Presentation - Business.govt.nz
advertisement
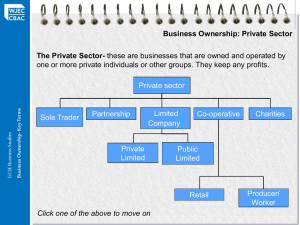
Understanding Business Structures Types of Business Structure • • • • • Sole Trader Partnership Limited Companies Co-operatives Franchises Sole Trader Benefits Benefits include: • Easy to set up and run • Only small amount of capital needed • Owner has total control and doesn’t have to share profits Sole Trader Drawbacks Drawbacks include: • Unlimited liability • Lack of economies of scale • The business relies on the owner 100% Partnership Benefits Benefits include: • Shared responsibility • Allowing partners to specialise • Partners bring in more capital investment • Decisions, costs are shared Partnerships Drawbacks Drawbacks include: • Each partner has unlimited liability • Shared responsibility can lead to disagreements • Profits have to be shared according to Deed of Partnership Limited Companies There are two types: 1. Private Limited Company (Ltd) 2. Public Limited Company (Plc) Private Limited Companies Benefits include: • Company can raise more capital by selling more shares • Shareholders can keep control of the business Private Limited Companies Drawbacks include: • Accounts must be audited • Limited companies are more difficult to set up • Shares cannot be sold publicly on the stock market Public Limited Companies Benefits include: • Easy to raise capital for expansion by selling shares on the stock market • Economies of scale are better than a private Ltd company Public Limited Companies Drawbacks include: • Expensive to set up (a lot of capital is required) • Annual accounts must be made public • Anyone can buy shares – so it’s vulnerable to takeovers Co-operatives There are two types: 1. Worker Co-operatives 2. Consumer Co-operatives Worker Co-operatives… …Are owned by the whole workforce …Everyone has a say in the business Consumer Co-operatives… …Are local Co-op shops owned by the customers …The profit is paid out or used to keep prices down Franchises • An existing company (the franchisor) lets someone else (the franchisee) use its business idea and name • The franchisee buys a licence to carry out the business of the franchisor • The franchisee must also run the business in the same way as the franchisor • In return, the franchisor helps the franchisee set up the business Find out more with Business.govt.nz: Business.govt.nz provides free access to a wide range of resources, including tools and interactive content. It acts as a gateway to government and private sector business information, news and services. Next steps: • • • • • Overview of business structures Understanding business structures Focus on sole traders Focus on partnerships Focus on companies