Figurative Language in Haroun Powerpoint

Figurative Language
Haroun and the Sea of Stories
Warm up:
“All names means something.” Rashid replied…
What is the story behind your name--What does your name mean? Where did it come from?
What is figurative language?
Figurative language is language that means more than what it says on the surface, it has meaning that goes beyond the literal level.
Whenever you describe something by comparing it with something else, you are using figurative language.
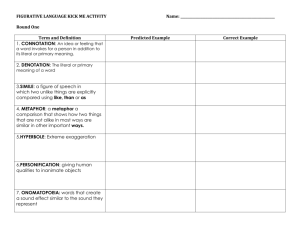
Similes
A figure of speech which involves a direct comparison between two unlike things, usually with the words like or as.
Example: Black smoke poured out of the chimneys of the sadness factories and hung over the city like bad news.
Metaphors
A figure of speech which involves a comparison between two unlike things.
The comparison is not announced by like or as.
Example: One minute you’ve got a lucky star watching over you and the next instant it’s done a bunk.
Personification
A figure of speech which gives the qualities of a person to an animal, an object, or an idea.
Example: There was once, in the country of Alifbay, a sad city, the saddest of cities, a city so ruinously sad that it had forgotten its name.
Onomatopoeia
The formation or use of words such as buzz or murmur that imitate the sounds associated with the objects or actions they refer to.
Example: The Shah of Blah sounded like a stupid crow. ‘Ark, ark ark’.
Imagery
Language that appeals to the senses.
Descriptions of people, places, things, ideas are stated in terms of our senses. o Sight o Hearing o Touch o Taste o Smell o Example: “It was true that it was raining so hard in the sad city that you could almost drown just by breathing in.”
Example: “The moon shined brightly on the road’s slippery gaze.”
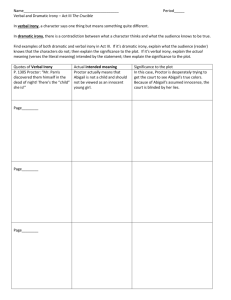
Irony
Irony is a figure of speech in which words are used in such a way that their intended meaning is different from the actual meaning of the words. It may also be a situation that may end up in quite a different way than what is generally anticipated. In simple words, it is a difference between the appearance and the reality.
There are two basic kinds of irony i.e. verbal irony and situational irony.
A verbal irony involves what one does not mean. When in response to a foolish idea, we say, “what a great idea!” it is a verbal irony.
A situational irony occurs when, for instance, a man is chuckling at the misfortune of the other even when the same misfortune, in complete unawareness, is befalling him.
Verbal Irony
Why do author’s use figurative language?
It helps the reader to visualize (see) what the writer is thinking.
It puts a picture in the readers mind.
It allows us to make connections.
Practice
Find one example of each figure of speech (simile, metaphor, personification) in your assigned chapter. We will share these.
Ticket To Leave
Explain Mr. Butt's assertion that "'A figure of speech is a shifty thing; it can be twisted or it can be straight." (33)