B3 Active Transport slc
advertisement
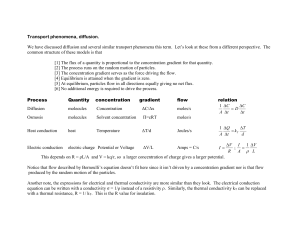
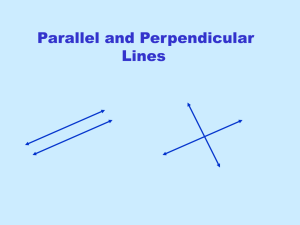
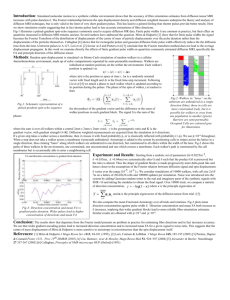
B3 Active Transport Mrs S Carpenter TITLE: Active Transport Objectives • What is active transport – grade C • Describe the process and know where active transport occurs in plants and animals? Grade B • Explain the benefits to the organism of using active transport. Grade A Outcomes: Pupils will: • Produce their own definition and amend it to B3 – grade A standard. • Produce a table with plant and animal examples of active transport. • answer exam style questions KEY WORDS: Active transport Diffusion Concentration gradient Starter Complete the following: Diffusion is the movement of particles ………… a ………….. gradient from an area of ……………….. concentration to an area of ………………………….. What is a Concentration Gradient? • Hills and graphs have gradients 1) Which one has the steepest gradient? 2) Which one moves up a gradient and which moves down a gradient? moving down a concentration gradient Which way will the particles move? What does the phrase active transport mean? • Look for clues in the words above. Write a definition Can you think of any places in plants and animals where this may occur? Produce a table and add/change details as the lesson continues Now watch this clip • Diffusion and Active Transport - My GCSE Science • What did you learn? Add details to your notes. Do you want to change your definition? Amend as necessary. moving UP or against a concentration gradient ENERGY The particles can move up the concentration gradient if energy is used This is active transport Higher Sometimes it is worth using up energy when a resource is particularly valuable and its transport is really important! Do you remember the name of the ‘energy currency’ that is used? Add this term to your definition. AQA Science © Nelson Thornes Ltd 2006 9 Active transport • This DOES Require energy • Particles move against a concentration gradient. • The energy is needed to make “pumps” move particles the wrong way. • E.g. glucose from the intestine into the blood Active Transport Active transport in plants Active Transport • Active transport occurs across semi permeable membranes and moves particles from a low concentration to a higher concentration. This is against the concentration gradient. • Transport or carrier proteins are needed to get these molecules into the cells and these use energy. • Cells that do active transport contain large numbers of mitochondria. Why? Important in both plants & animals • PLANTS – Allows the absorption of dilute minerals into the plant against a concentration gradient • ANIMALS – Allows the absorption of glucose (essential for respiration within nervous tissue) into the blood from the kidneys and ileum against a concentration gradient Rate of active transport Rate of active transport depends on the rate of respiration 0 Draw a quick sketch. Describe what this graph shows you. Rate of respiration Active Transport Inside of cell Outside of cell ATP ADP P Na+ high concentration Glucose Lumen of small Intestine Co Transport Na+ low concentration Glucose Epithelial Cell K+ Active Transport Facilitated Diffusion Glucose K+ Blood Capillary Why? Important in both plants & animals • SEA LIFE – High concentration of salt in sea water • To absorb salt: SALT GLANDS – Located near the eyes – Remove salt from water against concentration gradient – Excrete a salt solution 6x stronger than urine What affect does cyanide have on the body? Challenge. • Statement. Cyanide stops active transport Cyanide affects mitochondria. What will happen? Mitochondria are involved in respiration, so no respiration. This means the organism dies. Questions a) Explain how active transport works in a cell b) Give some examples of a situations when a substance cannot be moved into a cell by osmosis or diffusion, and how active transport solves the problem c) The processes of diffusion and osmosis do not need energy to take place. Why does an organism have to provide energy for active transport and where does it come from? Plenary • Make a list of similarities and differences between active transport and diffusion Reflect and assess your learning • What grade are you working at for this topic?