class5_3
advertisement

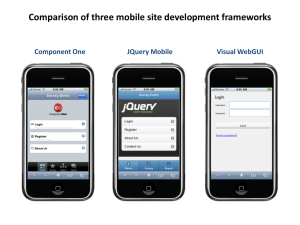
JQUERY Mobile Overview
Norman White
What is JQUERY Mobile?
• jQuery Mobile is a touch-friendly UI framework built on
jQuery Core that works across all popular mobile, tablet and
desktop platforms.
• “jQuery Mobile is a user interface framework based on jQuery
that works across all popular phones, tablet, e-reader, and
desktop platforms. Built with accessibility and universal access
in mind, we follow progressive enhancement and responsive
web design (RWD) principles. HTML5 Markup-driven
configuration makes it easy to learn, but a powerful API makes
it easy to deeply customize the library.”
JQUERY Mobile Introduction page
New Additions - data-roles
pages and dialogs
A page in jQuery Mobile consists of an element with a datarole="page" attribute. Within the "page" container, any valid
HTML markup can be used, but for typical pages in jQuery
Mobile, the immediate children of a "page" are divs with datarole="header", class="ui-content", and data-role="footer".
The baseline requirement for a page is only the page wrapper
to support the navigation system, the rest is optional.
A page can be styled as a dialog that makes the page look like
it's a modal style overlay. To give a standard page the
appearance of a modal dialog, add the data-rel="dialog"
attribute to the link. Transitions can also be set on dialog links.
Ajax enhancments
jQuery Mobile includes an Ajax navigation system to
support a rich set of animated page transitions by
automatically 'hijacking' standard links and form
submissions and turning them into an Ajax request. The
back button is fully supported and there are features to
prefetch & cache, dynamically inject, and script pages
for advanced use cases.
Link and Form interception
• Whenever a link is clicked or a form is submitted,
that event is automatically intercepted by the Ajax
navigation system and is used to issue an Ajax
request based on the href or form action instead of
reloading the page. While the framework waits for
the Ajax response, a loader overlay is displayed.
• Note: This is all done seamlessly by JQUERY Mobile
and the user does not realize that the page is being
rebuilt on the fly, possibly with content being fetched
over the internet.
Page loading and transitions
Everything happens without refreshing page
• When the requested page loads, jQuery Mobile parses the
document for an element with the data-role="page" attribute and
inserts that code into the DOM of the original page. Next, any
widgets in the incoming page are enhanced to apply all the styles
and behavior. The rest of the incoming page is discarded so any
scripts, stylesheets or other information will not be included. The
framework will also note the title of the incoming page to update
the title when the new page is transitioned into view.
• Now that the requested page is in the DOM and enhanced, it is
animated into view with a transition. By default, the framework
applies a fade transition. To set a custom transition effect, add the
data-transition attribute to the link.
Content and Widgets
Inside your content container, you can add any standard
HTML elements - headings, lists, paragraphs, etc. You can
write your own custom styles to create custom layouts by
adding an additional stylesheet to the head after the
jQuery Mobile stylesheet.
jQuery Mobile includes a wide range of touch-friendly UI
widgets: form elements, collapsibles, collapsible sets
(accordions), popups, dialogs, responsive tables, and
much more. For best performance, use the download
builder to pick the components you need.
Listviews
Puts lists on steroids for easy navigation on a mobile device
jQuery Mobile includes a diverse set of common listviews that are coded as lists with a
data-role="listview" added. Here is a simple linked list that has a role of listview. We're
going to make this look like an inset module by adding a data-inset="true" attribute
and we add a dynamic search filter with data-filter="true" and a text field.
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
<form>
<input id="filter-for-listview" data-type="search" placeholder="Type to
search...">
</form>
<ul data-role="listview" data-inset="true" data-filter="true" data-input="#filterfor-listview">
<li><a href="#">Acura</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Audi</a></li>
<li><a href="#">BMW</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Cadillac</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Ferrari</a></li>
</ul>
Forms
The framework contains a full set of form elements that are automatically enhanced into touch-friendly
styled widgets. Here's a slider made with the new HTML5 input type of range, no data-role needed. Be
sure to wrap these in a form element and always properly associate a label with every form element.
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
<form>
<label for="textinput-s">Text Input:</label>
<input name="textinput-s" id="textinput-s" placeholder="Text input" value="" data-clearbtn="true" type="text">
<label for="select-native-s">Select:</label>
<select name="select-native-s" id="select-native-s">
<option value="small">One</option>
<option value="medium">Two</option>
<option value="large">Three</option>
</select>
<label for="slider-s">Input slider:</label>
<input name="slider-s" id="slider-s" value="25" min="0" max="100" data-highlight="true"
type="range">
</form>
Responsive Design
Automatically adapt to different devices
• jQuery Mobile has always been designed to work
within a responsive web design (RWD) context
and our docs and forms had a few responsive
elements from the very start. All the widgets are
built to be 100% flexible in width to fit easily
inside any responsive layout system you choose
to build.
