EER - Hiram College
advertisement
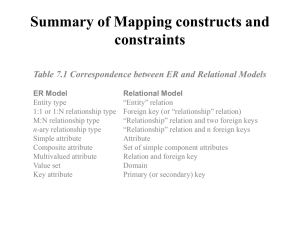
Extending ER Diagrams (13)
CPSC 356 Database
Ellen Walker
Hiram College
(Includes figures from Database Systems: A Practical Approach to Design, Information
and Management, by Connolly and Begg, © Addison Wesley 2010)
Basic ER Diagram Cannot Capture
Specialization/ Generalization
• Examples
– Doctors and Nurses are Medical Staff
– Staff includes Medical staff, Secretarial staff,
Housekeeping staff, etc.
• Relationships might include Doctors, Medical
Staff, and/or Staff
• ER diagram cannot represent the fact that
Staff > Medical staff > doctors
• EER diagram can!
Entity Type Hierarchies
• An entity type E1 is a subclass of the entity
type E2 when
– Every entity instance of E1 is also an instance of
E2
– Every attribute in E2 is also in E1
• The opposite of a subclass is a superclass
• Subclasses are related to superclasses
through the IS-A relationship
When to Use?
• When you have an entity that needs to have
extra / different attributes “sometimes”
• When you have two entities that overlap on
many or most of their attributes
Subclass / Superclass Example
• Doctor is a subclass of medical-staff
• Staff is a superclass of medical-staff
Staff
• Attributes
– Staff - name, addr, salary
– Med-staff - pager #
– Doctor - license #
Medical-Staff
Doctor
Admin-Staff
Nurse
Attribute Inheritance
• Each entity type inherits all attributes of its
superclass(es)
– Staff has name, address, salary
– Medical staff has {n,a,s} + beeper-number
– Doctor has {n, a, s, b#} + license #
• In EER diagram, inherited attributes only
appear once (in the highest superclass)
Generalizing Type Hierarchies
• Multiple superclasses for the same subclass
– A student-employee is both a student and an
employee
• Overlapping subclasses
– Subclasses of person are student and employee
– There is at least one individual who is both a
student and an employee
• Non-overlapping subclasses are called
“disjoint”
Specialization of Staff (13.2)
Extended ER (EER) Diagram
• IS-A relationships
• Notation for disjoint (vs. overlapping)
subclasses
– Disjoint = “or”, overlapping = “and”
• Notation for “covering”
– Can someone be staff without being Medical or
administrative?
– If so, “optional”; if not “mandatory”
More Staff Types (13.3)
Additional Semantic Relationships
• Aggregation and Composition
– Collecting together related entities that represent ‘parts’ of a
‘whole’
– Aggregation (non-exclusive subpart): parts can change
parents
– Composition (exclusive subpart): single parent, very strong
association - parts make no sense without parent
– Examples:
• Branch (whole) has Staff (part)
• Newspaper (whole) contains Story (part)
Aggregation
Composition
• EER representation is diamond with arrow from “part”
– Open for aggregation, closed for composition
– (see 13.9, 13.10)