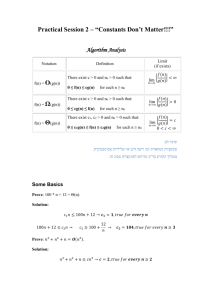
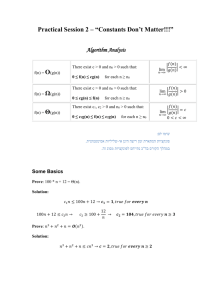
problem_solving_-_final
advertisement

סדנה מתקדמת בהוראת המתמטיקה מרצה :דר' בוריס קויצ'ו מתרגל :מר איגור קונטורוביץ' חברי הקבוצה: יוליה אלקין עביר סלאמה אמאני חיר רועי לחמי פיתרון בעיות -הקדמה • • • • פיתרון בעיות מפוליה עד היום – ענף גדול במחקר חינוך מתמטי פתרון בעיות וחיבור בעיות למידה מתרחשת דרך פתרון בעיות ולכן בעיות טובות עשויות לשפר תהליך מורה – דמות שעשויה לחנך את התלמידים לפתור בעיות פיתרון בעיות -היסטוריה • התפתחות התחום: – היוריסטיקות ואסטרטגיות – מאפיינים של פותר בעיות מוצלח מול גורמים אשר מביאים להצלחה בפיתרון בעיות (רגשות ,אמונות וכו') השוואה בין המומחה לבין הטירון – מודלים המסבירים תהליך פיתרון בעיות – עקרונות פדגוגיים ועקרונות הקשורים לתלמידים (כמו עיקרון חסכנות) English, L. & Sriraman, B. (2010). Problem solving for the 21th century. In B. Sriraman & L. English (Eds.), Theories of Mathematics Education: Seeking new frontier. Berlin: Springer, 263-290. Mousoulides, M. Sriraman, B., Pittalis, M., & Christou, C. (2007). Tracing students' modeling processes in elementary and secondary school. Paper presented at 5th Congress of the European Society for Research in Mathematics Education (CERME – 5), Cyprus. מתמטיקה בעייה The best way to teach mathematical ideas is to start with interesting problems whose solution requires the use of ideas. Use problem solving as a powerful means to develop substantive mathematical concept. בעייה Real word problem מתמטיקה Integration within all topic areas Outside the class a. complex systems. b. plan, monitor and assess progress c. adapt quickly to technologies. מתמטיקה * גורן ,ב .אלגברה חלק ב' ,הוצאת עצמית ,עמ' 155 בעייה Mathematical models = "systems of elements, operations, relationships and rules that can be used to describe, explain, or predict the behavior of some other familiar system” Modeling problems are realistically complex situations where the problem solver engages in mathematical thinking beyond the usual school experience and where the products to be generated often include complex artefacts or conceptual tools that are needed for some purpose, or to accomplish some goal. Modeling Mathematical models = "systems of elements, operations, relationships and rules that can be used to describe, explain, or predict the behavior of some other familiar system” Elicit my own Make sense meaningful mathematics sorting organizing selecting Modeling quantifying Transforming large data making representation Interpreting Cyclic process selecting identifying University’s Cafeteria Construct models for selecting the best among a number of employees Not just one right answer Reformulating the problem Elicit my own mathematics בעייה מתמטיקה סטטיסטיקה Complex system Hours, money, seasons sorting Real world organizing selecting Outside the class quantifying Transforming large data making representation Interpreting Cyclic process selecting identifying 1. What aspects of the targeted mathematical theory can students come to appreciate through their individual or collective problem solving processes? 2. What aspects of the theory are difficult to be noticed by students only through their natural problem solving processes? Nunokawa, K. (2005). Mathematical problem solving and learning mathematics: what we expect students to obtain. The Journal of Mathematical Behavior, 24 (34), 325-340. Leikin, R. (2004). Towards high quality geometrical tasks: reformulation of a proof problem. In M. J. Hoines & A. B. Fuglestad (Eds.) Proceedings of the 28th International Conference for the Psychology of Mathematics Education, Vol. 3, 209-216. : קריטריונים לקביעת איכות הבעייה4 The person has to be motivated to find a solution No readily available procedures The person has to make an attempt and persists to reach a solution Several solving approaches בעייה : קריטריונים לקביעת איכות הבעייה4 The person has to be motivated to find a solution No readily available procedures The person has to make an attempt and persists to reach a solution Several solving approaches בעיית חקר challenging Cognitively demanding High motivated עד כמה לפתוח את הבעייה? .1הוכח שגובה הטרפז שווה לקטע האמצעים .2השווה בין הגובה לקטע האמצעים. .3מצא יחסים אפשריים בין הקטעים היוצאים מאמצעי הצלעות הנגדיות. .4אותה שאלה ללא הנחייה לבניית עזר( .לא רבלנטי לבעייה לעיל). .5מצא גדלים שווים בטרפז זה. .6מה תוכל לומר על טרפז זה? מסעיף 2שימוש בתוכנת גיאומטריה דינמית. מה ההבדל? דוגמאות לבעיות מתמטיות "טובות" הקריטריונים של "לייקן" לבעיות מתמטיות טובות: א -לפותר הניגש לבעיה ,צריכה להיות מוטיבציה כדי למצוא את הפתרון. ב -לפותר אין פתרונות זמינים. ג -הפותר צריך לנסות ולהתעקש כדי להגיע לפתרון. ד -לבעיה יש גישות שונות לפתרון. דוגמה ראשונה: לחבר בעיות מילוליות שלפתרונן דרוש לחבר ולפתור את המשוואה הבאה: 1 1 x 1 x2 בטכניון קיימות שתי בריכות בעלות צורה מלבנית בשטח 1ק"מ בריבוע. מידות הבריכה הראשונה הן xy ומידות השנייה הן . ( x 2) z המורה לספורט רצה לאתגר את הסטודנטים וביקש שיחשבו את ידוע ש- z y 1 x אם . במרוץ החייזרים של שנת 2800השתתפו 100חייזרים מגלקסיה במרוץ בין הכוכבים. החייזר הגיע לקו הסיום לפני החייזר בשתי שניות. כמה זמן לקח לחייזר כדי להגיע לנקודת הסיום אם ידוע לך שהמהירות של החייזר יותר גדולה מהמהירות שלו ב sec ? 1 km דוגמה שנייה: הוכח את המשפט: "במשולש שווה צלעות ,סכום המרחקים של כל נקודה שאינה חיצונית למשולש ,מצלעות המשולש ,שווה לאורך הגובה של המשולש". B . C A A+B+C=H אפשר להמיר את הבעיה ולפתחה לבעיות שונות באמצעות השיטה "מה אם לא?" ,וזה עבור סוגי משולשים אחרים ,או למשל עבור מרובעים ,כמו בטבלה הבאה: מרובע האם קיימת תכונה מיוחדת עבור סכום המרחקים של נקודה פנימית מצלעות המרובע? מהי? מקבילית מלבן מרובע מעוין קמור מרובע כלשהו אפשר לשאול את השאלה "מה אם לא?" במישור אלא במרחב. למשל רואים שמתקיימת אותה התכונה עבור טטראדר משוכלל מארבע הדפנות שלו ורואים שמתקבלת תכונה מעניינת שהיא: "סכום המרחקים של נקודה פנימית בטטראדר מארבע הדפנות שלו שווה לגובה הטטראדר" קשיים אפשריים: קשיים בפתרון הבעיה המקורית בקרב התלמידים. -קשיים במציאת בעיות נוספות לפי השיטה של "מה אם לא?".