HDR Capture and Display
advertisement

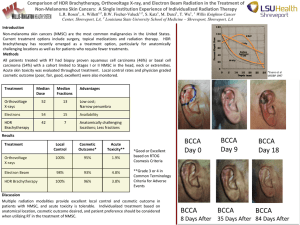
Practical aspects of HDR capture and acquisition (Deconstructing HDR) Francisco Imai CREATE 2010 June 08 2010 Disclaimer Only representing self Views in this presentations are not of any current or past employer Image as representation Ideal Real Tone editing Ansel Adams What about color HDR? Merced River and El Capitan in Winter, Yosemite Valley [in Nature] Image manipulation Definition Dynamic Range maximum non-saturated signal DR = ------------------------------minimum signal Sensor technologies www.pixim.com HDR sensor technology: 1. Multiple gains sensor Advantages: Good low light performance Good linearity Drawbacks: Limited DR extension Additional silicon area Additional power dissipation e.g. Dual column Level amp and ADC [Fowler 09], LOFIC [Adachi 05] from Boyd Fowler [HDRI workshop 2009] HDR capture technology: 2. Non-linear pixel response sensor Advantages: Wide DR > 120 dB Instantaneous measurement High fill factor Simple operation Drawbacks: No low-light video Larger FPN Different sensor architecture No solution for color sensors e.g. Logarithmic sensor [Dierickx 95], Dynamic well capacity adjustment [Sayag 91, Decker 98] from Boyd Fowler [HDRI workshop 2009] HDR capture technology: 3. Well-capacity recycling sensor Advantages: Good linearity Good color imaging Large DR > 100 dB Best SNR Drawbacks: Large pixel size Poor low light performance High power dissipation Needs high speed read-out e.g. Sigma delta pixel level ADC [Fowler 94], Asynchronous self-reset with multiple capture [Liu 02] from Boyd Fowler [HDRI workshop 2009] HDR capture technology: 4. Time to saturation sensor Advantages: Very HDR > 150 dB Drawbacks: High power dissipation Large pixel e.g. Time to saturation [Brajovic 96] from Boyd Fowler [HDRI workshop 2009] HDR capture technology: 5. Time varying exposures Advantages: Use conventional sensors Drawbacks: Motion blur e.g. Two sample CID [Nakamura 97], Two sample APS [Yadid-Peckt 97] Blended exposures HDR capture technology: 6. Spatially varying exposures Advantages: Excellent linearity Color Imaging DR > 100 dB Drawbacks: High power dissipation Large pixel Poor low light performance Needs high speed read-out e.g. DPS pixel [Yang 99], Fuji Super CCD from Boyd Fowler [HDRI workshop 2009] and www.pixim.com Pixim DPS There are plenty of publication on HDR imaging sensors but most of cameras still do not use them. WHY? Example Spherican 180-360 degrees 26 f-stops, 50 Mpixel 20 s to 1 minute 20 f-stops in HD-video Example FujiFim SuperCCD EXR F200 EXR, F70EXR, F80EXR and S200 EXR What to do with captured HDRI? -Tone map to display in conventional displays -Global tone mapping -Local tone mapping -iCAM -Retinex -Build an HDR display How to adjust colors in HDR display? Off-the-shelf components HDR display SIGGRAPH 2005 - Seetzen et al. 14 bits 1300 cd/m2 HDR display modeling HDR display forward model • All possible sextuplets combination is 6256 = 281 trillion • Inaccurate colorimetric measurement in dark region (resulting in green cast in dark areas when model is used) • Problem with cross-terms between LCD and DLP • More robust physical based model is necessary Radiance based Forward model Decompose 12 Component XYZ and perform a priori eigenvector analysis LCD display spectral radiance Red, green and blue ramps LCD additivity Comparison sum of red, green and blue Channels with gray measurements Spectral radiance measurements Photo Research PR-650 Spectral radiance measurement DLP light reflected on MgO2 Close-up measured area for green ramp Measurement Red, Green, Blue Ramps Additivity DLP channels? White is not active White channel White is active Transmittance LCD LCD Radiance Transmittance LCD DLP Radiance Compare LCD radiance between measurement and estimation using forward model Blue Green Red Comparison measured and estimated LCD radiance Estimation Final Radiance Training set Verification 100 “random” samples (20 samples with white on white on DLP) luminance x chroma Hue angle x chroma Inverse HDR model Colorimetric performance 100 Random Samples Extra Verification set (280 samples) Neutral ramp (14 levels) 4 octaves of Color Checker 170 objects (Vrhel) Mean CIEDE2000 = 2.4 Maximum CIDE2000 = 7.7 Excluding 7 outliers (out-of-gamut samples) HDR rendering accuracy assessment Veiling glare Scene-dependent scatter in optics/camera and in the human eye reduce the HDR Talvala SIGGRPAH 2007 Other IQ aspect: SNR from Boyd Fowler [HDRI workshop 2009] Other IQ aspect: Resolution Quick MTF Other IQ aspect: Colour EyeRex – SW by Media Chance Evocative HDR look Nina Aldin Thune Fantoft stavkirke –www.pappafrezzo.com Tunliweb Hype Cycle HDRI Acknowledgments Unanswered questions 1. When are we going to have HDR cameras on cellphone cameras? 2. How to deal with white balance in HDR? 3. What set of metrics is appropriate for HDR display quality?