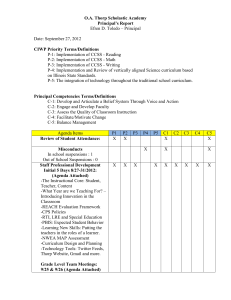
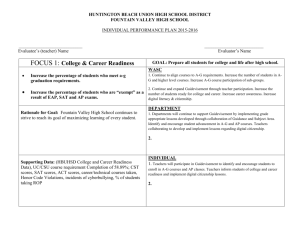
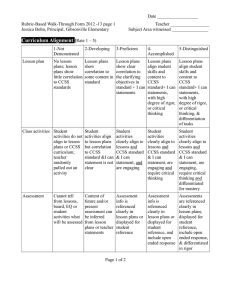
Day Two Wilson Posted
advertisement

Discovery Education What is a Guaranteed and Viable Curriculum in the Wilson School District? Wilson School District March 20, 2013 Karen M. Beerer, Ed.D. Karen_beerer@discovery.com Johnna_Weller@discovery.com Today’s Learning Targets I CAN define what learning targets are and what they aren't as well as the role they play in a guaranteed and viable curriculum. I CAN explain my role as a leader in ensuring the effective use of learning targets to align to the look fors we established at our last meeting. Norms: 1. Be “present.” 2. Everyone has something to contribute, so share your thinking openly, honestly and with respect to other’s ideas and thinking. 3. “It’s okay to disagree.” --- Be willing to challenge the thinking of others, but in a thoughtful and respectful way. 4. Recognize and celebrate varying degrees of knowledge; it helps you grow as an organization. 5. Be willing to engage in “system’s thinking.” Today’s Agenda • Why learning targets? • What are learning targets? (and what aren’t they…) • Using learning targets in instruction • Getting everyone on board using learning targets • - A Learning Target Framework • - A Learning Target Walk-Through • Grounding learning targets in the CCSS • Getting Started CCSS Unit Plan Template Combining the work of : • Wiggins and McTighe (UBD) • Beers, S. • Tri-State Quality Review Rubrics Essential Questions frame the unit: Example - Can fiction reveal truth just as much as nonfiction? • Import the standards • Determine the standards the unit is explicitly teaching and assessing. • Delete the rest. Essential for designing assessments Key Question: What will students know and be able to do as a result of the instruction? Complex Texts and Text-Based Answers Writing from Sources Academic Vocabulary Integration of digital media and technology Essential for designing assessments Key Question: What will students know and be able to do as a result of the instruction? Today’s Focus The Research Behind Learning Targets • Ames & Archer (1998). Achievement goals in the classroom. • Andrade & Krathwohl (2010). Rubric-referenced selfassessment. • Brookhart (2008). How to give effective feedback to your students. • Brophy (2004). Motivating students to learn. • Hattie (2012). Visible learning for teachers: Maximizing impact on learning. • Moss, Brookhart, Long (2011). Knowing your learning target. • O’Connor. (2009). How to grade for learning. • William. (2010). An integrative summary of the research literature and implications for a new theory of formative assessment. A Close Reading CLARIFYING THE TERMINOLOGY Objective Learning Target I CAN Statement DEFINITIONS OF TERMS Objective: Instructional objectives are about instruction, derived from content standards, written in teacher language, and used to guide teaching during a lesson or across a series of lessons. They are not designed for students but for the teacher. -Know Your Learning Target, S. Brookhart Learning Target: A learning target frames a lesson from the students' point of view. A learning target helps students grasp the lesson's purpose—why it is crucial to learn this chunk of information, on this day, and in this way. -Know Your Learning Target, S. Brookhart I CAN Statement: A learning target that is written in a student friendly way beginning with the words “I CAN.” -Stiggins (2004) EXAMPLES: Objective: Students will be able to distinguish between elements and compounds and classify them according to their properties. Learning Targets: Know the definition of an element Know the definition of a compound Distinguish between elements and compounds Identify properties Classify them according to their properties I CAN Statements: I CAN tell what an element is. I CAN tell what a compound is. I CAN tell the difference between an element and a compound. I CAN identify at least 3 different properties. I CAN classify elements and compounds by their properties. Attributes of Clear Learning Targets Learning Targets Are: Learning Targets Are Not: • Accomplished in a few days at most • Long-term • Specific to what and how • Global and Ambiguous • Learned using a variety of instructional activities, strategies, contexts and tools • Learned by a single approach or a single activity • Transferrable to a variety of contexts • Focused on one thing that needs to be done I can identify the protagonist, theme and voice in a piece of literature. I can flip a coin 100 times to determine the probability of heads. I can watch a video about the causes of the Civil War. I can use authentic Egyptian techniques to mummify a chicken. I can describe how materials change when they are heated or cooled. Review: Qualities of Effective, Somewhat Effective and Ineffective Learning Targets Ideas for Using I CANs Topic Review Observations & Inferences Review Experiments, Analysis & Conclusions I Can Statement Understanding Evaluation I can make detailed quantitative and qualitative observations. 