Introduction to Technical Graphics - t4
advertisement

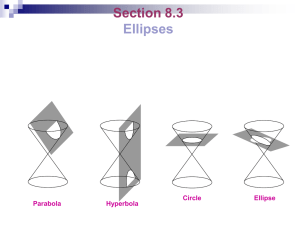
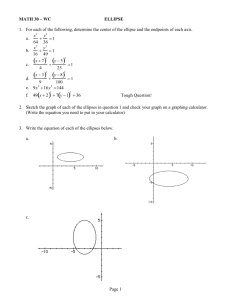
Semicircle Quadrant Introduction or Tester Programme Technical Graphics is a Universal Language • • • Technical Graphics is one of the technology subjects offered at junior cycle. In Technical Graphics students use drawing equipment to create precise and accurate drawings. These drawings are used to communicate ideas or solve problems. How to produce neat drawings of everyday items How to represent 3-D objects on paper How to create models of objects on the computer How to use freehand sketching, colouring and shading to represent objects Communication skills Problem solving skills Computer skills Creative thinking skills Technical Graphics can be very useful in other subjects such as: Mathematics Construction Studies Materials Technology Wood Engineering Technology & Metalwork Junior & Leaving Certificate Technology Art Technical Technical Graphics Graphics Applications of Geometry and Problem Solving Project Maths Project Maths Ordinary Level ◦Paper 2 ◦Leaving Certificate Higher Level ◦Paper 2 ◦Leaving Certificate Higher Level ◦Paper 2 ◦Leaving Certificate Q R P From these exercises you will learn: ◦ The difference between construction lines and finish lines ◦ The importance of draftsmanship ◦ The effect of shading and rendering on a drawing ◦ What indexing is, and how it can assist complicated drawings Activity 1 Activity 1 Activity 2 Activity 2 Activity 3 & 4 Activity 3 & 4 Activity 5 Activity 5 5 4 3 1 2 3 2 4 5 2 1 1 3 2 2 3 4 3 4 5 4 5 4 4 3 2 1 1 5 3 2 4 5 4 3 4 3 2 3 2 1 2 1 5 4 3 2 1 2 3 4 5 Activity 6 Activity 6 From these exercises you will learn: ◦ The name and properties of various polygons ◦ What indexing is, and how it can assist complicated drawings ◦ How to construct a Hexagon using a compass ◦ How to construct an Octagon using a square and a compass ◦ That joining points in a different order can produce different shapes ◦ The importance of draftsmanship ◦ The effect of shading and rendering on a drawing Polygons Equilateral Triangle Octagon Square Nonagon Pentagon Decagon Hexagon Heptagon Circle Activity 7 Activity 7 1 2 5 4 3 Activity 8 1 Activity 8 2 5 4 3 Activity 9 1 Activity 9 2 5 4 3 Activity 10 Activity 10 Set your compass at the required radius and do not change it. 4 5 3 6 2 1 Activity 11 Activity 11 4 3 5 2 6 1 Activity 12 Activity 12 4 3 5 2 6 1 Activity 13 Activity 13 4 3 5 2 6 1 Activity 14 Activity 14 4 3 5 2 6 1 Activity 15 Activity 15 4 10 5 9 11 8 12 6 3 7 1 2 Activity 16 Activity 16 4 7 5 3 9 8 2 6 1 Activity 17 Activity 17 4 10 5 8 11 6 3 9 12 7 1 2 Activity 18 Activity 18 4 10 5 9 11 8 12 6 3 7 1 2 Activity 19 Activity 19 6 5 4 7 3 8 1 2 Activity 20 Activity 20 5 4 6 7 3 2 8 1 Activity 21 Activity 21 5 4 6 7 3 2 8 1 Activity 22 Activity 22 5 4 6 7 3 2 8 1 Activity 23 Activity 23 5 4 6 7 3 2 8 1 Activity 24 Activity 24 5 4 6 7 3 2 8 1 From these exercises you will learn: ◦ How to construct an ellipse using the trammel method ◦ How to construct an ellipse using the compass method ◦ Application of the ellipse in everyday life ◦ The importance of draftsmanship ◦ The effect of shading and rendering on a drawing Ellipse Ellipse Cylinder C Inside an Atom Activity 25 & 26 Activity 25 ½ Minor Axis A B ½ Major Axis Minor Axis P Major Axis Activity 26 Minor Axis Major Circle Major Axis F1 F2 Minor Circle Activity 27 Activity 28 Activity 29 Activity 30 Activity 31 1 3 1 3 2 3 2 3 3 3 3 4 4 2 2 3 Activity 32 2 3 2 1 1 2 3 1 1 4 1 1 2 1 1 Activity 33 3 4 1 2 2 2 4 2 2 4 Activity 34 1 3 3 3 3 4 4 1 1 2