Constitution and Bill of Rights
advertisement
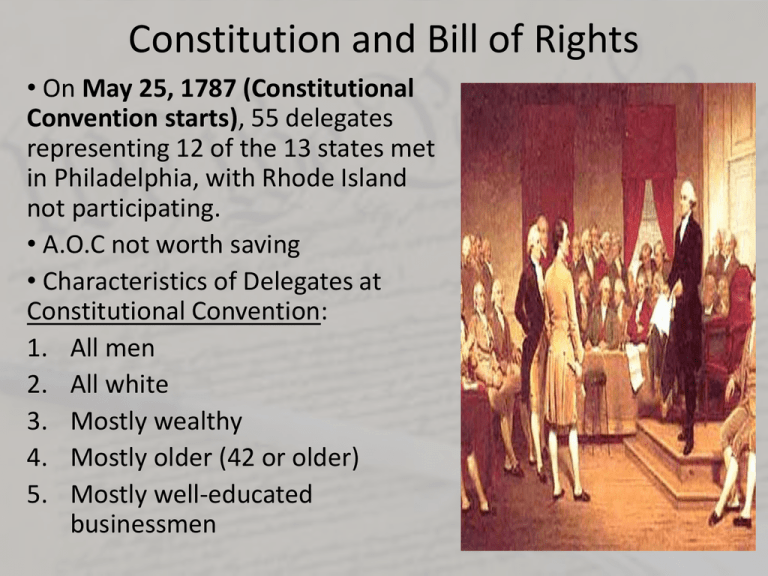
Constitution and Bill of Rights • On May 25, 1787 (Constitutional Convention starts), 55 delegates representing 12 of the 13 states met in Philadelphia, with Rhode Island not participating. • A.O.C not worth saving • Characteristics of Delegates at Constitutional Convention: 1. All men 2. All white 3. Mostly wealthy 4. Mostly older (42 or older) 5. Mostly well-educated businessmen Constitution and Bill of Rights • ISSUES to be determined at Convention: 1. Representation in government 2. Slavery 3. Economics The public knew what was going on, but the delegates kept the details quiet. (James Madison’s notebook) GEORGE WASHINGTON CHOSEN TO LEAD THE CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION Constitution and Bill of Rights VIRGINIA PLAN -JAMES MADISON - PRESIDENT, COURTS, AND 2 HOUSE CONGRESS -REPRESENTATION BASED ON POPULATION - LARGE STATES GET MORE VOTES - FAVORED BY LARGE STATES NEW JERSEY PLAN GREAT COMPROMISE -AKA CONNECTICUT COMPROMISE - TWO HOUSE LEGISLATURE: - HOUSE – BASED ON POPULATION - SENATE – EQUAL REPRESENTATION - PRESIDENT & COURT SYSTEM -WILLIAM PATERSON - ONE HOUSE CONGRESS - EACH STATE HAS EQUAL REPRESENTATION IN CONGRESS - PROMOTED STATE’S RIGHTS - EQUAL VOTES AMONG THE ALL THE STATES Constitution and Bill of Rights • 3/5 COMPROMISE • COMPROMISE: Every 5 enslaved persons would count as three free persons. (or 3/5 of a whole person) Constitution and Bill of Rights • The Commerce and Slave Trade Compromise • Southern states agreed that Congress could regulate trade between the states, as well as with other countries • Northern states agreed that Congress could NOT tax exports, nor could it interfere with the slave trade before 1808. Constitution and Bill of Rights • The Electoral College Compromise – addressed how the President would be chosen. – Group of people named Electors select the president and vice president Constitution and Bill of Rights • After 4 main compromises and several other debates, a committee was chosen to write the plan of government • Virginian Gouverneur Morris wrote the majority of the document we call the Constitution (even though James Madison is considered the “Father of the Constitution” • The delegates signed the Constitution on September 17, 1787. • They decided that the Constitution would become law once 9 of the 13 states had ratified, or agreed to it. • They didn’t realize the process would be so long and difficult. Opening Activity (Put in with your notes) • 1. How did the Great Compromise appease both the large states and small states? • 2. What are some common characteristics of the delegates at the Constitutional Convention? • 3. How do we know what happened at the Constitutional Convention if they did not allow the public to attend? • 4. When did the delegates sign the Constitution? • 5. What were the three main issues that needed to be resolved at the beginning of the Constitutional Convention? The Federalist (Federalist Papers) • Constitution would create FEDERALISM, government in which power is divided between the federal (national) government and states. • Federalist Papers – 85 essays written by Alexander Hamilton, James Madison, and John Jay. (Essay #10 – Federalism) – #84 – Federalists agree a Bill of Rights need to be added – BUT only after states approve constitution Federalist Papers Clip Federalists vs. Anti-Federalists Constitution • On June 21, 1788 New Hampshire became the 9th state to ratify the Constitution, and made it law. The last, Rhode Island ratified it in 1790, and we became the United States of America. (N.C. in 1789 was 12th) • Constitution became the basic law of the United States and the highest authority of the nation • “preserve, protect and defend, the Constitution of the United States.” Sections of the Constitution • Preamble – states the Constitution’s purpose – The people of the United States have the right and power to govern themselves. • The preamble lists 6 goals for the United States government. They are: – To form a more perfect union – To establish justice – to insure domestic tranquility – to provide for the common defense – to promote the general welfare – to secure the blessings of liberty to ourselves and our posterity Sections of the Constitution • After the preamble, the Constitution is broken into 7 parts: • Article 1 – Outlines lawmaking powers of legislative branch (House and Senate) • Article 2 - defines and describes the powers and limits of the President and the executive branch • Article 3 - defines and describes the powers of the Supreme Court and other federal courts, meaning the judicial branch of our government Sections of the Constitution • Article IV - describes and defines how the states and federal government must respect the laws and rulings of each another • Article V - describe the process for changing, or amending, the Constitution • Article VI - discusses debts and treaties of the states, and establishes “the supremacy clause”, defining the Constitution and federal laws as supreme when in conflict with those of the states. • Article VII - defines how and when the Constitution will be approved and take effect.