1 2 3 4 5 I can tell observations from inferences. 1 2 3 4 5 I can make inferences based on observations. 1 2 3 4 5 I can explain why it is important to control variables in an experiment. 1 2 3 4 5 I can explain why you need to run multiple tests in an experiment. 1 2 3 4 5 I can analyze results of an experiment and take into account the role of chance. 1 2 3 4 5 I can explain why your experimental results never prove your hypothesis. 1 2 3 4 5 I can explain what heritable alleles are. 1 2 3 4 5 I can explain the difference between genotype and phenotype. 1 2 3 4 5 I can explain what dominant and recessive alleles are and how they reveal themselves differently in phenotypes. 1 2 3 4 5 I can explain what DNA is as well as how it store and uses information to build organisms. 1 2 3 4 5 Review Genetics Can I?…I CAN Exit Slips Name:_______________________________ Dates:______________________ Period:___________ Objective (“Can I…”) Rank: (Beginning) 1 Show (“I can…by…”) 2 3 4 5 2 3 4 5 Rank: (End) 1 How do you get everyone to drink from the same watering hole? How do you get everyone to drink from the same watering hole? One Strategy: Provide a framework The Four-Step Framework The four starter prompts of the framework are: • We are learning to… • We will show that we can do this by… • To know how well we are learning this, we will look for… • It is important for us to learn or be able to do this because… Examining Two Framework Examples Discuss: 1. Where are your teachers in the use of learning targets in instruction? 2. What evidence do you have to prove your beliefs about the first question? 3. What is the next step? 4. How will you help them take the next step? How do you get everyone to drink from the same watering hole? Another Strategy: Collect Walk-Through Evidence Your Strategies as the Learning Leader Did you see evidence that the teacher had a learning target for this specific lesson? ☐Yes, I saw evidence that the teacher had a specific learning target for today’s lesson – a statement of what the student would be able to do or come to know as a result of today’s lesson. ☐No, however, I saw evidence that the teacher had an instructional objective that was used to guide the teacher and that could have covered more than one lesson. ☐No, I could not find evidence that the teacher had a learning target for this lesson, nor was there evidence of an instructional objective. Describe what you observed –the evidence you gathered to support your response. Where To Start A Quick Trip Through the ELA and MATH CCSS • Find a partner. • With your partner, take a trip through the CCSS ELA and Math Standards and Appendices. • When you finish, complete the “ticket” together on your table. Deconstructing the Standards Example: Grade 5 Measurement and Data Represent and interpret data. 2. Make a line plot to display a data set of measurements in fractions of a unit (1/2, 1/4, 1/8). Example: Grade 1 Writing Produce writing to communicate with different audiences for a variety of purposes. Knowledge Targets Reasoning Targets Skill Targets Product Targets Know what a sentence is. Distinguish which words are the most appropriate for the purpose Use capitals and periods correctly. Spell words correctly. Write a letter, an email, a personal narrative, an informational piece and an opinion piece. Your Turn • Grade 3 Informational Text: Determine the main idea of a text; recount the key details and explain how they support the main idea. • Grade 7 Informational Text: Determine two or more central ideas in a text and analyze their development over the course of the text; provide an objective summary of the text. • Grade 11-12 Informational Text: Determine two or more themes or central ideas of a text and analyze their development over the course of the text, including how they interact and build on one another to produce a complex account; provide an objective summary of the text. Today’s Learning Targets I CAN define what learning targets are and what they aren't as well as the role they play in a guaranteed and viable curriculum. I CAN explain my role as a leader in ensuring the effective use of learning targets to align to the look fors we established at our last meeting.