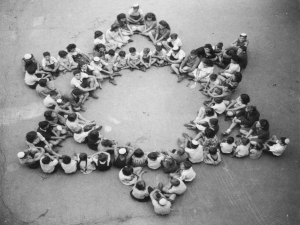Jewish Children in the
Warsaw Ghetto in 1942
A History of Jewish People in
Europe
An estimated 9 million Jews lived in the 21
countries that would be eventually
occupied by German forces during WWII
By the end of WWII, two thirds of
European Jewry were murdered
Nazi Racism
“Germanic Races” were
better than all others
Nazi scientists developed
extensive tests to prove
that they were anatomically
superior.
Aryan race must remain
pure so that it could one
day take over the world
Hitler’s ideal Aryan was tall,
blond haired and blue eyed
Jesse Owens
1936 Olympics
Germany
As early as April 1, 1933,
Germans boycotting
their businesses
Kristallnacht
November 9, 1938:
the “Night of Broken
Glass”
– 1000+ synagogues
burned
– 7000 Jewish
businesses were
trashed and looted
– dozens of Jewish
people were killed
– Jewish cemeteries,
hospitals, schools,
and homes were also
looted
– police and fire
brigades stood by
and did nothing
The Nuremburg Race Laws
Jews to be second-class
citizens
Jews were no longer eligible to
Fascination With Noses
German Nose
Jewish Nose
– Vote
– Marry
– Sex with German ‘blood’
Christians with Jewish
grandparents = Jew
Yellow Star of David
Identified as Jew.
- Mr. / Mrs.
- Seats
- Stores
Other “inferiors”
- “J” stamp on Id. Cards
Jehovah’s Witnesses, Gypsies (Roma),
- ‘Sterilization’
and Homosexuals
- Medical Experiments / Twins
Ghettos
By 1939, 80,000
Jewish people were
forced into ghettos—
designated areas in
the city where Jews
were compelled to
live
The Final Solution
By 1941, Hitler ordered that all Jews in
Nazi-occupied Europe be rounded up and
sent to the extermination camps to be
killed en masse
Dachau
Concentration Camps
Families
Split Apart
Labour
Camps
Concentration / Death Camps
Electrified barbed-wire fences
kept prisoners within the confines
of the camps
A door to the gas
chamber in Auschwitz.
The note reads:
“Harmful Gas! Entering
Endangers Your Life”
NAZISM 1919-1945 – Reading p.1100
Death Camps -Jews from all over occupied
Europe to death (extermination) camps in Poland where
they were killed en masse
Shoes
Gas Lorry
Ovens
A mass grave in the Bergen-Belsen
concentration camp, 1945
Gas Chambers / Shower
Concentration / Death Camps
Corpses of women piled up in
Auschwitz, February 1945
An SS guard stands among the
prisoners killed in his concentration
camp April 27-30, 1945
The Aftermath
In 1945, when Allied troops
entered the concentration and
death camps, they discovered
piles of bones and ashes—
testimony to Nazi genocide.
Soldiers also found thousands of
survivors suffering from starvation
and disease. After liberation,
many Jewish survivors refused to
return to their former homes
because of the antisemitism that
persisted in Europe.
Consequently, there were many
displaced persons who sought
refuge in other countries.
Auschwitz Survivors Greeting
their Liberators
AS SOLDIERS ENTERED THE
CAMPS THE REAL TRUTH WAS
SEEN FOR THE FIRST TIME
General Eisenhower
“Take pictures because someday someone
will say this never happened”
http://www.blinkx.com/watch-video/memories-of-the-camps-frontline-documentary-part-1-of-6/edtgG2fVjMoDzfZMCtYa4A
“None is too Many”: Canada’s Role
PM Mackenzie King “Nothing can be gained by
creating an internal problem in the effort to
meet an international one”
Canadian secretary of State in 1939:
“So long as Canada has an unemployment
problem, there will be no ‘open door’ policy to
political refugees here.”
After Kristallnacht Thomas Crerar suggested that
10,000 Jews be allowed to immigrate to Canada
Cabinet Immigration Minister Fred Blair :
“None is too many”
“None is too Many”: Canada’s Role
Canada’s policy had tragic consequences in
1939 when the ocean liner St. Louis that
was carrying 900 Jewish refugees was
denied permission to dock in Canada
The St. Louis was forced to return to
Europe, where most of the passengers died
in concentration camps
“None is too Many”: Canada’s Role
Between 1933 and 1945, Canada opened
its doors to less than 5,000 Jewish people
Of the 65,000 refugees let into Canada
through 1948, only 12% were Jewish
Number of Jewish refugees brought
into countries during 12 year Nazi Rule:
United States
200,000
Palestine
125,000
Britain
70,000
Argentina
50,000
Brazil
27,000
China
25,000
Bolivia and Chile 14,000
CANADA
5,000
LESSONS OF THE HOLOCAUST
A Personal Reflection
And I Said Nothing
In Germany they first came for the Communists
and I didn't speak up because I wasn't a
communist. Then they came for the Jews, and I
didn't speak up because I wasn’t a Jew. Then
they came for the trade unionist, and I didn't
speak up because I wasn't a trade unionist.
Then they came for the Catholics, and I didn't
speak up because I was a Protestant. Then they
came for me and by that time no one was left to
speak up.
(Cont. next page)
For Discussion:
“The World is too dangerous to
live in—not because of the people
who do evil, but because of the
people who sit and let it happen.”
–Albert Einstein
Do you agree or disagree with
Einstein’s statement? Why?
A PERSONAL REFLECTION - Keep these questions in mind:
Who is to blame for the Holocaust? (Germans??, Hitler??, Nazis??,Others??)
Could the Holocaust have been stopped?
How do the "Stages of Isolation" show the gradual persecution leading to
the annihilation of the Jews?
What would you have done if you lived in Germany during the Third
Reich?
How does the passage "And I Said Nothing" portray the actions of the
people in Germany during Third Reich? What is the danger in saying or
doing "nothing"?
What lessons must be learned from the Holocaust?
How do we, as responsible and aware human beings, ensure that an
event such as the Holocaust or any type of racial genocide never occurs
again?
Do you think we have “learned our lesson” from the Holocaust,
use examples to support your point of view from more recent
history
“On a Brooklyn Subway”
FUNNY?????????
Sent to a local
grocery store
in 2012.