File - Ms. Myer`s AP World History
advertisement

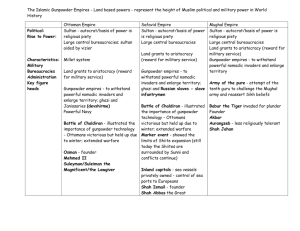
The Islamic Empires Chapter 27 Intro: Formation of the Islamic Empires • 3 empires divided up Dar al-Islam • All began as warrior principalities in frontier areas, expanded, developed administrative and military techniques The Ottoman Empire • Founded by Osman Bey in 1289 (dynasty lasted until 1923) on Byzantine borders • 1300s: expanded, with capital at Bursa • Military organization: light cavalry and volunteer infantry (and later, heavy cavalry) – Janissaries (Christian boys from conquered Balkans) – specially trained, known as excellent warriors – Effective use of gunpowder weapons The Ottoman Empire (cont.) • 1453: Mehmed the Conqueror (r. 1451-1481) conquered Constantinople (became capital, Istanbul) – Laid foundations for highly centralized absolute monarchy – Expansion: Serbia, S. Greece, Albania, (later into Syria and Egypt) The Ottoman Empire (cont.) • Suleyman the Magnificent (r. 1520-1566): height of Ottoman imperialism – Kanun (laws): “the lawgiver” – Lots of expansion efforts: Baghdad, Siege of Vienna, Yemen, Rhodes, etc. – Became naval power -> could challenge Christian vessels The Safavid Empire • Founded by Shah Ismail (r. 1501-1524) in Persian heartland • Used propaganda: Sufi ancestry, changed religion – Twelver Shiism: 12 infallible imams, red hats (= red heads), Ismail as 12th imam • Mandated conversion to Shiism -> enemies, esp. Ottomans (feared spread of propaganda) The Safavid Empire (cont.) • 1514: Battle of Chaldiran – Ottomans vs. Safavids – Ottomans used gunpowder weapons, Safavids didn’t (believed in protection of the Shah) – Ottomans won, but didn’t occupy -> constant conflict for next 200 years • Safavids recovered: Persian bureaucracy and admin. Techniques, abandoned extreme ideology (maintained twelver shiism), land grants to red heads = support The Safavid Empire (cont.) • Shah Abbas the Great (r. 1588-1629): revitalized empire – Moved capital to Isfahan (more central), encouraged trade, reformed admin and mil institutions (slaves in army, gunpowder weapons, alliances with Europeans) – Military victories: Uzbeks, Hormuz The Mughal Empire • 1523, founded by Babur in Northern India using gunpowder weapons to invade – Goal was to use Indian wealth to expand into central Asia (never happened) • Grandson, Akbar (r. 1556-1605): brilliant, charismatic – Centralized admin with bureaucracy to govern provinces – Military campaigns to consolidate power in north and expand in south – Interest in religions and philosophy: religious tolerance, syncretic religion (divine faith) The Mughal Empire (cont.) • Aurangzeb (r. 1659-1707): ruled when empires was at greatest extent – Expansion efforts in south – Problem: rebellions due to religious tension (religious intolerance, destroyed Hindu temples, jizya tax) Intro: Imperial Islamic Society • Lots of similarities between the three empires: – Turk/Mongol/Islamic steppe-based bureaucracy, – economic policies, – policies for dealing with multi-ethnic/religious populations, – legitimacy through providing welfare, – association with literacy and the arts The Dynastic State • Absolute power over government and military, plus ownership of all land • Importance of religious piety (Sufi association, devotion to Islam) and military prowess as source of power and prestige • Steppe tradition of relatives managing parts of empire -> problems with succession – Solution: locked sons away (S), killed brothers or confined to palace (O) The Dynastic State (cont.) • Women in Politics: not supposed to have any, but there were many exceptions, especially for ruler’s mother and favorite/chief wife Agriculture and Trade • Agriculture (wheat and rice) = foundation of empires – Surplus supported bureaucracy and army • American food crops were introduced, but didn’t have huge impact on population • Tobacco: spread quickly, along with coffee -> coffeehouses (became important social institutions in O. empire) Agriculture and Trade (cont.) • Population growth: M – due to intensive agri. Techniques, S – less rapid, O – changed with empire’s boundaries • Trade: all were