Click here ()
advertisement

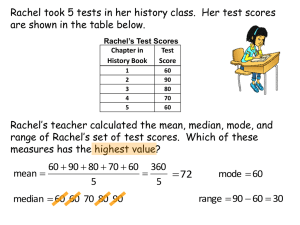
HOW LEADERS IMPACT CLASSROOM TEACHING AND LEARNING Where to Show Up and What to Do Jon Saphier Research for Better Teaching, Inc. Objective Leave with a plan for leading in a new arena of influence on classroom teaching or augmenting the way way you already lead in an arena. (Picking what will be the Big Rocks for your school.) What is the most significant variable in increasing student achievement? Teaching Expertise What Teachers Know, Believe & Can Do Increased Student Achievement FIFTH GRADE MATH SCORES ON TENNESSEE STATEWIDE TEST BASED ON TEACHER SEQUENCE IN GRADES 3, 4, 5 (Second Grade Scores Equalized) Research by Sanders & Rivers (1996) 96 100 T e 80 s P t e r S c c e 60 o n r t e i s l e 40 b y 79 44 20 0 Students with 3 Least Effective Teachers Students with 3 Average Effective Teachers Students with 3 Most Effective Teachers CHANGES IN MATH SCORES ON TENNESSEE STATEWIDE TEST AMONG STUDENTS WITH EQUALIZED SECOND GRADE SCORES BASED ON TEACHER SEQUENCE IN GRADES 3 ,4 ,5 Research by Sanders & Rivers ( 1 9 9 6 ) 80 75 70 60 Percent ile 50 St udent s wit h 3 Most Ef f ect ive Teachers in Grades 3 ,4 ,5 50 Dif f erence of 5 0 percent ile point s St udent s wit h 3 Least Ef f ect ive Teachers in Grades 3 ,4 ,5 40 30 25 20 10 0 Equalized Second Grade Scores Fif t h Grade Scores Poll Mathematics, Grade 4 Use the diagram below to answer question 19. 3 19 4 5 How long is the truck? A. 5 34 inches 27 B. 2 34 inches 39 C. 5 12 inches 27 D. 2 12 inches 6 6 7 8 Mather School student responses to this question. Reporting Category for Item 19: Measurement (p.230) Questions and Sequence of Steps For Teams Doing Error Analysis 1. What might the student have been thinking to make this error? 2. How can we find our which of these hypotheses is right? 3. What different teaching strategies could we use to “fix” or undo whatever lead to this error- and help the student solidify his/her skills and concepts? Questions and Sequence of Steps For Teams Doing Error Analysis 4. How are each of us going to plan and manage tasks and time during the instructional period so that we’ll get 15 minutes to re-teach skills and concepts at least 3 times a week for those students who made errors? 5. How can the team help? High Functioning Results Orientation Teams Accountability for Norms Legitimate Decisions Open, passionate debate Trust I can be vulnerable Research for Better Teaching The Five Dysfunctions of a Team, 2002 Overcoming the Five Dysfunctions of a Team, 2005 by Patrick Lencioni Research for Better Teaching LEADERSHIP TEAMS The charter of your leadership team (that is, its purpose, its mission, its main reason for being) is to improve the teaching and learning in every classroom in the building. It’s primary purpose is not management. Leadership Teams The starting point is PD of the Leadership Team itself to do these things skillfully. LEADERSHIP TEAMS You are colleagues, under the leadership of the principal, and you form a common vision of what good teaching and learning looks like. You make a plan of action to achieve that vision in increments, and you implement that plan it together. This team, working under the leadership of a clear and mission-driven principal, is the necessary condition for large scale improvement of teaching and learning. You can’t do it alone. Principals, as the instructional leaders of the building, need multiple allies, many teacher leaders, to improve teaching and learning. The leadership team should consist of those who have maximum access and influence over the teacher corps in the building. High Functioning Grade Level and Subject Specific Teams: How would you know if you had one? A Professional Learning Community is teams of teachers who teach the same content and have common planning time together regularly. That’s only the start. What they do and how they act together defines whether they are really a PLC. Here’s what they do: Mathematics Which list of numbers is in order from GREATEST to LEAST? A) 0.08, 0.4, 0.29, 0.107 13.86% B) 0.08, 0.107, 0.29, 0.4 22.89% C) 0.4, 0.29, 0.107, 0.08 39.16% D) 0.4, 0.08, 0.29, 0.107 24.10% KEY CONCEPTS • Areas of Performance • Repertoire • Matching Overarching Objectives Curriculum Design CURRICULUM PLANNING Objectives Assessment Learning Experiences Personal Relationship Building Class Climate MOTIVATION Expectations Clarity Space Principles of Learning Time Models of Teaching INSTRUCTIONAL STRATEGIES Routines MANAGEMENT Attention Momentum Discipline FOUNDATION OF ESSENTIAL BELIEFS So to summarize… A big idea of this day for me is…… One thing I think I’ll try is….. A question I have is…..