*The land between two rivers* Sumer*Babylon*Assyrians Ms. Jerome
advertisement

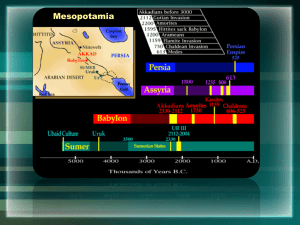
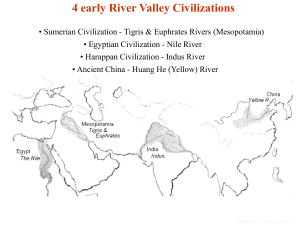
“The land between two rivers” Sumer--Akkad—Babylon— Hittites—Assyrians—Babylon— Persian Ms. Jerome Do Now Read excerpt and answer questions from The Epic of Gilgamesh The Epic of Gilgamesh is an epic poem from Mesopotamia and is among the earliest known works of literature. Scholars believe that it originated as a series of Sumerian legends and poems about the protagonist of the story, Gilgamesh king of Uruk, which were fashioned into a longer Akkadian epic much later. The most complete version existing today is preserved on 12 clay tablets from the library collection of 7th-century BC Assyrian king Ashurbanipal. The epic was originally titled He who Saw the Deep (Sha naqba īmuru) or Surpassing All Other Kings (Shūtur eli sharrī), which are the first few words of the epic in different versions. Map: Why is the outlined location of Mesopotamia an ideal location for a civilization? Modern Day Iraq The Unpredictable Floods The Tigris and Euphrates flooded unpredictably Washed settlements away Others learned to build canals and dikes and built uphill Sumer developed in southern Mesopotamia Over 100,000 people Sumerian cities were the center of political and military authority Marketplaces were economic centers Also cultural centers with priests and scribes Sumer Sumerian Civilization River management was key to early success Developed cuneiform—why is this important to the longevity of a culture? Write down laws Treaties Social and religious customs Record keeping (who paid their taxes? Who didn’t?) Each symbol stands for a word First wheeled vehicles Polytheism Each city state had its own god that was worshipped only by its people. Sumerians built ziggurats to honor their deities. Each city state had a ziggurat http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=w8v2vRlLL5 8&feature=related Video on Sumer What continuous contributions does the video discuss about the legacy of Sumer? What was at the center of each City State? What contributions did the Sumerians give to the world? Sumerian social structure Sumer became attractive to raiders for its wealth This developed the need for a recognized military By 3,000 b.c.e. all Sumerian cities had kings who claimed absolute authority Most of the population was comprised of peasant farmers Which tells you what about the civilization? The Rise of the Babylonians The Akkadians and Babylonians of northern Mesopotamia soon overshadowed Sumer Led by Akkadian warrior Sargon, Mesopotamian city states merged into an empire until his death. Akkad was overrun by a new powerhouse, Babylon, under the leadership of its King, Hammurabi Sargon the Great: ca. 2270 BC – 2215 BC Hammurabi’s Empire Hammurabi’s Code activity Groups of 3 Each group has to skim through 50 different codes of Hammurabi http://www.phillipmartin.info/hammurabi/hammurabi_code index.htm Make a list of 10 different facts you can defer about Mesopotamian/Babylonian culture based on its laws Consider values, social structure and level of punishment per offense The Jeromeurabi Code Rules regarding homework Rules regarding attendance Rules regarding class work Rules regarding leaving the classroom Rules regarding group work Rules regarding writing assignments … Enter the Hittites, exit the Babylonians! Babylon falls By 1500 b.c.e. the Hittites became the dominant force in Anotolia (Turkey), invading the riches of Mesopotamia Why? Because they used iron—a stronger metal than bronze. Enabled them to become a military powerhouse But good news travels fast… Enter the Assyrians The Rise of the Assyrians The Assyrians A military powerhouse Military dominated life in this culture Military rank based on merit rather than noble birth Also, good administration like Hammurabi Preserved literature The Fall of the Assyrians Too big to administer (this is a common theme through history!) Internal strife Assyrian empire began to collapse by 612 b.c.e. with the death of King Assurbanipal Built first library Maintained Mesopotamia’s literature (epic of Gilgamesh) Nebuchadnezzer and the New Babylonian Empire Nebuchadnezzer rebuilt Babylon—canals, walls, temples, a defensive mote Built first great, illustrious city of the ancient world Summary Contributions of the Hittites Introduced ironworking Contributions of Contributions of the Assyrians Founded the first library the Babylonians Established first great ancient city Hanging Gardens of Babylon The growing Persian Empire would soon encompass all of Mesopotamia