Effects that Effect Research ppt.
advertisement

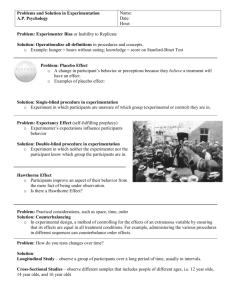
Effects that Effect Research The Hawthorne Effect Reactivity whereby subjects improve an aspect of their behavior being experimentally measured simply in response to the fact that they are being studied The Hawthorne Effect Western Electric manufacturing facility outside Chicago). Hawthorne Works had commissioned a study to see if its workers would become more productive in higher or lower levels of light. The workers' productivity seemed to improve when changes were made and slumped when the study was concluded. It was suggested that the productivity gain was due to the motivational effect of the interest being shown in them. Examples http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=b_YAJtJ mPLE The John Henry Effect The John Henry effect is when people in your control group views itself as being in competition with the treatment group and so changes its behavior. This comes from the story of John Henry trying to lay railroad track faster than the The Novelty Effect: Human Performance, is the tendency for performance to initially improve when new technology is instituted, not because of any actual improvement in learning or achievement, but in response to increased interest in the new technology Example: Build a new baseball stadium = Temporary increase in attendance because its new. Texting vs. Calling The Placebo Effect: Placebo Effect- The phenomenon of an inert substance resulting in a patient's medical improvement if the substance is viewed as helpful, it can heal, but if it is viewed as harmful, it can cause negative effects Examples? The Influence of the Researcher Bias Bias- scientists view results differently based on other influences. Possible Influences: • Money • Ideology • Laziness • Career • Conflicts of Interest Data Manipulation Fabrication – the actual making up of research data and (the intent of) publishing them Falsification – manipulation of research data and processes in order to reflect or prevent a certain result Obfuscation – The Omission of critical data or results Eliminating Bias • Eliminating Bias: • Run many trials • Keep accurate notes of observations • Have other scientists run the exact test and compare results Peer Reviewed Research: Peer Reviewed Studies Research that is published in prestigious journals that must pass the scrutiny of other researchers Double Blind Studies: Two groups of individuals are tested. One group is the control and given a placebo. The other group is given the experimental variable. Anecdotal Evidence: • Weakest form of evidence Observations about a treatment or substance that have not been verified by science