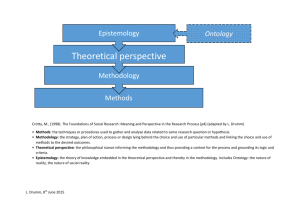
ROLE OF MIDDLE LEVEL MANAGERS IN STRATEGY PROCESS
advertisement

ROLE OF MIDDLE LEVEL MANAGERS IN STRATEGY PROCESS B.V.L.NARAYANA FPM III 1 SCHEME OF PRESENTATION • MOTIVATION • THEORETICAL BASIS • THE MODEL • ROLE OF ACTION RESEARCH 2 MOTIVATION • STRATEGY – EXPLOITATION OF SIGNALS FROM ENVIRONMENT • ENVIRONMENTAL DYNAMISM • SHIFT IN BASIS FOR STRATEGY-- POSITION BASED TO CAPABILITY BASED • INCREASED IMPORTANCE OF ROLE OF MIDDLE LEVEL MANAGERS 3 MOTIVATION changing orientation of middle management work Traditional orientation Present orientation Developing coordination within functional boundaries Boundary spanning( relationships across boundaries) Controlling growth Finding innovation( championing) Executing plans Synthesizing information Applying new technologies to production Facilitating learning (transferring technology). ADAPTED FROM FLOYD AND WOOLRIDGE 1996 4 THEORETICAL BASIS • ROLE OF MIDDLE LEVEL MANAGERS IN STRATEGY FORMATION: • IDEA GENERATION: CENTRE OF INFORMATION NETWORK (DUTTON ET AL 1997) • STRATEGIC INITIATIVES: CREATION OF SOCIAL NETWORKS, KNOWLEDGE CREATION, UNDERSTANDING OF ORGANISATION PROCESSES( NONAKA 1994, FLOYD AND WOOLRIDGE 1996) • CAPABILITY SET: DEVLOP NEW CAPABILITIES 5 THEORETICAL BASIS • THREE CRUCIAL REQUIREMENTS FOR SUCCESS OF MIDDLE MANAGERS— • ACCESS TO KNOWLEDGE • DYNAMIC AND FLEXIBLE LEADERSHIP • INTEGRATION OF NEW INTIATIVES AND NEW ROUTINES 6 THEORETICAL BASIS • FOUR ROLES OF MIDDLE MANAGERS • SYNTHESIZING(SENSE MAKING)--attend, frame and diagnose issues • FACILITATION (SENSE MAKING AND SENSE GIVING)-generation of variant behavior, cooperation and experimentation • CHAMPIONING(ISSUE SELLING)--bring entrepreneurial and innovative proposals to the notice of the top management • IMPLEMENTATION(SENSE GIVING)--translate strategic plans into operational plans 7 THEORETICAL BASIS • Sense making -way managers understand, interpret and make sense out of information . • Sense giving-attempts to influence outcomes through communication of thoughts and gain support. • Issue selling -process by which individuals affect others attention, understanding of events, developments and trends that impact organisational performance • ORGANISATIONS ARE- INTERPRETATION SYSTEMS(WIECK 1979) • COMPLEX ADAPTIVE SYATEMS • SOCIAL SYSTEMS –PATTERNED RELATIONSHIPS TRANSMITTING INFORMATION AND INFLUENCE( WEICK AND SUTCLIFFE 2005) 8 Model—individual factors 9 Model –individual capabilities 10 Model –organisation factors 11 Model –organisation capabilities 12 Model 13 Research setting • • • • Health a pillar of social policy Health status of population impacts economic growth Health care services – credence good For effective health services crucial is the trust between service provider and consumer • Thus is a setting where influence determines service delivery. • India- health services are in public domain 14 Research context • Chiranjeevi scheme in Gujarat • Aim to facilitate reduction of MMR/IMR • Main cause of MMR– lack of access to institutional delivery mechanisms for pregnant women– high incidence of morbidity of both women and new borns • Government scheme facilitating payment through vouchers to increase institutional deliveries using private facilities 15 Research context • • • • • • Role of doctor in charge– PHC Identification of target families Awareness generation Identification of certified facilities Contract management Motivation of people to use institutional facilities 16 Proposed methodology • • • • Interviews with Doctor in charge of identified PHC Interviews with paramedical staff of that PHC Secondary data collection– increase in number of institutional deliveries • Problems noticed in implementation • Role of doctor in problem solving 17 Any questions? 18