to be used to pass on information or data. It should be used only for company business." TEAMWORK Quote from the boss: "Teamwork is a lot of people doing what 'I' say." RISK "What I need is a list of specific unknown problems we will encounter." "This project is so important, we can't let things that are more important interfere with it." "Doing it right is no excuse for not meeting the schedule." RISK Management and Contingency Planning – part of planning AND execution What kinds of risk are there? – Scope – Schedule – Financial – Safety Where are the tasks recorded? Some Key questions – KEY TASKS – What Could Go Wrong? – Is it a Big Deal if That Happens? – How Will I Prevent That? – ACTION – What Will I Do When it Happens Anyway? THE NEW ACTIONS GO INTO THE WBS. 4/13/2015 32 RISKS and Contingency Planning Know and use Potential Problem Analysis – PPA – – – – Identify the Critical Tasks from the WBS? Ask what could go wrong at this step? Ask “Is it a big deal if that happens?” Is it is a big deal then how will I prevent it? – What ACTION will I take? Document the action. – What will I do when it happens anyway? THE ACTIONS GO INTO THE WBS. 4/13/2015 33 Risk Management Planning RISK IS: An uncertain event that can have positive or negative effects on our project. The WBS allows us to consider the circumstances and conditions of each deliverable for risks within our project. Once risks are identified, we can then run them through qualitative and quantitative analysis to capture which risks need mitigation and which ones we can live with 4/13/2015 - 34 PPA Form Action Item 4/13/2015 Potential Problem Risk ? PA CA 35 Summary Plan the work – Handle the details – Document the results Use task list, schedule, and budget to measure progress Actively manage and communicate Amount expended AND work completed are necessary to know status When a project ends – document Again and again – Communicate 4/13/2015 36 Class Objectives – how did we do? 1. 2. 3. 4. Define a project? Introduce a PM Process Show how PM elements fit together Intro supporting processes – communications, EV management, risk management 4/13/2015 37 Questions? 4/13/2015 38 Using the Graded Approach to Project Management First – It Has to Be Safe! Think “VALUE ADDED” – Value added – Value enabling – Waste Graded Approach to Planning and Implementation Don’t Spend a Dollar to Monitor a Nickel’s Work How Would I Do It At Home? Start With Common Sense BUT: Some Requirements are Not Negotiable – Safety – Environmental permits 4/13/2015 – Waste management 39 Project Management & Lean Principles Understand Value Added Flow – the Schedule – the Plan Recognize Value Added, Enabling, and Waste in Your Planning, Tasks, and Implementation Critical Path – Critical Chain References – “Building a Project Driven Enterprise” and “Critical Chain” 4/13/2015 40 TEAM CHARTER – a form to use to document “it” (setting up a project) – agreement / contract? Project Team Charter Team – _______________ Date – _______________ Project Objective Statement: Mission / Desired Results: Scope / Guidelines / Schedule: (what is included and excluded) Required Resources: – – – – Equipment: Materials: Support: Budget: Accountability / Communicating Results: (Who, how, and how often) Client: Team: Management: Deliverables / Outcomes / Consequences: Team Members: Approvals – Sign offs 4/13/2015 41 Project Risk Management Project Risk Management processes include: – – – – – – Risk Management Planning - deciding how to approach, plan, and execute risk management activities for a project. Risk Identification - determining which risks might affect project and documenting their characteristics. Qualitative Risk Analysis - prioritizing risks for subsequent further analysis or action by assessing and combining their probability of occurrence and impact. Quantitative Risk Analysis - numerically analyzing effect on overall project objectives of identified risks. Risk Response Planning - developing options and actions to enhance opportunities, and to reduce threats to project objectives. Risk Monitoring and Control - tracking identified risks, monitoring residual risks, identifying new risks, executing risk response plans, and evaluating their effectiveness throughout project life cycle. PM History Video http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=C 1uxCBx2-UQ&feature=fvwrel 4/13/2015 43