Opportunity Costs
advertisement

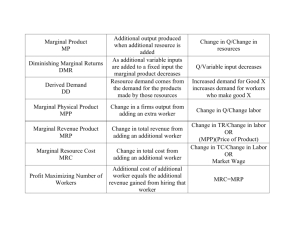
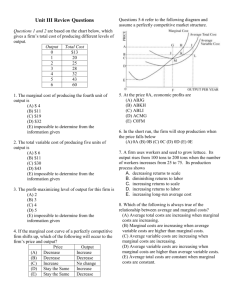
OPPORTUNITY COSTS People’s choices involve costs Use of scarce resources can be costly so tradeoffs must be made Opportunity Cost – the highest value alternative that must be Sacrificed as the result of choosing an option - “What you lose when you choose” If I didn’t go to Mt Lemmon this weekend I would have gone out to dinner with my husband Think of an example of an opportunity cost and write it down TANSTAAFL There Ain’t No Such Thing As A Free Lunch Use of a resource to produce a pair of jeans diverts it from another use Going to school is free of charge but it is not free Individuals choose purposefully Economizing behavior – choosing the option that offers the greatest benefit at the least possible cost Purposeful or rational decision making Going out to dinner – you don’t choose the most expensive option unless it gives you more pleasure If there were 3 dinner specials that all cost $15, you would choose the one that you like best In your notes Write down a non food example of economizing behavior Opportunity Cost What is the opportunity cost of getting married? All the other people you could be dating 2. The OC of government fixing the roads is the labor and materials. False 3. The OC of hiring police officers is funding an after school arts program. True 4. The OC of coming to school are the wages you could earn working at a job. True 1. Opportunity costs for women - 1945 Laundry by hand (4 hrs washing, 41/2 ironing Now - washing 41 minutes, 1 ¾ hrs ironing Opportunity cost much higher to work outside the home in 1945 so less women did it Todd recently purchased his own car on credit. He works at a part-time job at an auto-wrecking firm to earn the money he needs to make payments on his new car. Lately, his work in school has declined. When his teacher asked him if he was studying for the tests, he replied, “Not really. I’d like to study more, but I have no choice. I’ve got to keep working to pay off my car loan.” Describe situations where you may have felt you had no choice. For example: “I have to put gas in the car so I can get to work tonight.” Write example in your notes. A. What was Ashley’s problem? B. What alternatives did Ashley have? C. What were the costs of each alternative? D. What were the benefits? Utility – benefit or satisfaction a person expects from a choice or course of action Cost/Benefit Analysis: comparison of what you will sacrifice and gain by a specific action Marginal Cost: the extra cost of adding one unit Marginal Utility: the extra benefit of adding one unit Marginal Revenue (benefit) = Marginal Cost Costs Explicit costs – out of pocket expenses The price of the movie ticket Implicit costs – the value of resources that could have been used elsewhere Pay you would have earned if you had gone to work rather than gone to the movies – making the decision for 1 more “how much” is a decision at the margin What should I do for the next hour? At what mileage should I change the oil? Production Possibilities Frontier – understand the trade offs