Synonyms, antonyms and acronyms
advertisement
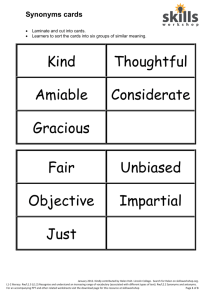
Synonyms, antonyms and acronyms Teaching notes Jan 2012. Kindly contributed by Helen Holt, Lincoln College. Search for Helen on www.skillsworkshop.org Visit the download page for this resource to find detailed teaching notes, curriculum links and related resources. This PPT accompanies four other resources: a Smart Notebook file and three worksheets. All are available on www.skillsworkshop.org Curriculum links. Rw/L1.2 Recognise and understand the vocabulary associated with different types of text, using appropriate strategies to work out meaning (a) Understand the types of word likely to be used in different kinds of text, depending on the context and purpose (b) Understand the use and effect of specialist vocabulary in particular text types Rw/L1.3 Recognise and understand an increasing range of vocabulary, applying knowledge of word structure, related words, word roots, derivations, borrowings (a) Understand that some words are related to each other in form and meaning, and use this knowledge to help understand new words (b) Understand that prefixes and base/stem/root words can provide clues to meaning (c) Understand that languages borrow words from each other (d) Understand that suffixes can provide clues to word class Rw/L2.2 Use reference materials to: find the meanings of unfamiliar words to research a subject or topic (a) Understand that there are different sources of information for word meanings, how they are structured, and the conventions they use, e.g. paper and electronic dictionaries, glossaries, keys (b) Understand that there are different types of dictionary, e.g. contemporary usage, slang, quotations, etymological, antonyms and synonyms (c) Understand that it is possible to research a subject or topic from different sources, e.g. encyclopaedia, text books, internet, journals Reference: Excellence Gateway (2009), Skills for Life, Core Curriculum http://www.excellencegateway.org.uk/sflcurriculum SfL LITERACY SYNONYMS, ANTONYMS AND ACRONYMS Helen Holt 2 Session Outcomes You will be able to: • understand and know the difference between synonyms, acronyms and antonyms • increase own range of vocabulary and use of alternative words • improve dictionary and thesaurus skills Helen Holt 3 What are synonyms? • They are different words with similar meanings • …and can be any part of speech (e.g. nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs). Helen Holt 4 Synonym Examples: • Confused – muddled – puzzled – addled • Love – affection – desire – lust • Run – sprint – jog – trot – hurry Helen Holt 5 Why learn synonyms? …because, by giving us numerous ways to say the same thing, they make our language and writing more interesting and skilful. Helen Holt 6 Activity Using the hand-out, replace the highlighted words with appropriate synonyms. He went up the noisy stairs to the attic. The key to the old door was muddy: he had dug it up from the garden earlier that day. The lock made a clunk as he turned the key and the door creaked as he slowly pushed it open. It was cold and dark in the attic. He could not believe what he saw between the flashes of thunder from the angry storm. Helen Holt 7 antonyms? What are An antonym is the opposite meaning of a word. For example: • Narrow - • Hard - • Strong - wide broad open soft supple limp weak fragile shaky Helen Holt 8 Write 3 antonyms for each of the following words : • Large – • Noisy – • Ugly – • Easy – • Young – • Clever – Helen Holt 9 What are acronyms: Acronyms are shortened versions of a word. They are usually formed using the initial letter of each word. For example: - BBC (British Broadcasting Corporation) - USA (United States of America) - UN (United Nations) Helen Holt 10 Activity 5: What do the following acronyms stand for? EMA MP PM CV VAT PIN BT VW NI DVD CD JSA FE ISA Helen Holt 11 Any Questions? Helen Holt 12