Concept Mapping
advertisement
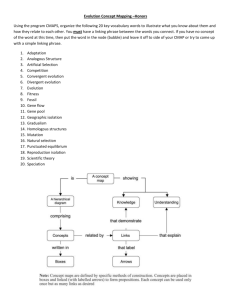
Concept Mapping - helps you to link information Dr. Joanne Broggy Project Officer – Teaching and Learning (Science) Concept Mapping 1 The Purpose of today To help you understand what a concept maps is. To develop your skills in generating concept maps To discuss the use of and construction of concepts maps in any of your classes To highlight the benefits of using the tool to help you learn Concept Mapping 2 Agenda Introduction Information on Concept Mapping Drawing Concept Maps Task 1 Drawing Concept Maps Task 2 Discussion Concept Mapping 3 Graphical representational tool Assessment tool What is a Concept Map? Practical learning tool Manageable teaching tool Instructional tool Concept Mapping 4 What are Concept Maps made of? In a concept map two or more concepts are linked by words that describe their relationship. Food Contains Energy Two negative numbers multiplied results in a positive number Teaching requires good classroom management Communication can be verbal, nonverbal Concept Mapping 5 What does a Concept Map look like? Concept Maps are tools for to Learning Represent data In a diagram Concept Mapping 6 A Concept Map Includes: Maths 1) Nodes (terms or concepts) Linking Phrase contains 2) Linking lines (usually with a unidirectional arrow) 3) Linking phrases Linking Phrase numbers Linking Phrase Linking Phrase Linking Phrase Linking Phrase 4) Propositions: Smallest Unit of Meaning Concept Mapping 7 Concept Mapping 8 Concept Mapping 9 Focus Questions Every concept map is constructed with reference to a ‘focus question’ which clearly specifies the problem or issue that the concept map should help to resolve (Novak and Cañas, 2006). Encourage students to construct a map that explicitly answers the focus question What are the characteristics of light? Why do we need food? What is Trigonometry? What are the components of animal cells? Concept Mapping 10 Aim of Concept Maps To gain insight into the way students view a topic. To examine the understandings and misconceptions students hold. To assess the complexity of the relationships students hold. Concept Mapping 11 Why use Concept Maps? Good for planning ahead ◦ ‘Advance Organisers’ Helps you learn more easily ◦ Promotes you to talk about concepts ◦ Relate new concepts to previous concepts Good for revision A new assessment tool Highlights the connections between different aspects of theory Concept Mapping 12 How to create a Concept Map Decide on a focus question that you want to answer Identify the Major Concepts ◦ Start with a general (key) concept at the top of the map Arrange the concepts on paper ◦ Work your way down through a hierarchical structure to more specific concepts Link the concepts using linking phrases Make crosslinks ◦ Include applications and examples where possible Refer back to the focus question to ensure you are answering it at all stages Concept Mapping 13 Tips When Making Maps: Use unlined paper and pencil. Relax and allow yourself to concentrate on the focus question. Write down the major terms or concepts relating to the topic in a list. Create a map with the most general terms on top and getting more specific as you move down the map. Ask yourself questions as you generate the map, use the concepts you have to help you generate more. Concept Mapping 14 Practice makes Perfect!! Concept Map 1 – Any Topic In groups of two/three construct a concept map on a concept/topic you are interested in. The topic is your choice – firstly generate a focus question that the concept map will answer. Pick any topic – music, sport,TV etc. Concept Mapping 15 Reflect on the process of Constructing Concept Maps? 1. Did you enjoy constructing the concept map in pairs? 2. Can you see a potential use for the tool in any of your classes? 3. Did you find the task of constructing a Concept Map difficult/easy? What was difficult/easy about the process? 4. Do you understand the importance of the focus question? 5. What one piece of advice would you give your friends if they were to construct a concept map on a topic they are familiar with? Concept Mapping 16 Concept Map 2 – Your Subject Area In groups of two/three – generate a concept map on a topic related to your subject area What is the focus question? You can use textbooks to help you. Identify the important concepts Link the concepts using linking phrases Concept Mapping 17 Take-Home Messages Start with small steps – generate small maps at the start and then increase them Use them to help you understand any concept Make sure and answer the focus question – keep FOCUSED Concept Mapping 18 Thank You Any Questions??? A ROAD MAP SHOWS YOU HOW TO GET FROM ONE PLACE TO ANOTHER – A CONCEPT MAP SHOWS YOU HOW TO GET FROM ONE IDEA TO ANOTHER Concept Mapping 19