Social Learning Theory - PsychologyResources-Y13
advertisement

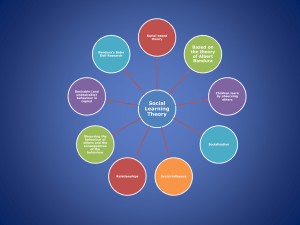
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KHi2dxSf9hw Social Learning Theory Albert Bandura Research Study Bandura et al. (1961) Video Clip http://www.youtube.com/results?search_query=bandura+bobo+doll&search_type= Learning Outcomes By the end of this lesson you should be able to: describe Social Learning Theory apply Social Learning Theory to gender Social Learning Theory Key Terms Graphic Organiser Observational Learning Vicarious (Indirect) Reinforcement Vicarious (Indirect) Punishment Model Imitation Mental Representation (Cognition) Social Learning Stages Attention Retention Reproduction Motivation Social Cognitive Theory Bandura added more factors to the SLT to explain the cognitive factors of role development... Modelling What makes someone likely to copy what you are doing? Appropriateness! Males would imitate other males or someone with similar characteristics to them Eg) Boys may learn a good deal about homemaking, but rarely adopt such activities (Bandura and Bussey, 1999) How might children’s experiences change as they grow up? As children grow up, their mobility improves. Their variety of social reactions increase! This is known as: ENACTIVE REPRESENTATION Direct Tuition Appropriate gender instructions begin as children acquire language. “Instructors” can be parents or children. Anyone with an authority oh children Can you remember any of your gendered instructions? Discussion Can you remember anything/anyone that had an influence on your gender identity growing up? Can you remember the context/what was said? If you were rearing a child of your own, do you think you would influence their gender development? The Influence of Parents Parents are a primary socializing agent, especially when children are young Starting at birth, parents treat girls and boys differently, and believe them to possess different characteristics The Influence of Peers Peers are important because they offer a model of genderlinked behaviours (Bandura, 1999) In their interactions, peers reward each other for gender appropriate activities and vice versa. Boys are more likely to criticise activities considered feminine (Fagot, 1985) The Influence of Schools Teachers are another source of influence. They can reinforce gender appropriate behaviour and act as role models themselves Media Influences Messages about gendered behavior and interactions are also conveyed through television, movies, magazines, and books On average, each day a 4-year-old watches 2 hours of television and a 12year-old watches 4 hours (Comstock and Scharrer, 2001) Some European nations ban ads before, during, and after children’s television programming Men are more likely to be seen controlling events, while women are at the mercy of them (Hodges et al, 1981) Review True - False 1 Social learning theory explains how behaviour is learnt by observing others. 2 A child is more likely to imitate the behaviour of a model who is younger than them. 3 Vicarious reinforcement is when the child is directly rewarded for copying the models behaviour. 4 Social learning theory fails to take into account the role of cognitive factors. 5 Bandura further adapted the social role theory to explain gender development 6 Social learning theory can explain how behaviour can be learnt without necessarily being performed. 7 Enactive representation is when the variety of social reactions of children is increased through greater mobility 8 Girls are more likely to imitate male models as males are generally more aggressive. 9 Direct Tuition begins as children learn to write 10 Children are more likely to show aggression if they observe someone being punished for aggressive behaviour.