Sociology Chapter 18.1
advertisement

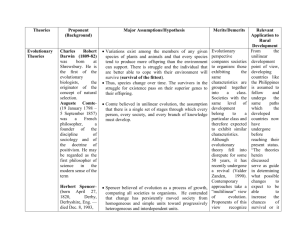
WarmUp: Review Open your books to Chapter 3, Section 3 & identify the 6 factors of social change discussed in that section. In your journals, copy & summarize each of those factors. Chapter 18.1 Social Change & Modernization Objectives Summarize the theories that social scientists have offered to explain the process of social change. Explain how theories of social change have evolved. Social Change alterations in various aspects of society over time Spengler & Sorokin CYCLICAL THEORY Cyclical Theory of Social Change views change from a historical perspective assumes natural stages of development likely to gain popularity during periods of upheaval Oswald Spengler German historian deeply troubled by WWI wrote Decline of the West ◦ asserted that West was well into decline in the 1900s & collapse was inevitable Pitirim Sorokin Russian-American sociologist presented 2 extreme forms of culture ◦ ideational culture: truth & knowledge sought through faith & religion ◦ sensate culture: people seek knowledge through science Early & Modern EVOLUTIONARY THEORY Evolutionary Theory of Social Change views change as a process that moves in one direction – toward increasing complexity Early Evolutionary Theories 1800s: believed that all societies progress through the same distinct stages of social development stages should improve over time justified political & social conditions in Europe & U.S. Modern Evolutionary Theories said that societies have a “tendency” to become more complex over time attempts to see why societies change EQUILIBRIUM THEORY Equilibrium Theory of Social Change built on functionalist idea that society resembles a living organism occurs as society adapts to maintain stability after a change in one area; involves differentiation & integration Marx & Class Conflict, Dahrendorf & Social Conflict CONFLICT THEORY Conflict Theory of Social Change change results from conflicts between groups with opposing interests Karl Marx & Class Conflict all human history is history of class conflict most interested in how this occurs in industrial societies Ralf Dahrendorf & Social Conflict holds that social conflict can take many forms ◦ racial, ethnic, political, religious, labor, gender, age, etc. Social Change Through Technology: Social Media & Climate Change Participation culture, creativity & social change Do you agree with Gauntlett’s assertion that we need to become more of a “making-and-doing culture” as opposed to a “sit-back-and-be-told culture?” Why or why not? How do you think technology & social media will influence social movements of the future? Do you think that people will be happier & more productive if they are engaged in the process of creating? Why or why not? What role will social media play in helping us transition into a society that has to adapt to new environmental challenges? What challenges might we be facing? CHAPTER 18: CLASSWORK Page 470: #3-4 Page 479: #2-3 Page 480: #1-10 Identifying People & Ideas Page 480: #1-6 Understanding Main Ideas Page 481: #1-4 Building Social Studies Skills