• The library also includes a number of responsive
widgets like responsive grids, reflow tables and
column chooser tables, and sliding panels.
RWD Basics
RWD has three key elements:
CSS media queries, used to target styles to
specific device characteristics such as screen width
breakpoint or resolution.
A fluid grid, that specifies elements and widgets
in flexible units with the goal of making them flow
to fill their containers.
Flexible images and media, are also sized in
relative units so they re-size to fit within their
containers.
RWD Allows document to
automatically reformat based on size
• By creating all screen elements to be fluid and flexible, it
allows the media queries to focus primarily on controlling
layout rules for containers; the modules inside simply resize to fit their containers.
• A simple responsive example may be two stacked
containers, each with flexible content or widgets inside. At
greater widths, media queries are used to float both
containers to create a two column layout to take better
advantage of the wider screen.
• Since the content inside each container is designed to reflow to fit its parent, the media queries can focus just on
the rules for making the columns stack or float, and to
override or add styles only needed at greater widths.
Progressive Enhancement
(built into Jquery)
In addition to these three core RWD principles,
we advocate following progressive
enhancement (PE) practices. This means always
starting with semantic HTML which will work on
any device, then unobtrusively layering in
advanced CSS and JS only for capable browsers.
This provides a solid foundation for the devicelevel optimizations that RWD provides and is
how the jQuery Mobile library is built.
Responsive Web Design Tips
•
•
•
•
•
•
Create a style override stylesheet and include it after the jQuery Mobile framework stylesheet.
This will hold all your custom styles, tweaks to the default widgets and media queries.
Start by writing the styles you want to see at the narrowest screen width (i.e. "mobile first").
These should be outside a media query. This mobile-first approach is efficient because you can lay
down the core typography, colors and styles for mobile knowing that these tend to also be used for
wider breakpoints.
Choose the breakpoints based on your content, not a specific device. Since there are devices of
every imaginable width, it's smarter to choose breakpoints based on how your content looks in
your design system. As you re-size the window to greater widths, identify where your content hits a
point where it could adapt to take advantage of a wider width.
Write media queries' widths in ems, not pixels. This ensures the layout will adapt to font size
changes in addition to screen widths. To calculate the width in ems, divide the target breakpoint in
pixels (320px) by 16px (the default font size) to get the em-based width (20em).
Use min-width breakpoints that build on top of the mobile styles. The first breakpoint applies
layout adjustments on top of the standard mobile styles so these can be fairly lightweight.
Additional min-width breakpoints can be added for even wider screens that each build on the
previous breakpoint styles.
To override framework styles only for smaller screens, use a max-width breakpoint instead. This
allows you to constrain your style overrides to only apply below a certain screen width. Above this
width, all the normal styles will apply so this is good for certain types of overrides.
Example of RWD
build for mobile first
/* Start with core styles outside of a media query that apply to mobile and up */
/* Global typography and design elements, stacked containers */
body { font-family: Helvetica, san-serif; }
H1 { color: green; }
a:link { color:purple; }
/* Stack the two content containers */
.main,
.sidebar
{ display:block; width:100%; }
/* First breakpoint at 576px */
/* Inherits mobile styles, but floats containers to make columns */
@media all and (min-width: 36em)
{ .main { float: left; width:60%; }
.sidebar { float: left; width:40%; } }
/* Second breakpoint at 800px */
/* Adjusts column proportions, tweaks base H1 */
@media all and (min-width: 50em)
{ .main { width:70%; }
.sidebar { width:30%; }
/* You can also tweak any other styles in a breakpoint */
H1 { color: blue; font-size:1.2em } }
Theming
jQuery Mobile has a robust theme framework that supports
up to 26 sets of toolbar, content and button colors, called a
"swatch". Just add a data-theme="b" attribute to any of the
widgets on this page to turn it black.
Cool party trick: add the theme swatch to the page and see
how all the widgets inside the content will automatically
inherit the theme.
When you're ready to build a custom theme, use ThemeRoller
to drag and drop, then download a custom theme.
Takeaway
• JQuery Mobile takes much of the work out of
developing a layout that works on a mobile
device, and also allows for web pages that
automatically adapt to any device size,
smartphone, tablet, desktop.
• Themes allow the developer to choose from a
variety of User Interfaces, which they can then
customize.