WBL Framework Awards
advertisement

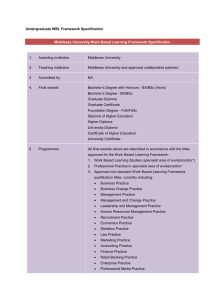
Employer Engagement; Curriculum Refinements Carol Costley Institute for Work Based Learning Employer-led curriculum • Staff Development • On-line support • Module enhancement • University Structures and systems 2 WBL Framework Awards FHEQ Level Middlesex University Taught Awards Minimum Total Credits 4 University Certificate 40 4 Certificate of Higher Education 120 5 University Diploma 40 5 Higher Diploma 120 5 Diploma of Higher Education 240 5 Foundation Degree 240 6 Graduate Certificate / Advanced Diploma 60 6 Graduate Diploma 120 6 Bachelor’s Degree 300 6 Bachelor’s Degree with Honours 360 7 Postgraduate Certificate 60 7 Postgraduate Diploma 120 7 Master’s Degree 180 FHEQ Level Middlesex University Research Awards Minimum Total Credits 7 Master’s Degree 180 8 Doctorate Degree 540 3 WBL Framework Programme elements 4 The WBL Framework • Schools and University partners can use the framework by: • Constructing programmes using various combinations of validated WBL framework modules (with or without other University validated modules) • Integrating the modules within subject-specific programmes • Constructing programmes using combinations of accredited in-company higher-level provision and framework modules • Constructing programmes using combinations of APEL and WBL framework modules • Can lead to a comprehensive range of current University awards from level 4 to 7 (8). 5 WBL modules • Review of learning (can include APEL claim) • Search and Review of relevant knowledge and information • Professional Development/ Planning • Practitioner Enquiry • Negotiated WBL Projects 6 Review of learning • Enables work based learners to: – Review their learning journey using reflective / reflexive practice – Recognise the contribution of both certificated and experiential learning to their personal and professional development. – Often this process can be used to generate a claim for accreditation of prior certificated and experiential learning (APEL). 7 Search and Review of relevant knowledge and information • How to look for and review knowledge and information to create new practices and solve a practical problem. • Using academic conventions of referencing and citation • Includes professionally based knowledge and information found in work-related sources 8 Professional Development/ Planning • Designed to support the initiatives and continuing development of an individual’s knowledge, understanding and skills as a work-based learner. • Provides the opportunity to establish and develop professional practitioner identity. • Reflection on current work/practice leading to the formulation and articulation of personal and professional development needs. • Planning of a future programme taking above into account. 9 Practitioner Enquiry • Practitioner Inquiry modules enable work-based learners to: – enquire into their own work/practice and promote skills in investigation, data acquisition, analysis and evaluation, – develop an academic argument using evidence to inform decisions concerning work/practice enhancement. 10 Negotiated WBL Projects 1 • Projects, enquiries and other work-based activities, enable work-based learners to consider, create or construct proposals for work/practice development and change. • Negotiated aspects of the modules provides: – flexibility in framework programme construction and – responds to organisational development needs of employers/ organisations. 11 Negotiated WBL Projects 2 • A compulsory element of WBL programmes lead to awards of Foundation, Bachelor’s and Master’s Degrees. • Designed to enable individuals to apply active experimentation and enquiry skills to the experience of their work/practice. • The negotiated approach enables individuals, employers or other organisations to identify aspects of work/practice that can be enhanced. • Can be in the form of a clearly defined ‘project’ that has identified and planned outcomes. • Can also represent a more open-ended ‘enquiry’ or ‘other worked-based activity’ designed to enhance awareness 12 and/or to promote innovation in work/practice. Accreditation • • • • In-house training Other accredited courses Certificated Learning Experiential Learning At Middlesex up to two thirds of a programme can be learning achieved outside of the University. Other Universities vary, usually from 50% to 75% 13 Building learning and programmes • Can start with accredited Learning. • A second step could be a University certificate. • The certificate may then be built into a degree programme. 14 Negotiated Programmes • Studies through ‘Employer Engagement’ arrangements are negotiated initially with employers. • Curriculum content is designed to meet the needs of the organisation and the individual’s position and strengths within the organisation • Content is negotiated within the university’s validated programme award structures, specifications and regulations. 15 The Value of Work-Based Projects • The aim is to change or enhance practice. • A tangible outcome that has a positive effect on practice to the organisation and/ or the field. • Builds on the practitioner’s current expertise. • Brings University level learning and expertise of higher education, e.g.research and development capabilities, reflection/ reflexivity in professional learning, critical and creative approaches, a discipline to working with sources of knowledge. 16 Enhanced Work-Based Projects • Setting out aims that focus upon outcomes that are realistic, appropriate and meet level requirements (requires a 3 way agreement). • Ethical considerations incorporating workplace values and university requirements • Relevant approaches to research or at undergraduate level, ‘enquiry’. • ‘Conclusions and Recommendations’ that draw from the enquiry process and the practitioner’s expertise. 17