part of global trade network – O: British and French merchants, important in spice and silk trade – S: Isfahan as commercial center, foreign merchants, provided silk, carpets, ceramics, traded with English/French/Dutch East India Companies, developed good rel. with English – M: regional trade more important, allowed European trading posts, some Indians formed their own companies Religious Affairs in the Islamic Empires • • • • All 3 had diverse populations O: Christians, Jews S: Zoroastrians, Jews, Christians M: Hindus, Jains, Zoroastrians, Christians, Sikhs – Portuguese Jesuit mission at Goa: Jesuits tried to convert Akbar (just wanted to talk) – Akbar wanted religious synthesis to unify empire – -> divine faith: heavily based on Islam (monotheistic, Shiite and Sufi influence), loyalty to empire, elements from Zoroastrianism Religious Affairs (cont.) • Religious minorities: • Jizya and loyalty -> personal freedom, property, religion, legal affairs • Difficulty in Mughal Empire: Muslims were rulers (with a few Hindu bureaucrats), population was Hindu – Akbar: abolished jizya, religious tolerance, discussions among leaders of different religions – Many Muslims feared this -> Aurangzeb reinstated jizya, religious intolerance, promoted Islam -> Hindu bitterness and tension Cultural Patronage of the Islamic Emperors • Emperors tried to enhance prestige and power through public works projects and patronage of scholars – Tried to attract religious scholars, poets, artists, architects – Spent a lot on mosques, palaces, gov’t buildings, bridges, fountains, schools, hospitals, soup kitchens Cultural Patronage of the Islamic Empires (cont.) • Istanbul: revived and prospered after conquest – Topkapi palace, Suleymaniye Mosque (by Sinan Pasha) – combines Islamic (minarets) and Byzantine (dome) elements, Hagia Sofia mosque Cultural Patronage of the Islamic Empires (cont.) • Isfahan: Shah Abbas focused on building up the capital – Markets, palace, mosques, polo field, shaded avenues, bridges, courtyards, palace with balconies and verandas (visibility of king) Cultural Patronage of the Islamic Empires (cont.) • Fatehpur Sikri: Akbar’s capital (1569-1585) – Mint, treasury, royal residence, mosque and mausoleum for Sufi guru – Combined C. Asian traditions with Hindu architectural elements (verandas, stone elephants) Cultural Patronage of the Islamic Empires (cont.) • The Taj Mahal: built by Shah Jahan as mosque and mausoleum for his wife Intro: The Empires in Transition • Big changes in all 3 between 1500-1700 – 1722: Safavid collapse with invasion of Afghans – 1707: Mughal weakening – rebellions, foreign invasion, British rule (1750s) – 1700s-1800s: Ottomans lost land, plus pol, econ, and mil pressure from Europe and Russia Deterioration of Imperial Leadership • All 3 had strong rulers initially; but, eventually, incompetent rulers who spent too much on themselves and ignored the state • Plus, factions formed in courts of all 3 – O: by locking away princes, they didn’t learn how to rule -> increasingly weak rule -> army mutinies, revolts, corruption, economic oppression, insecurity Religious Tensions • Also led to problems for rulers with conservative Muslim clerics (strong influence due to education, legal affairs) – Disapproved of Sufism, women and non-Muslims in gov’t roles, contradictions to sharia law Economic and Military Decline • increasing dependence on foreign items and control by Europeans due to cost of mil and admin • Expansion brings $ in, once it stops, resources become limited – Ottomans: empty treasury -> debased money -> revolts -> raised taxes, sold public offices, etc. • Also, relied on foreign trade for income, but didn’t go abroad – O: privileges to foreign merchants – M: encouraged Dutch and English trading posts Military Decline and Cultural Conservatism • Did not try to improve technology, instead, relied on out of date European weapons – By late 1700s, Ottoman navy stopped building it’s own ships • Also, made little effort to learn about the outside world – When they tried to introduce new elements, conservative Muslims shut it down (e.g., telescope, printing press) -> fear of change