Photosynthesis and Respiration
advertisement

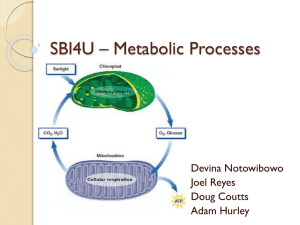
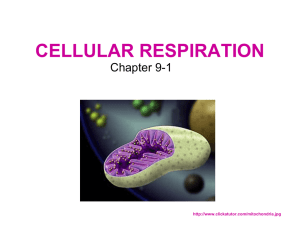
Do Now 1) How does the mitochondrion use ATP? How does it use ADP? 2) How does the mitochondrion get the energy it needs to form ATP from ADP? 3) Explain the relationship between the mitochondrion and the chloroplast. Photosynthesis and Respiration Do Now Transport review…transport practice problem set Who uses photosynthesis? AUTOTROPHS! Plants and organisms that can make their own food What is Photosynthesis? The process by which plants make food. This process takes place in the CHLOROPLAST (mostly found in the leaves). Autotrophs use energy from sunlight to make sugar (GLOCOSE) Cellular Respiration uses the glucose and converts it into ATP, which cells use for energy Where does Photosynthesis take place? In the Chloroplast https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Wi60tQa8jfE Why are plants green? Because of CHLOROPHYLL! Chlorophyll is pigments located in the chloroplast Plants are green because the green wavelength is reflected, not absorbed. Absorption of Light by Chlorophyll 9 Chlorophyll absorbs blue-violet & red light best Absorption violet blue green yellow wavelength orange red When does Photosynthesis take place? When autotrophs are able to capture sunlight energy and produce usable energy So, mostly during daylight hours Why does Photosynthesis take place? To convert unusable (light) energy to usable energy In other words, turning SUNLIGHT (unusable) into GLUCOSE (usable)! What is the Equation for Photosynthesis? 6CO2 + 6H20 + sunlight → C6H12O6 + 6O2 (Carbon Dioxide + Water+ Sunlight Glucose + Oxygen) What are the Reactants of Photosynthesis? Carbon Dioxide, Water and Sunlight What are the Products of Photosynthesis? Sugar and oxygen What Factors affect the rate of Photosynthesis? Light intensity Carbon Dioxide concentration Temperature What is the efficiency of ATP formation? Photosynthesis uses ATP to produce sugars (glucose) Why is this important to us? We cannot make our own food (glucose, energy), we must get our food from plants. Plants are the first step in the food chain. Why is this important to us? The oxygen released during photosynthesis is necessary for all living things. EOC Question! 10.The diagram below shows the relationship between photosynthesis and cellular respiration and the organelles in which they occur. Which statement describes how photosynthesis and cellular respiration are interrelated? IP: Students will answer the following question: With the increase in carbon dioxide emissions from factories and cars. How would this affect the rate of photosynthesis in plants? …What if the plants do not have enough stomata to absorb the increased carbon dioxide? A. Oxygen is produced during cellular respiration and stored during photosynthesis. B. Carbon dioxide and water released by cellular respiration are used in photosynthesis. C. Photosynthesis releases the energy that is stored during the process of cellular respiration. D. Glucose is used during cellular respiration to produce food that is broken down during photosynthesis. Cellular Respiration! Who uses Cellular Respiration? BOTH autotrophs and heterotrophs What is Cellular Respiration The transfer of energy from various molecules (oxygen and glucose) to produce ATP. The process by which both plants and animals release energy from food (sugar) to make energy cells can use. Where does Cellular Respiration take place? In the mitochondria of eukaryotes In the cytoplasm of prokaryotes. When does Cellular Respiration take place? 24 hours a day Why does Cellular Respiration take place? To convert sugars to ATP (form of energy in which it is most easily broken down) What is the Equation for Cellular Respiration? C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H20 (Sugar + Oxygen Carbon Dioxide + Water+ATP) What are the Reactants for Cellular Respiration? Sugars and oxygen What are the Products for Cellular Respiration? Carbon dioxide, water and ATP What are the factors that affect the rate of Cellular Respiration? Oxygen concentration Temperature What is the efficiency of ATP formation? For each glucose molecule: AEROBOIC: 36 ATPs WITH OXYGEN ANAEROBIC: 2 ATPs WITHOUT OXYGEN (We are going to talk more about Aerobic vs. Anaerobic tomorrow!) Check Point 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What is ATP? What is chlorophyll? What are chloroplasts? What are mitochondria? What is cytoplasm? What are eukaryotes? What are prokaryotes? Photosynthesis vs. Cellular Respiration Foldable • Directions: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Everyone has 2 sheets of paper Stack the 2 sheets 1 inch apart Fold hamburger style Left hand side: Photosynthesis Right hand side: Cellular Respiration Flap 1: WHERE Flap 2: INGREDIENTS Flap 3: EQUATION Photosynthesis Respiration WHERE WHERE INGREDIENTS INGREDIENTS EQUATION EQUATION What is Photosynthesis? What is Cellular Respiration? The process by which plants make food. This process takes place in the CHLOROPLAST (mostly found in the leaves). The process by which both PLANTS and ANIMALS release energy from food. This process takes place in the cells MITOCHONDRIA. AUTOTROPHS only! Autotrophs AND Heterotrophs Where does photosynthesis take place? Where does respiration take place? When does respiration take place? When does photosynthesis take place? (PICTURE) (PICTURE) Where does the energy come from? Where does the energy come from? Picture Picture REACTANTS: REACTANTS: PRODUCTS: PRODUCTS: EQUATION: EQUATION: REACTANTS PRODUTS REACTANTS PRODUTS Exit Ticket 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Where does photosynthesis take place in a cell? Where does cellular respiration take place in a cell? What organisms can carry out cellular respiration? What is the equation for photosynthesis? What is the equation for respiration?