MS PowerPoint
advertisement

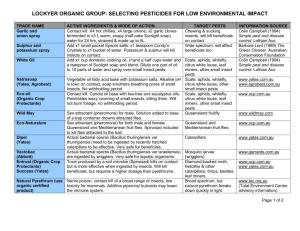
Prepared by Dr. Mike Klahr, Boone County Horticulture Extension Agent Edited by Dr. Tim Coolong, UK Extension Vegetable Specialist Organic Pesticides • Variety of organic pesticides. – Oils – Soaps – Derived from plants – Natural occurring pathogens. • READ THE LABEL! • Follow all label instructions. Trade names are used as examples. No endorsement is intended, nor criticism implied of similar products not mentioned. Always read and follow the product label. Insecticidal Soap • Generally considered to be among the least toxic pesticides available. • Used to control softbodied pests such as aphids and mealybugs. • Must have direct contact. Aphid Mealybug Insecticidal Soap • Non toxic to beneficial insects such as parasitic wasps and ladybugs. • No residual effect. • Once the spray has dried, walking over the soap residue will not harm a moving insect. Aphid Mealybug Insecticidal Soap • Some plants are sensitive to soaps. – – – – – Japanese Maple Lantana Bleeding Heart Ferns Palms • If unsure about plant sensitivity, spray on a small test section. Horticultural Oil: Dormant Oil • Refined petroleum products. • Used to control pests, such as scale, mites, etc. • Interferes with the pest's respiration and membrane function. • For oil to be effective, it must come in direct contact with the pest or egg; therefore, thorough coverage is essential for proper control. Cottony Maple Scale Euonymus Scale Obscure Scale Horticultural Oil: Dormant Oil • Do not use when temperatures are below 40°F or above 100°F. • Don’t spray when humidity will be over 90% for 36 hours; slows drying which may burn plants. • May damage plants when flowering buds are forming and shoot elongation is occurring. • Consult label for list of oil sensitive plants. – Maple, hickory, black walnut Cottony Maple Scale Euonymus Scale Obscure Scale Horticultural Oil: Summer Oil • Highly refined petroleum oil (mineral oils). • May be used during growing season. • Avoid oil sensitive plants. • Oils will also kill predatory mites. • Oils are toxic to fish. Pine Needle Scale Bt-Bacillus Thuringiensis• Naturally occurring bacteria. • Different strains of Bt. • Bt israelensis: mosquito and fungus gnat larva. (MosquitoDunks) • Bt kurstaki: Leaf-eating caterpillars. • Does not control sawfly larva. – Not a true caterpillar. Bt-Bacillus Thuringiensis • Apply when larva are small. • Most be eaten. • Will kill “pest” caterpillars and “desirable” caterpillars. • Do not use in or near a Butterfly Garden! Parsleyworm a.k.a. Black Swallowtail larva Pyrethrin (Pyrethrum) • Mixture of compounds extracted from the flower of pyrethrum daisy (Chrysanthemum coccineum and C. marshalli) • Primarily grown in Kenya. • Used on many plants including fruits and vegetables. • Broad target insecticide also kills mites and spiders. • Quickly paralyze insects. Pyrethrins • Attacks the nervous system. • Very effective contact spray. • Target must be hit directly and spray may need to be repeated. • Broken down quickly by sunlight, moisture, and air. • No residue is left behind. • Toxic to fish and tadpoles. • Toxic to beneficial insect such as honeybees. • Pyrethroid = Synthetic (Man made) Slug Traps • Beer Traps – Alcoholic or nonalcoholic – Fill saucer and sink saucer to ground level – Slugs are attracted to smell, fall in and drown. – Check and replace often. – Dogs may drink the beer. • Cardboard or wooden board. – Slugs hide during the day. – Check board daily. – Drown slugs in soapy water. Beneficial Insects: Ladybugs • Many species of ladybugs – Native and non native. • Ladybugs can feed on as many as 5,000 aphids in its lifetime. • Adult and larva both feed on aphids. Beneficial Insects: Lacewings • Eggs may be laid singly or small groups; usually close to a food source. • Eggs resemble a q-tip. • Larvae are also known as “Aphid Lions” • Adults are weak fliers and feed mostly on nectar and pollen. • More expensive than ladybugs. Beneficial Insects: Braconid Wasps • Many species of braconid wasps. • Species Costesia congregatus attacks tomato hornworm and tobacco hornworm. • Female lays eggs just under the skin. • Larva feed on host from inside and tunnel out. • Once outside, they build cocoons on host. Beneficial Insects: Braconid Wasps • When adults emerge, host soon dies. • Adults are small; about 1/8”. • If you find a hornworm covered in cocoons, leave it. • It will soon die. • It is now the host to a new generation of wasps. Prepared by Dr. Mike Klahr, Boone County Horticulture Extension Agent Edited by Dr. Tim Coolong, UK Extension Vegetable Specialist