management and change - businessstudiesandcommerce
advertisement
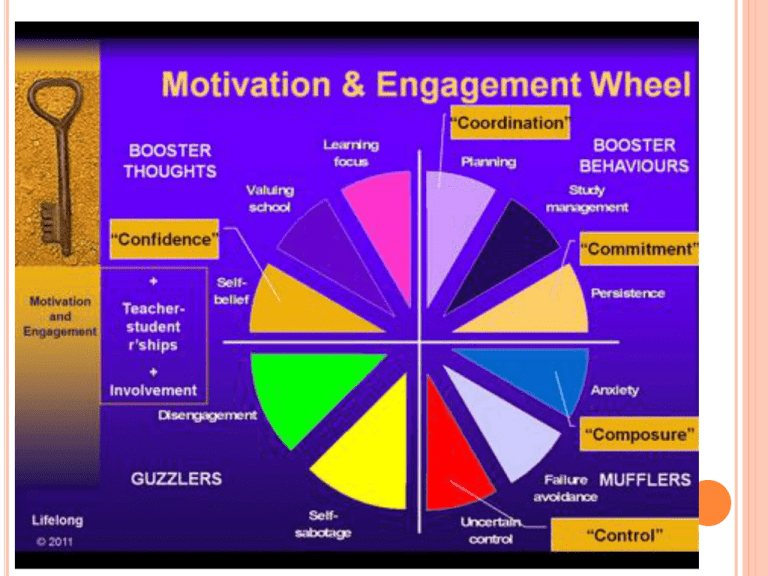
BUOYANCY – STAY AFLOAT 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Self belief Control Persistence Composure – don’t let anxiety overwhelm Planning – being able to see risk before it engulfs you! OFFSET RISK We can all be anxious but it is the way that we respond to anxiety that is important: Do we work harder or do we ‘avoid’ Or 5 c’s from previous page MANAGEMENT AND CHANGE To improve is to change; to be perfect is to change often. MANAGEMENT AND CHANGE Year 12 slideshow on same topic responding to internal and external influences managing change effectively identifying the need for change business information systems setting achievable goals resistance to change management consultants WHAT IS ORGANISATIONAL CHANGE? CHANGE IS THE ONE CONSTANT IN THE BUSINESS WORLD. COMPLETE THE FOLLOWING TABLE.... External influences on businesses Social Changing consumer trends Historical (Business) Methods of management Economic Global financial crisis Environmental Triple bottom line Political New government and their policies RESPONDING TO INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL INFLUENCES Organisational change is the adoption of a business’s new idea or behaviour in response to internal or external influences. Internal influence could be? External influence? RESPONDING TO INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL INFLUENCES The ability to embrace, manage and adapt to change will increasingly determine a business’s competitive advantage. Successful managers are the ones who anticipate and adjust to changing circumstances. FROM SMH : HOW TO SURVIVE AND THRIVE Julianne Dowling October 19, 2009 Work as a team to thrive Companies which work more closely as a team, and think about their impact on the wider community have a greater chance of survival, says a leading academic studying organisational change. Read more: http://www.smh.com.au/business/clevel/how-tosurvive-and-thrive-20091019h4ix.html#ixzz1T0RLB2cK WHAT TYPES OF CHANGE ARE THERE? • Changes can be major (transformational) or minor (incremental) Can you think of an example of each type of change Major/transformational: Minor/incremental: RESPONDING TO FORCES OF CHANGE When a business responds to the forces of change, the result will be a change to its: - organisational structure, including outsourcing, flatter structures and work teams - business culture; for a business to survive in the long term, changes should be reflected in its culture - human resource management practices, including recruitment and selection, training, performance appraisal, and redundancy procedures - operations management, including flexible manufacturing and quality assurance. MANAGING CHANGE EFFECTIVELY To manage change effectively requires the change to be as productive as possible; to make it a process for revitalising and strengthening the business. Managers must develop strategies for managing change effectively. Identifying the need for change and setting achievable goals are two low-risk strategies for managing change. A business’s success or failure to accurately identify what needs to be changed depends on its ability to collect, organise, process and retrieve information quickly. Manipulation and threat are two high-risk strategies for managing change. RESISTANCE TO CHANGE What factors or who do you believe resist change? RESISTANCE TO CHANGE At the same time as managers are undertaking — driving — change for the best of reasons, there will be restraining forces working against the change, creating resistance. The main reasons for resistance to change include: – management – why? – fear of job loss – why? – disruption to routine – why? – time – why? – fear of the unknown – why? – inertia – why? – cost – why? RESISTANCE TO CHANGE – management (may make hasty decisions or be indecisive) – fear of job loss (fearful of changes that threaten job security or require new work routines) – disruption to routine (worried that they cannot adapt to the new procedures that threaten established work routines) – time (either poor timing, or lack of time) – fear of the unknown (feelings of lack of control and anxiety) – inertia (prefer to stay with the safe and predictable status quo) – cost (financial cost of implementing major changes can be substantial). DRIVING FORCES FOR CHANGE VS RESISTING FORCES AGAINST CHANGE • Driving forces are those forces that initiate, encourage and support the change. • Restraining forces are those that work against the change, creating resistance. • Resistance to change is common among managers and employees. . • Two strategies for overcoming resistance to change include: – creating a culture of change (encouraging teamwork) – providing positive leadership (sharing the vision). • The main role of management consultants is to help businesses improve their performance and assist with change management.