Culture
advertisement

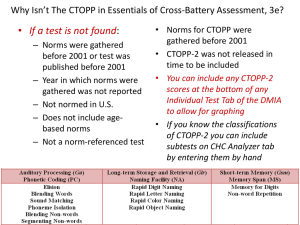
Culture Today: Norms Cultural Relativism Concrete Culture-Share artifacts Language About Test 1 “When a person is down in the world, an ounce of help is better than a pound of preaching.”Edward G. Bulwer-Lytton (Novelist, Playwright, Politician) Values: shared beliefs about what is important Norms: shared rules of conduct • Outline what is acceptable, appropriate • Guide behavior • Based on values Value: respect for elders Norm: give up your seat on the bus if there is someone elderly standing How do we learn norms? • positive and negative sanctions • Sanctions: reactions people get for breaking or following norms Positive Sanctions Negative Sanctions Approval for following a norm Disapproval for breaking a norm Ex: holding an elevator-smile or thank you Ex: stand too closely to someonestep back or weird look 3 Types of Norms: Folkways, Mores (more-ays), Taboo Folkways Mores Taboo Norms that are not strictly enforced Norms that we take seriously and are part of core values Norms that are very strongly ingrained in us and almost unimaginable to violate 3 Types of Norms: Folkways, Mores (more-ays), Taboo Folkways Mores Taboo Norms that are not strictly enforced Norms that we take seriously and are part of core values Norms that are very strongly ingrained in us and almost unimaginable to violate Husband and wife live in the same home Being faithful to husband/ wife -Open marriages -Multiple wives/husbands 3 Types of Norms: Folkways Mores Norms that are not Norms that we strictly enforced take seriously and are part of core values Mom and Dad sleep in one room, children in another Parents provide children with a safe place to sleep Taboo Norms that are very strongly ingrained in us and almost unimaginable to violate Dad and teenage daughter sleeping in the same bed 3 types of norms Mark didn’t bring a gift to his friend’s birthday party. Mark violated a folkway ___________________________ Mark exchanged his daughter’s hand in marriage for money. In the United States this is _______________________________. taboo mos Mark was hitting his dog badly at the park . Mark has violated a _______ Folkways Mores Taboo Norms that are not strictly enforced Norms that we take seriously and are part of core values (often reflect laws) Norms that are very strongly ingrained in us and almost unimaginable to violate (often reflect laws) Exchanging your daughter’s hand in marriage for monetary compensation Bringing a gift to a birthday party Caring for your pets 1. • • • Assignment 3. Share your cultural artifact. Tell us: your name what you brought what meaning it has for you 2. As people are sharing, record which category of culture you think each item falls under: • Race/ethnicity/nationality • Language • Gender • Socio-economic status • Age • Family Sports • Religion • Political ideology • Interests/hobbies • Experiences • Other:_____ • Subcultures • Culture within larger culture • Have own values, customs etc, • Shares many values of the larger culture Ex: Youth culture, DJ’s, surfers, doctors Counter cultures Holds values that stand in opposition to those of the dominant culture Ex: Swingers, gangs, mafia Culture of society as a whole subculture Counter culture Freeganism and dumpster diving View Info More details Quick Write: 1. Do you think Freeganism is a subculture or counter culture? 2. Why? 3. What are their values? 4. What types of norms might they follow? Subculture: • Culture within larger culture • Has some own values, customs etc, • Shares many values of the parent culture Counter culture: • Holds values that stand in opposition to those of the dominant culture Cultural relativism Examining cultures without judging its elements as superior or inferior to ones own way of life Study habits Favorite team Political beliefs Religious beliefs Child rearing + Positive Is cultural relativism a good thing? Can it be a bad thing? -Negative Language Defined: Set of symbols that • expresses ideas • allows people to think and communicate Language The Summer Institute for Linguistics (SIL) Ethnologue Survey (2012) lists the following as the top languages by population: (number of native speakers in parentheses) Mandarin Chinese (937,132,000) Spanish (332,000,000) English (322,000,000) Bengali (189,000,000) Hindi/Urdu (182,000,000) Arabic (174,950,000) Portuguese (170,000,000) Russian (170,000,000) Japanese (125,000,000) German (98,000,000) French(79,572,000) Language Guides perceptions There are words that exist in certain languages that do not have a an equivalent in others Examples: •girlfriend/boyfriend doesn’t exist in Urdu •Kuya/Ate (older brother/sister in Tagalog) •Ta’arof- Farsi term referring to etiquette, politeness, cultural obligations doesn’t exist in English Culture and Language are interdependent because • Humans learn and transmit our culture through language Culture and Language What we say influences what we think what we feel and what we believe What think, feel, and believe influences what we say Language Moribund (endangered language) • Moribund = spoken only by a few older people and unknown to children • Many world languages will be extinct or moribund within the next 100 years • An entire way of thinking is lost each time a language becomes extinct Endangered Languages • View National Geographic Map of endangered languages • View Enduring Voices Project How to study for Test 1 1) Use the study guide on the website! 