File
advertisement
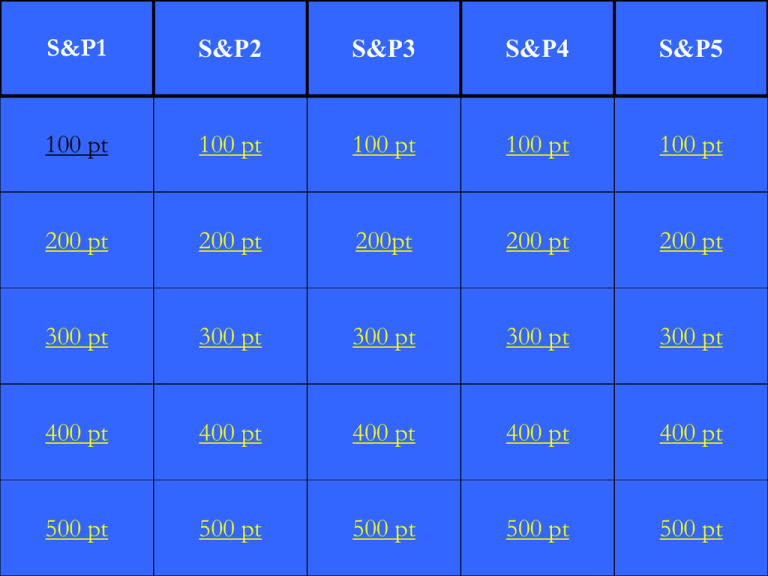
S&P1 S&P2 S&P3 S&P4 S&P5 100 pt 100 pt 100 pt 100 pt 100 pt 200 pt 200 pt 200pt 200 pt 200 pt 300 pt 300 pt 300 pt 300 pt 300 pt 400 pt 400 pt 400 pt 400 pt 400 pt 500 pt 500 pt 500 pt 500 pt 500 pt Drivers detect traffic signals more slowly if they are talking on a cell phone. This best illustrates the impact of SP1-100 Answer: Selective Attention SP1-200 If you move your watchband up your wrist an inch or so, you will feel it for only a few moments. This best illustrates SP1-100 Answer: Sensory Adaptation SP1-200 Some stroke victims lose the capacity to perceive motion but retain the capacity to perceive shapes and colors. Others lose the capacity to perceive colors but retain the capacity to perceive movement and form. These peculiar visual disabilities best illustrate our normal capacity for SP1-300 Answer: Parallel Processing SP1-300 Damage to the basilar membrane is most likely to affect one's SP1-400 Answer: Audition/Hearing SP1-400 Afterimages is most useful in explaining what vision theory SP1-500 Answer: Opponent Process Theory SP1-500 Receptor cells for the vestibular sense send messages to the SP2-100 Answer: Cerebellum SP2-200 The fact that we recognize objects as having a consistent form regardless of changing viewing angles illustrates SP2-200 Answer: Perceptual Constancy SP2-200 People perceive an adult-child pair as looking more alike when told they are parent and child. This best illustrates the impact of A.Shape constancy B.Perceptual set C.Precognition D.Interposition SP2-300 Answer Perceptual Set SP2-300 The way in which you quickly group the individual letters in this question into separate words best illustrates the which gestalt grouping principle SP2-400 Answer: Proximity SP2-400 Interpreting new sensory information within the framework of a past memory illustrates SP2-500 Answer: Top-down processing SP2-500 The size of the difference threshold is greater for heavier objects than for lighter ones. This best illustrates SP3-100 Answer: Weber’s Law SP3-100 The central focal point in the retina where cones are heavily concentrated is known as the SP3-200 Answer: Fovea SP3-200 The sensory experience of bending one's knees or raising one's arms exemplifies SP3-300 Answer: kinesthesis SP3-300 The distance between our right and left eyes functions to provide us with a cue for depth perception known as SP3-400 Answer: retinal disparity SP3-400 Railroad tracks appear to converge in the distance. This provides a cue for depth perception known as SP3-500 Answer: linear perspective SP3-500 A door casts an increasingly trapezoidal image on our retinas as it opens, yet we still perceive it as rectangular. This illustrates SP4-100 Answer: shape constancy SP4-100 Grass seen through sunglasses appears equally as green as it does without glasses. This best illustrates SP4-200 Answer: color constancy SP4-200 After some practice, Carol was able to read books while holding them upside down. This best illustrates SP4-300 Answer: perceptual adaptation SP4-300 The pitch is determined by point of maximum vibration on the basilar membrane. SP4-400 Answer: Place Theory Helps explain “HIGH” pitch sounds SP4-400 Hearing loss caused by damage to eardrum or bones in middle ear. SP4-500 Answer: Conduction Hearing Loss SP4-500 Spinal cord can either block pain (large fibers) or allow it to be sensed (small fibers, open) SP5-100 Answer: Gate-Control Theory SP5-100 Name the 5 Gestalt Grouping Principles SP5-200 SP5-200 Name the two binocular cues for depth SP5-300 Answer: Retinal Disparity Convergence SP5-300 Name the perceptions of “movement” SP5-400 Answer: Phi Phenomenon Stroboscopic Effect SP5-400 Name the 4 Types of Extrasensory Perception SP5-500 Answer: 1. Telepathy – Mind-to-mind communication. One person sending thoughts and the other receiving it. 2. Clairvoyance – Perception of remote events (Skype without the video, sense a friend’s house on fire!) 3. Precognition – Ability to see future events (Psychic)(i.e., seeing a political leaders death) 4. Psychokinesis – perform physical task with mind SP5-500 REVIEW SLIDES • Detection: Anytime your senses pick up something • Absolute Threshold: 50% of the time going to detect at a certain level…think music, sight, when do you first see it… • Subliminal Threshold: might pick up below absolute threshold here and there • Difference Threshold: being able to pick up what is higher or louder 50% of the time…can you see the light get brighter? Sounds get louder? • Signal Detection Theory: expecting to hear sound because you are in a hearing test, look for it, new parents…waitress, late at night in a parking not…motivation, expectations… The Eye Vitreous Humor ‘HAS’=Ossicles (Tympanic Membrane) # Monocular Cue 1 Relative Height Description We perceive objects that are higher in our field of vision to be farther away than those that are lower. Nearby objects reflect more light into our eyes than more distant objects. Given two identical objects, the dimmer one appears to be farther away 2 3 Light & Shadow Relative Size Objects are similar in size, we perceive the one that casts a smaller retinal image to be farther away. 4 Interposition Objects that block other objects tend to be perceived as closer 5 6 Linear Perspective Parallel lines appear to converge in the distance. More the lines converge, the greater perceived distance. Texture Gradient 7 Relative Clarity 8 Relative Motion Surfaces: walls, roads, fields of flowers in bloom, have a texture. Surface gets farther away texture gets finer, appears smoother Light from distant objects passes through more light, perceive hazy objects as farther away than sharp clear objects. When moving our head from side to side, nearby objects appear to move more than distance objects; far objects appear to move slower than nearby objects