Basic Kinesiology
advertisement

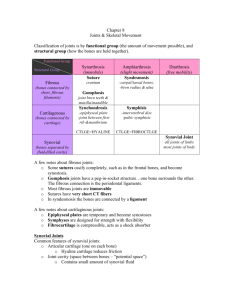
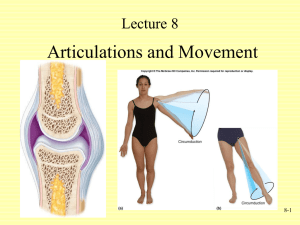
Kinesiology-the study of movement Brings together anatomy, physiology, physics, and geometry as they relate to the human bodies movement. Biomechanics-mechanical principles that relate directly to the human body. Can be relative to the extremities or an implement such as a bat or racket Can be static(nonmoving) or dynamic(moving) activities. Read paragraph 3-4 on page 3 and paragraph 1 on page 4-6 Anatomical Positionhuman body standing upright, eyes forward feet parallel, arms at side, and hands with palms facing forward. Linear Motion- a straight line from one point to another. Rectilinear Motion-straight line like a player running across a field. Curvilinear Motion- straight line but in a curved path, like a diver leaving the diving board. Angular Motion- Rotary motion is when all the parts of the object move through the same angle, same direction at the same time, but do not move the same distance. When you flex your elbow your hand and wrist travel a different distance through space. Generally speaking most movement within the body is angular, most movement outside the body is linear. Get into groups of 3 and create a list: 2 linear movements 2 angular movements 2 combination movements Arthrokinematics: relationship of joint surface movement. The humeral head’s movement within glenoid fossa of scapula. Osteokinematics: relationship of the movement of bones around a joint axis. Humerus moving on scapula Kinesiology Movements of Synovial Joints Flexion-decrease angle between 2 bones Extension-increase angle between 2 bones Hyperextension-increase angle between 2 bones beyond the normal range of motion (ROM). Kinesiology Movements of Synovial Joints Abduction-Limbs only-limb moves away from the midline of the body. Adduction-Limbs only-limb moves toward the midline of the body. Rotation-when a bone turns on its axis towards or away from the midline of the body Movements of Synovial Joints Circumduction- the ability of a limb to move in a circular path around an axis. Supination- moving into a supine position. Pronation- moving into a prone position. Plantarflexion- pointing toes down, “planting the foot” Dorsiflexion- bringing the toes up Kinesiology Movements of Synovial Joints Plantarflexion- pointing toes down, “planting the foot” Dorsiflexion- bringing the toes up Kinesiology Movements of Synovial Joints Inversion- turns the sole of the foot inward, medially. Eversion- turns the sole of the foot outward, laterally. Protraction- occurs in the transverse plane, moving the body part forward Retraction- occurs in the transverse plane, moving the body part backward Research Kinesiology Project Look at page 16 in text You are going to choose 5 of the words on the list to give the following information for. Marking Describe in your words Example Picture-draw a depiction of Be able to point it out on the skeleton in class