PDNA - early recovery
advertisement
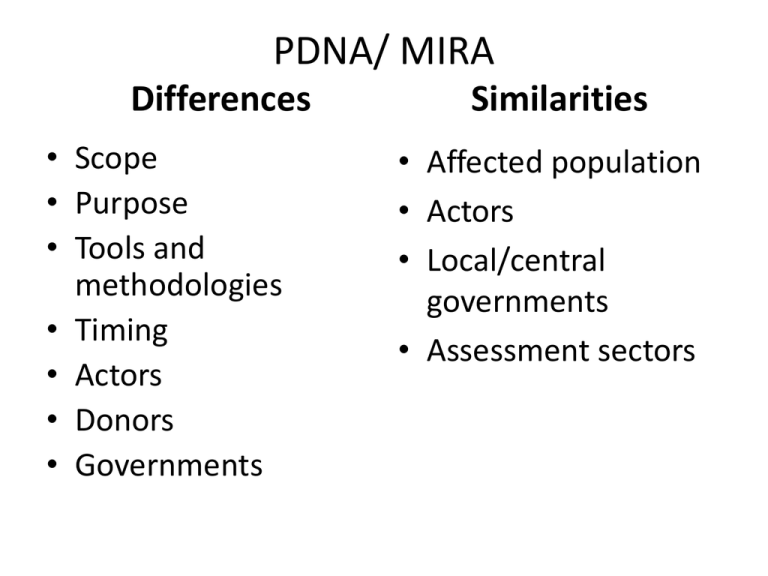
PDNA/ MIRA Differences • Scope • Purpose • Tools and methodologies • Timing • Actors • Donors • Governments Similarities • Affected population • Actors • Local/central governments • Assessment sectors Post Disaster Needs Assessment (PDNA) Hossein Kalali, Disaster Reduction and Recovery Team, UNDP HUMANITARIAN ASSESSMENT Phase 1 Phase 2 Phase 3 Phase 4 Initial Rapid Assessments In-Depth Assessments Multi-cluster Initial and Rapid Assessment (MIRA) Cluster/ Sector Assessments Flash Appeal Revised Flash Appeal, Sector/Cluster Responses, PDNA/PCNA Post-crisis cooperation agreements • Joint Declaration on Post-Crisis Assessments and Recovery Planning (UNDG – World Bank and EC) • • United Nations-World Bank Partnership Framework for Crisis and Post-Crisis Situations • • signed 25 September 2008 October 2008 United Nations Development Group- World Bank Post-Crisis Operational Annex • signed 24 October 2008 • Common platform for partnership and action • Integrated efforts to work with national authorities and partners to strengthen national capacity for effective prevention and response • Support implementation of national recovery • Common methodology, toolkit and capacities A COMMON PLATFORM FOR SUPPORT TO RECOVERY PDNA/PCNA : Differences PCNA • Led by DOCO from the UN side • Modular approach to allow Flexibility and adaptability • It is based on ‘’Transitional Results Framework’’ • One planning and assessment process from cessation of hostilities to process to full recovery • Includes conflict analysis and political dimensions; PDNA • Led by UNDP form the UN side • A set of sectoral methodologies based on both the development and humanitarian sectors • Includes a Recovery Framework, • Triggered by a request from the Government • Based on a Disaster Risk Reduction analysis and plan HUMAN DEVELOPMENT IMPACT ? ECONOMIC LOSSES? RECOVERY NEEDS? PHYSICAL DAMAGES? ACCESS TO BASIC SERVICES ? INCREASED RISK? DONOR CONFERENCE ? RECOVERY FRAMEWORK GOVERNANACE FUNCTIONS ? MACROECONOMIC IMPACT ? A holistic, systemic conceptual and operational framework HUMAN -Health -Education SOCIAL NATURAL -Social networks (security and solidarity) -Family ties and extended family -Violence and security PHYSICAL -Clean water -Clean air -Biodiversity and ecosystem (microclimate) -Type and quality of settlement and housing -Infrastructure conditions (basic lifeline services) -Geomorphologic conditions (slopes, coasts, floodplains) FINANCIAL -Access to credit -Land tenure and ownership - Formalizing asset’s value PDNA PROCESSES DISASTER Assessment of Disaster Effects: Sectoral Level Assessment of Disaster Impact: Agregate Level Assessment of Post Disaster Needs • Damages • Losses • Disruption of Access to basic services • Disruption of gouvernance • Increase of Risk • • • • Economic & Fiscal Social & Culture Human Development Environment • • • • reconstruction Economic recovery Restablishment of Services Restoration of governance Functions • Risk Reduction( BBB) REHABILITATION AND RECONSTRUCTION ACTION PLAN National Government : Role • Initiate the process • Coordination between sector ministries , national and district level • Planning : Data collection, decision on categories of damage , Unit costs • Ownership and use of the assessment report • Institutionalization of process • Resource allocation and donor coordination PDNA Deliverables • Consolidated government-owned set of sector reports (one per sector) representing the dual perspectives of valuation of damage and loss and human recovery needs and factoring crosscutting issues in recovery; • Recovery Framework presenting the early, medium and long term recovery needs in the order of priority, cost, timeline and the actors most likely involved in such recovery activities;





















