Approaches to Dealing with Resistive Clients
advertisement

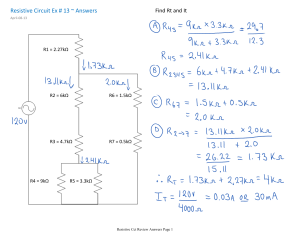
Approaches to Dealing with Resistive Clients What are resistive clients? Those willing to engage in counseling and appear outwardly receptive but who exhibit various qualities or characteristics that hinder progress toward their self-identified goals Might welcome the interaction but resist taking action What causes resistive clients Fear, inertia, mistrust Some might envision all financial professionals as disdainful and self-righteous in dealing with other’s $ Afraid they will be looked upon as failures Admission of failure or guilt Don’t want to face fixing their problem Fear they will be coerced into something they don’t want to do Dispositions and attitudes Don’t want to share financial matters Overcoming normal resistance Warm inviting atmosphere Sincere interest and concern Respecting right to privacy Providing appropriate, reliable, and honest service Avoiding apparent, actual, or potential conflicts of interest Legitimate sources of resistance Counselor not listening Counselor not properly counseling client Financial counseling does not fit the client’s need Client participation is coerced How to avoid legitimate resistance Avoid things that might attract or cultivate legitimately resistive clients Proper labeling, describing, and marketing what your counseling program offers Program flyers and brochures should make clear the types of clients and problems your programs serves. How to avoid legitimate resistance “Client Dumping” Clients are automatically and indiscriminately referred to another service provider Rationalized on the grounds that almost anyone can benefit from financial counseling This practice can generate an excess of resistive clients Will take time, energy, and resources from others who will use it Mechanisms to discourage indiscriminate referrals Contact the agency and work out an agreement for making appropriate referrals Insist that appt. requests be made by the clients themselves, not by someone acting on their behalf Screen applicants when they call by asking them if the counseling is something they want to do someone else wants them to do it Don’t turn suitable clients into resistive clients due to improper treatment Provide good options Provide good analysis Provide good judgments Provide good guidance Keys to avoiding legitimately resistive clients Avoid the attraction and referral of resistive clients by Clearly labeling and describing nature of services Not accepting involuntary and indiscriminate referrals Discouraging clients without purposeful agendas Insisting that all clients be willing participants Referring clients with serious disorders Avoid creating resistance in normally disposed clients by Not prejudging or categorizing any client Listening carefully and openly to each client Basing counseling on what each client wants Providing remedies specifically fitted to each client Accepting and enabling a client’s selfdetermination Guidelines for dealing with resistive clients Do not make quick assumptions Place the responsibility of the client’s success on the client If progress slows down or appears hopeless, restate what the client wants to achieve Don’t get sidetracked by the small stuff Don’t aim to cure the client but the client’s situation Don’t attempt to make every conceivable change that could benefit the client