Stimulus and Response - aiss-science-9
advertisement
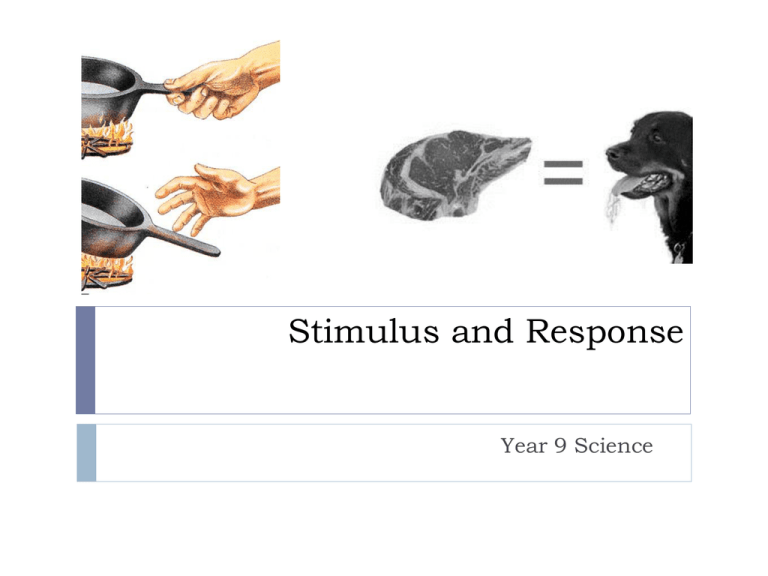
Stimulus and Response Year 9 Science Stimulus Any change in an organism’s environment that causes the organism to react. (“cause”) Stimuli (singular) can be: •External •Internal Response How an organism reacts to a stimulus (“effect”) Responses can be: •Voluntary •Involuntary Response Stimulus Touch a hot surface... ...pull back your hand Hear a loud bang... ...flinch/yell out Raise your body temp... ...start to sweat Feel cold... ...put on something warm Stimulus-Response Model Stimulus Receptor (senses the stimulus) Messenger (nerve cells carry a signal to give a response) Effector (causes a response) Response Stimulus-Response Example Stimulus (bright light) Receptor (light sensitive cells in eye) Messenger (nerve cells carry the signal to the eye) Effector (ciliary muscles) Response (pupil contracts) Learned Responses Some responses are instinctual (we are born with them) Other responses can be learned. A famous demonstration of learned response is known as “Pavlov’s Dog” •A dog is given an external stimulus (the bell) during meals •The dog learns to associate the bell with food and gives the same response Involuntary responses Some responses happen without any thought whatsoever. These are known as involuntary responses. Can you think of others? Reflex arc – fast! A reflex arc is a fast response that occurs automatically, without any thought. These are the fastest responses in your body For example, when you touch something hot, you pull your hand away before you “think” about it being hot. The stimulus (heat) is relayed along the sensory neuron through the spinal cord to the effector which makes you move your hand. Homeostasis Homeostasis: the maintenance of a stable internal environment in spite of external or internal environmental changes. The body is constantly working to maintain homeostasis inside us by coordination of our body systems. Blood Glucose Maintenance Feedback loops The body maintains homeostasis by responding in one of two ways: •Positive feedback – a response that enhances the effect of a stimulus (rare – production of oxytocin during labour to increase contractions) •Negative feedback – a response that counteracts the effect of a stimulus (these are the most common in the body)