Technical Writing vs. Academic Writing
advertisement
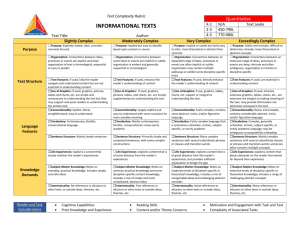
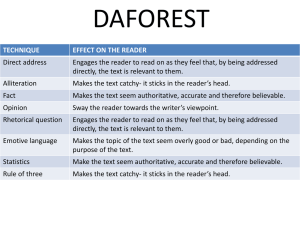
1 TECHNICAL WRITING vs. ACADEMIC WRITING TYPES of WRITING 1. PERSONAL 2. ACADEMIC 3. PROFESSIONAL 3 PERSONAL WRITING o Purpose/Objective: to entertain to inform o Evaluation: desired emotional response informed 4 PERSONAL WRITING o Graphics: emoticons text-messaging lingo o Formats: e-mail letters journals text messages 5 PERSONAL WRITING o Audience: equal knowledge friends colleagues o Informality 6 TECHNICAL WRITING vs. ACADEMIC WRITING *AUDIENCES* o o o o o o o Specific Audiences boss supervisor team committee politicians bank officers general public TC General Audience o generic reader o teacher o perhaps fellow students AW *AUDIENCES* 1 Document = Many Readers: (Many Readers = Many Needs) o o o o o o o o “food chain” boss, supervisor team engineers workers politicians bank officers general public TC 1 Document = 1 Reader: (1 Reader = 1 Need) o teacher AW PURPOSES o o o o Purpose = Writing Situation Objective Why was the document written? PURPOSES o o o o o Situation-Oriented see a need — address a need internal motivation professional motivation outcome-oriented: to get something accomplished Assignment-Oriented o passive (vs. active) o given a topic, test o given an assignment o external motivation o scholastic motivation o grade-oriented grade, g.p.a., degree TC AW EVALUATION CRITERIA o o o o Success satisfaction of the needs of all readers something was done informed persuaded TC o o o o o Success correct answer right information unity, coherence support, detail grammar AW APPLICATIONS Real-World Applications o case studies o illustrative scenarios o operations management o for a job o for a raise or promotion o for a bid practical TC o o o o o o o College Application “academic” writing essays essay exams for academics for grade for degree “show what you know” demonstrative AW DISCIPLINES o o o o Across Disciplines “interdisciplinary” computer sciences psychology mixture of: history math science technology Single Discipline o “discipline-specific” literary data for an English paper historical information on a history paper psychological ideas on a psychology test o rarely a mixture TC AW *PAGE DESIGN* o Paragraphs o o o o o o o o o o White Space Columns Headings Lists Graphics Varying Fonts Use of Color Relative Spacing Relative Margins Relative Justification 6-10 lines vary lengths for visual o Paragraphs o NO o o o TC Minimum of 3-5 sentences No maximum length White Space Columns Headings Lists Graphics Varying Fonts Use of Color Double Spacing Equal Margins Left Justification AW COMPONENTS Oral, Visual, Written o produce documents o present documents o write to be read o write to be seen o write to be heard Written o infrequent oral and visual components o predominant written component o write to be read by teacher o write to be graded o not to be seen or heard TC AW GRAPHICS o o o o o o o tables charts graphs diagrams photographs maps blue prints o uncommon o photographs TC AW FORMATS o o o o o o o o o o o essay questions o essays based on the rhetorical strategies memos e-mails letters cover letters resumes proposals manuals portfolio abstracts reports formal informal TC Description Narration Illustration Process-Analysis Division-Classification Comparison-Contrast Definition Cause-Effect Pro-Con Argument AW GRAMMAR o o o o o o o o Grammar-less visual-oriented grammar = less important fragments = permissible active voice descriptive writing concise sentences spelling! proofread! TC o o o o o o o o Grammar-full written-oriented grammar = key sentence errors = avoided active voice descriptive writing concise sentences spelling! proofread! AW 19 CONCLUSIONS o Technical Communication: Practicality in the employment world Real-World application o Academic Writing: Demonstration of knowledge Limited to academia 20 CONCLUSIONS o Technical Communication: By an informed writer Conveying necessary information Both visually & verbally To a lesser-informed reader (writer = teacher) o Academic Writing: By a student-learner for an expert reader 21 CONCLUSIONS o Technical Communication: Read by many, To satisfy the needs of many o Academic Writing: Read by one, To appease the criteria of one 22 CONCLUSIONS o Technical Communication: “Information Retrieval” organization & format = designed to help readers quickly & easily locate information o Academic Writing: “Information Retrieval” little concern beyond a logical organization 23 CONCLUSIONS o Technical Communication: Public Speaking component — formal conference speeches informal meeting speeches o Academic Writing: Limited Public Speaking opportunities conferences or rare class projects Public Speaking courses 24 DEFINITION Technical Communication: o o o o Encompasses a wide range of writing and speaking responsibilities required to communicate your ideas on the job. 25 26 SIMILARITIES o Grammar: active voice descriptive writing concise sentences spelling! proofread! 27 SIMILARITIES o Writing as a Process: Planning Drafting Revising EDUCATIONAL PHILOSOPHIES writing: process & product o HEURISTIC: process reader-focused how-to analyze-andcompose process o o o o writing: product prescriptive teach from models rhetorical strategies writer-focused o PRESCRIPTIVE: product writer-focused models/forms of TC writing AW 29 ACADEMIC WRITING o Purpose/Objective: to demonstrate knowledge to “show what you know” o Audience: superior knowledge teachers, perhaps peer editors o Evaluation: correct information unity, coherence, depth, clarity, grammar o Graphics: limited to explain or persuade 30 ACADEMIC WRITING o Formats: Description Narration Illustration Process-Analysis DivisionClassification (Rhetorical Strategies or Writing Models) Comparison-Contrast Definition Cause-Effect Pro-Con ArgumentPersuasion 31 TECHNICAL WRITING o Purpose/Objective: to entertain to inform o Audience: equal knowledge friends, colleagues o Evaluation: desired emotional response informed o Graphics: emoticons text-messaging lingo o Formats: e-mail letters journals text messages