Summer Conference 2012
advertisement

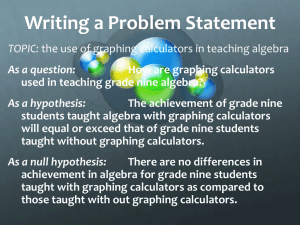
SUMMER CONFERENCE 2012 1 What is “Mixed Methods” Research • Research studies that include both QUALitative and QUANtitative data. • QUAL and QUAN data purposely integrated or mixed to answer specific research questions. • Therefore, one needs to understand the basic features of both qualitative and quantitative research. 2 Some Strategies for Getting Started With Mixed Methods Research • 1. Know distinction between quantitative and qualitative research, including sources of data. • 2. Familiarize yourself with some published mixed methods studies. • 3. Know how to formulate your own research questions that make effective use of mixed methodology. • 4. Plan your own study so that it could both answer your research questions and be feasible. 3 Purpose of this Session • Introduce and illustrate some uses of mixed methods research for answering specific research questions. This includes • introducing conceptual understanding of mixed methods research, • understanding some strategies for implementing mixed methods research by presenting brief descriptions of illustrative study designs, and • brainstorming with you some potential research questions that relate to the integration or mixing of QUAN and QUAL data. 4 Quantitative Methods • Data derived from tests, surveys, archived databases • Hypotheses constructed before data are collected • Statistics usually used to confirm or disconfirm hypotheses: • • Usually, comparisons made between means, or correlations examined among variables Statistics do not “work” without sufficient sample size. • Let’s brainstorm example quantitative research questions now…. 5 Qualitative Methods • Data derived from interviews, focus groups, transcripts, historical documents, observations • Data used to explore how and why a phenomenon occurs (not how many) • Statistics usually not used to make conclusions: • Data “analyzed” to determine themes or to construct a conceptual framework to explain the processes, impressions, opinions of participants, etc.. • Sample size is relatively smaller than quantitative methodology. • Let’s brainstorm example qualitative research questions now…. 6 Mixed Methods • Why combine qualitative and quantitative methods? • • • • • Development—Sequential designs: Phase 1 results used to inform/develop Phase 2 of the study. Triangulation—Convergence of findings from qualitative and quantitative data. Clarification—Findings from one method are used to clarify findings from other methods. Expansion—Qualitative and quantitative research used together produce more complete knowledge to inform theory/practice. Instrument development—Qualitative data employed to design a quantitative instrument. • Let’s brainstorm example mixed method research questions now…. 7 Mixed Methods Research: Example 1 • (Explanatory Sequential Design) • Qualitative data used to explain quantitative results. Quantitative Data Follow up with Qualitative Data Interpretation 8 The Effective Provision of Preschool Education Study (Sylva et al., 2008) • QUAN data used to identify high- and lowquality centers: • cognitive and social skills measured with tests • QUAL data used to explain differing characteristics of high- and low-quality centers: • case studies used to document processes • data gathering included document analysis, interviews, and observations 9 Mixed Methods Research: Example 2 • Convergent Parallel Design • Both types of data collected concurrently and compared and related in interesting ways…… Quantitative Data Compared Interpretation Qualitative Data 10 Mixed Methods Research: Example 2 • Convergent Parallel Design • Adolescents given quantitative survey concerning values about using alcohol. Then, students are interviewed in focus groups to see how attitudes about alcohol use diverge and converge with the survey. • Note that the QUAN and QUAL data are given equal priority in this design! 11 Mixed Methods Research: Example 3 • • Embedded Design to examine effects of reading intervention Both types of data collected, with one type collected before, during, or after other type. Quantitative Pretest Data collection • Intervention Qualitative data collection Quantitative Posttest Data collection Interpretation In this example, the main focus is quantitative, but the qualitative data can provide important information about reading implementation process: • e.g., fidelity of treatment implementation evidence from observations, barriers/facilitators of implementation, etc. 12 Mixed Methods Research: Example 4 • Embedded Design • Light’s (2009) study looked at impact of faculty development program for enhancing pre-tenure faculty’s teaching styles. Quantitative Pretest Data collection • • • Intervention Quantitative Posttest Data collection Interpretation Qualitative data collection Quantitative question—How did intervention affect teachers’ approaches to teaching as measured by a survey? Qualitative: (central question)—How did teaching strategies change as reported by participants? Qualitative: (subquestion) –What steps did teachers take to 13 implement the changes to teaching? Conclusion • Mixed methods research is useful for answering related QUAN and QUAL research questions. • Extra data collection is obviously needed to incorporate both QUAL and QUAN components into your research. BUT, IT’S WELL WORTH THE EXTRA EFFORT WHEN FEASIBLE!!!!! 14