2) Fill out answers 3) Master the information 4) Test yourself 5) Study with a classmate The test is 20 questions, 17 from the lecture and 3 based on the reading (with some overlap). Review your notes, the Power Point slides posted on the course website, and reading assignments. To do • • • • • • • Read Test 1 Coming Up Be on time-class continues after the test Bring a standard 50 question scantron E-882 and pencil Multiple choice, 15 questions Study class notes, ppt slides on website, and text reading Study guide posted on website Partner Activity-Language and Culture. Write down responses. What do you think these proverbs might tell us about what the culture values? 1. “Lower your voice and strengthen your argument.” (Lebanese proverb) 2. “A bird in the hand is worth two in the bush.” (American proverb) 3. “E moa i tangata ringa raupa.” “Marry a man with blistered hands.” (Maori Proverb, New Zealand) 4. “Anda tu camino sin ayuda de vecino.” “Walk your own road without the help of a neighbor.” (Mexican proverb) 5. "When the brothers fight to the death, a stranger inherits their father's estate.” (Nigerian proverb) What do these proverbs tell you about what the culture values? Lebanese Proverb “Lower your voice and strengthen your argument” American Proverb “A bird in the hand is worth two in the bush” Maori Proverb (New Zealand) “E moa i tangata ringa raupa.” “Marry a man with blistered hands.” Mexican Proverb “Anda tu camino sin ayuda de vecino.” “Walk your own road without the help of a neighbor.” Chinese Proverb “Don’t add legs to the snake after you have finished drawing it” Nigerian Proverb "When the brothers fight to the death, a stranger inherits their father's estate.” What is socialization? Socialization – the process by which we learn the ways of our society. In other words… how we become who we are ongoing lifelong process How others influence us: 1. Charles Horton Cooley-Looking Glass Self 2. Erving Goffman-Dramaturgy 3. George Herbert Mead-Development of self-concept Charles Horton Cooley Looking Glass Self 1) We use others as mirrors 2) Look at their eyes, body language, and listen to them to assess ourselves 3) We develop a self- concept. Determine if our actions are having the desired effect. Erving Goffmam Dramaturgy • Noticed a conflict between what we want to do and what we feel people want us to do • View of social life as a series of dramatic performances (theatre) Erving Goffmam Dramaturgy Impression management= actions and statements made to control how others view us Erving Goffman Dramaturgy Front stage: actor’s performance in front of an audience A model walking in a run way show A doctor performing surgery Someone out on a date Erving Goffman Dramaturgy Back stage: concealing some of the things that go into the “performance” Teacher preparing lessons, or speaking freely with co-workers about students ERVING GOFFMAN’S DRAMATURGY • Role conflict: conflict between 2 different roles you preform -student and mom • Role strain: conflict within one role -student taking many classes Be a sociologist •Sociologists study human behavior •Use your observations of student and teacher behaviors in college •Determine behaviors that help and hurt the classroom environment and student learning Underline the top 3 in every category Erving Goffman Dramaturgy • Noticed a conflict between what we want to do and what we feel people want us to do • Social life is a series of dramatic performances = theatre • Impression management= the techniques an “actor” uses to maintain certain impressions Erving Goffman Dramaturgy Front stage: is the part of the actors performance that functions in a generally fixed manner in front of an audience A teacher conducting his lesson in front of a class A model walking in a run way show A doctor performing surgery Someone out on a date Erving Goffman Dramaturgy Back stage: where facts suppressed in front stage or various kind of informal actions may appear. teacher prepares his lessons, or speaks freely with co-workers about students concealing some of the things that go into the performance Erving Goffman Dramaturgy •Role conflict: conflict between 2 different roles you preform -girlfriend and friend •Role strain: conflict within one role -making the right choice as a friend Summary • View How Beliefs and Values Define a Culture 3 types of norms Mark didn’t bring a gift to his friend’s birthday party. Mark violated a folkway ___________________________ Mark exchanged his daughter’s hand in marriage for money. In the United States this is _______________________________. taboo mos Mark was hitting his dog badly at the park . Mark has violated a _______ Folkways Mores Taboo Norms that are not strictly enforced Norms that we take seriously and are part of core values (often reflect laws) Norms that are very strongly ingrained in us and almost unimaginable to violate (often reflect laws) Exchanging your daughter’s hand in marriage for monetary compensation Bringing a gift to a birthday party Caring for your pets