Team Based Learning in Animal Physiology
advertisement

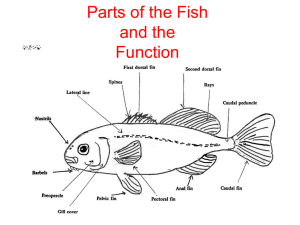
Team Based Learning in Animal Physiology Mary Kate Worden, PhD Dept of Neuroscience, UVA SOM BIOL 3230 Fall 2010 87 students in 13 teams, including Megan Barron and Jake McLean http://teambasedlearning.org The Team Based Learning Collaborative Team Based Learning™ Team-Based Learning (TBL) is an increasingly-popular form of small group learning. The four components of TBL are permanent teams, readiness assurance, application activities, and peer evaluation. TBL is possible even in large theater-style classrooms with fixed seats. TBL teachers report high levels of student attendance, preparation, participation and critical thinking. TBL students report being more motivated and enjoying class more, even when the subject is not in their major. Forming the teams • Students complete a survey on the first day of class • Teams (5-7 members) are balanced with novice learners (0-1 previous course in biology) and expert learners (4-5 previous courses, Bio majors). • Teams are permanent and sit together in class. TBL Course Design A. independent learning prior to class B. in-class “readiness assurance testing” of individuals (iRAT) and teams (group RAT) C. in-class “application activities” problem solving of real world problems D. Online peer evaluations hold students accountable for preparation and class participation in the team Animal Physiology (BIOL 3230) Examples of Learning Objectives for pre-class reading Define the following terms: natural selection, adaptation, adaptive significance, homeostasis, acclimation, acclimatization List the two central questions of physiology. Explain why knowledge of one does not imply knowledge of the other. Distinguish between those animals that exhibit conformity to external conditions and those that exhibit regulation to external conditions. Explain how a salmon shows conformity with respect to one parameter and regulation with respect to another. List five different time frames over which physiology changes and distinguish between them. TBL Course Design A. independent learning prior to class B. in-class “readiness assurance testing” of individuals (iRAT) and teams (group RAT) C. in-class “application activities” problem solving of real world problems D. Online peer evaluations hold students accountable for preparation and class participation in the team Individual RAT (10 questions) Q2. You buy a new fish for your aquarium and bring it home sealed in a bag of water. The seller advises you to float the sealed closed bag in your home aquarium for half an hour before you release the fish in order to help it adjust to the temperature of the aquarium. The physiological process the fish undergoes A. is adaptation B. is homeostasis C. has adaptive significance D. is acclimation E. is acclimatization Individual RAT (10 questions) Q2. You buy a new fish for your aquarium and bring it home sealed in a bag of water. The seller advises you to float the sealed closed bag in your home aquarium for half an hour before you release the fish in order to help it adjust to the temperature of the aquarium. The physiological process the fish undergoes A. is adaptation B. is homeostasis C. has adaptive significance D. is acclimation E. is acclimatization Exam is on hardcopy Collect responses using iClicker. Group RAT (same 10 questions) Q2. You buy a new fish for your aquarium and bring it home sealed in a bag of water. The seller advises you to float the sealed closed bag in your home aquarium for half an hour before you release the fish in order to help it adjust to the temperature of the aquarium. The physiological process the fish undergoes A. is adaptation B. is homeostasis C. has adaptive significance D. is acclimation E. is acclimatization Group RAT (same 10 questions) Q2. You buy a new fish for your aquarium and bring it home sealed in a bag of water. The seller advises you to float the sealed closed bag in your home aquarium for half an hour before you release the fish in order to help it adjust to the temperature of the aquarium. The physiological process the fish undergoes A. is adaptation B. is homeostasis C. has adaptive significance D. is acclimation E. is acclimatization Using same exam on hardcopy Collect responses using scratch cards Immediate feedback on assessment using scratch cards Students get immediate feedback on • which is the correct answer • how well they grasp the learning objectives • whether the team discussion was on track • which team members had a good grasp on the learning objectives and who made the key arguments. Immediate feedback on assessment using scratch cards Peer to peer learning occurs in discussion. Teams are invested in doing well as a group. (Group scores were worth 65% of the quiz grade, iRAT scores worth 35%) Energy levels and in-class engagement are high. “Social loafing” is minimized by the fact that peer evaluations will factor into grades. Follow-up to IRAT/GRAT quiz • Written appeals on quiz questions before deadline poorly worded question multiple answers/no answers are correct Q or A does not match the LOs or text High level of passion in the appeals process! TBL Course Design A. independent learning prior to class B. in-class “readiness assurance testing” of individuals (iRAT) and teams (group RAT) C. in-class “application activities” problem solving of real world problems D. Online peer evaluations hold students accountable for preparation and class participation in the team Reading and discussing the primary scientific literature in class • Abridged versions of articles from Journal of Experimental Biology (intro, methods, results including key figures) ~ 1.5 pages single spaced • Set of 3- 5 MCQs about the data and its interpretation, all related to the LOs • Students debate in teams and arrive at group answers (small group discussion) This is similar to reviewing a scientific paper, only in a more structured format and in a group setting. Voting on the “right answers” in class • All teams vote simultaneously by holding up a flag (color coded for A,B,C,D,E) • Instructor asks teams to justify their votes, encouraging debates between teams (large group discussion) • Instructor explains her choice for best answer, and reveals the authors’ answers. Advantages of TBL format • Students very willing to speak up because they have “previewed” their arguments in the group • High energy in class, teams are invested in drawing the correct conclusions based on their foundational knowledge • Instructor illustrates that the primary literature is not always perfect, authors can be wrong or illogical, reviewers can be faulty. Science is messy and advances through debate. • Class attendance was very high, even without grading. TBL Course Design A. independent learning prior to class B. in-class “readiness assurance testing” of individuals (iRAT) and teams (group RAT) C. in-class “application activities” problem solving of real world problems D. Online peer evaluations hold students accountable for preparation and class participation in the team15% of grade Course evaluations for BIOL 3230 Would you have preferred Animal Physiology to be taught in lecture based format, rather than TBL? 5.8% lecture based 83.5% TBL 10.6% no preference If this were a two semester course, how likely would you be to enroll? 73% very likely 16.5% somewhat likely 5.8% not sure at this time 4.7% unlikely Course evaluations for BIOL 3230 Animal Physiology Other biology courses Fall 2010 (Agree or Strongly agree) (Agree or Strongly agree) This course developed your ability to apply the basic concepts presented in new or different contexts: 98% 84% 94% 45% This course developed your ability to propose new research questions, models, and experiments: 94% 63% I learned a great deal in this course. 96% 84% This course developed your ability to interpret graphs, data sets or experimental results: TBL enables large enrollment courses to have the interactive class discussions characteristic of small seminars. 14 N= 560 Cell Biology and genetics 12 10 Number of Biology Dept courses offered in Fall 2010 N= 372 Genetics and Mol. Biol 8 6 N=216 Cell Biology 4 2 0 0-35 36-100 100-200 Class size (# students) >200 TBL enables large enrollment courses to have the interactive class discussions characteristic of small seminars. As of 3/30/2011: 614 Biology majors (Graduating 280 majors this year) Faculty size constant for 40 years. On course evaluation: True or false I have experienced difficulty in enrolling in Biology Department courses I want to take because classes fill to capacity before I sign up. 85% True 15% false My estimate: TBL would be workable with 25 teams of 7 students = 175 students