devt1

Normal Developmental
Milestones
An emphasis on anticipatory guidance
Ana Malinow, MD
Why we should teach parents about development
Parents who understand their child’s developmental state, are more likely to have appropriate expectations.
Having appropriate expectations makes for a healthier relationship between parent and child.
Healthier relationships facilitate development.
Objectives
• Principles of development
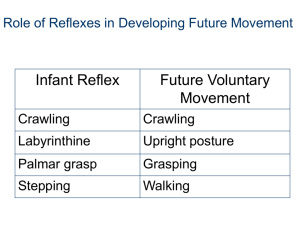
• Primitive Reflexes
• “Locomotion”: Gross Motor
• “Manipulation”: Fine Motor
• “Cognitive”: Language and Social
• Behavior and Personality
Principles of
Development
• A continuous process
• Sequence of development is the same, rate of development varies
• Not parallel
• Related to CNS maturation
• Involuntary movements give way to voluntary responses
• Occurs in cephalocaudal and proximal to distal
• Progresses from dependence to independence
Development Occurs in a
Cephalocaudal
Direction
Development begins in utero
Age
8 ½ wks
Responses/Reflexes tactile stimuli (reflex arc laid down)
12 wks
24 wks sucking sound
26 wks rhythmic breathing movements/ controls body temperature
30 wks
35 wks pupilary light reflex grasp/spontaneous orientation to light
All primitive reflexes develop during gestation and disappear by the 3 rd to
6 th month after birth
Primitive reflexes
• Tonic labyrinthine reflex
• Asymmetric tonic neck reflex
• Positive support reflex
Declining intensity of primitive reflexes and increasing role of definitive motor actions
Gross motor development
“Locomotion”
Locomotion begins with head control
Assessing Locomotion
• Ventral suspension
• Sitting position
NB-3m
NB-8m
• Prone position NB-9m
• Standing/Forw. Walking 9m-18m
• Running/Backw. Walking 2 yrs
• Balancing 3 yrs +
Ventral suspension
Head control
2 month head control
4 month head, arm control
6 month head, arm, trunk control
8 month head, arm, trunk, leg control
9 month pulls up to stand
12 month old locomotion
2 year old Running
Backward Walking
3 year old
Balance
“Manipulation”
Fine Motor Development
Manipulation: Assessing the pincer grasp from 0-6m
• NB
• 1m
• 2m
• 3m
• 4m
• 5m
• 6m primitive primitive starting to lose voluntary on ulnar hands together palmar grasp hand-mouth-hand; hand-to-hand
Manipulation: Assessing the pincer grasp 7-12 m
• 7m
• 8m
• 9m
• 10m
• 12m
• >12m thenar side, raking
1 block in each hand radial-digital grasp; inferior pincer index finger isolation fine pincer letting go, stacking
“Cognition”
Social Development
Problem solving
Play
Causality
Language Development
• NB
• 4-6wks
• 2m
• 3m
• 5m
• 6m
• 7m
• 8m
• 9m
• 10m
Assessing cognitive development
Problem solving visual exploration smiles, fixes, follows imitates mouth movements anticipates feeds object permanence looks to floor when toy dropped grabs 2 nd cube, drops first seeks object after fall (silent) uncovers hidden object under cloth isolates index finger
Assessing cognitive development
Play
Age
<12m
Play stage sensory-motor
12m-18m functional
18m-24m symbolic
2-5y
6y
11y + imaginary/magical hypothetical
Piagetian stage sensory-motor sensory-motor sensory-motor pre-operational logical thinking concrete operation formal operational
12-month 18-month
Functional Play
18-month 24-month
Symbolic Play
2-5 year
Imaginary/Magical Play
6 year old
Logical Thinking
11 years +
Hypothetical thinking
Assessing cognitive development
Causality
Age
Early
Early
4m
8m
10m
24m
Cause cries smiles kicks crib pulls string funny winds key
Effect mom comes mom responds mobile moves gets ring
+response/repeats toy moves
Conversational speech probably starts with smiling
2 month old language
Assessing cognitive development: Language
4m
6m
7m
8m
12m
Age
4-6wks
2m
3m
Milestone smiles vocalizes with vowels vocalizes with consonants squeals syllables non-specific combinations imitates sounds, understands “no”
1-3 words
Assessing language
4y
5y
6y
Age Expressive Receptive Jargon Sentence L. Intelligible
12m 1-3 100
18m 10-25 ID body
2y
3y
50
500
Pts. Body
Y
Y
N
Prepositions N none giant words holophrases
2 words
3-4 words
25-50%
75%
5 def.
Comparisons N
7 def.
N
4-5 words masters rules of grammar
100%
100%
Behavior
• One-way or two-way interactions
• Prenatal factors
• Bonding/attachment
• CNS maturation
• Match
• Schedule
• Language
• Instincts
Behavior
-continued-
• Cognitive, gross and fine motor development
• Illness, separation, feeding issues
• Birth order, family size
• Secondary attachments
• Environment
• Gender identification
Bonding
Personality
• Factors that influence behavior
• Create behavior
• Through adaptability and flexibility
• Produce personality/social behavior
Newborn “Personality”
4 month old
“Personality”
9-month old
“Personality”
Other “Personality”
Landmarks
• 2-year old independence/dependence
• 3-year old master of impulse control, sharing, wants to please, guilt
• 7-year old ability to see another’s point of view
• Adolescence begins identity formation
(idealistic)
• Adulthood completion of identity formation
Conclusion
• Development is a continuous process
• Sequence is always the same, rate varies
• Development does not run parallel
• Intimate relationship with CNS
• Generalized activity gives way to voluntary activity
• Cephalocaudal development
• Dependence to independence












![2.2 Reflex Actions [Recovered]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005391273_1-054579405a11249686dc3e18a88c3962-300x300.png)