Olmecs, Mayas, Aztecs, Incas
advertisement

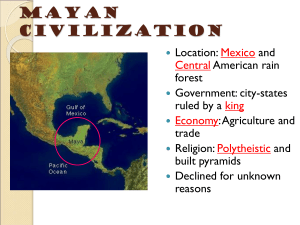
Development of South and Central America Societies Engineering an Empire: Aztec 1 SSWH8 Standard • SSWH8 The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America. • a. Explain the rise and fall of the Olmec, Mayan, Aztec, and Inca empires. • b. Compare the culture of the Americas; include government, economy, religion, and the arts of the Mayans, Aztecs, and Incas. Intro • Early Inhabitants – Migrated from Asia during the last Ice Age, crossing the Bering Strait by foot • Hunter-gatherers: – During global warming, they migrated east and south to follow the herds. – Different cultures formed as they spread out. – Cut off from Asia as Ice Age ended, they developed independently from cultures in the Eastern Hemisphere. Intro Intro • Technology: – Metal was rarely used – many cultures were still in the Stone Age. – Wheel was used, but not for transportation. Pyramids • Despite the towering reputation of Egypt's Great Pyramids at Giza, the Americas actually contain more pyramid structures than the rest of the planet combined. Civilizations like the Olmec, Maya, Aztec and Inca all built pyramids to house their deities, as well as to bury their kings. • In many of their great city-states, temple-pyramids formed the center of public life and were the site of much holy ritual, including human sacrifice. Ancient City of Teotihuacan Engineering an Empire: Aztec 2 OLMEC • 1200 -400 BC • Called “Rubber People” • Carved enormous stone heads of volcanic rock • Division of labor • Hieroglyphics • farm techniques - slash and burn The Olmecs The Olmec • • • • • • Meso-America 1st civilization 1200-400 BC They made Pyramids, mounds, monuments Sculptured heads - 44 tons Religion: polytheistic – many nature gods: Chief god was the jaguar god – Influenced - design, ceremonial centers, ball games, elite ruling class – Performed ritual sacrifices – Played pok-a-tok game – Went on pilgrimages • Government - ruler - god like Olmec • Influenced area through trade; evidence of trade confirmed by Olmec jade carvings found throughout Central America • Achievements: – Long Count Calendar • No idea what caused their decline Engineering an Empire: Aztec 3 Maya El Castillo, Chichen Itza: El Castillo "The Castle" It rises 79 feet above the Main Plaza of the ancient Maya city of Chichen Itza in Mexico (founded c. AD 600 ). Chichén Itzá • Yucatan Peninsula • Government: – City States • Religion: – Complex – two layers (now and otherworld) – polytheistic – Major role in society and rule – Human sacrifice • Economy: – Trade with other citystates MAYANS • Culture: Mayan • 2000 BC -900 Ad • 250- 900 million population • Cities - Tikal, Copan: Palaces, temples, pyramids • Social classes - warriors, priests, merchants, craft workers, peasants • Astronomy, math, 2 calendars - 1 for sun, 1 for religion • Math and astronomy to support religious beliefs • Pyramids • Glyphic writing system • No explanation for their decline – Possibly: war, drought, infighting The Mayans Palenque Engineering an Empire: Aztec 4 Aztec Aztec • Most powerful civilization in central and southern Mexico. • The capital city was Tenochtitlan. • Located on islands in Lake Texcoco – 1200. Tenochtitlan The Aztecs Aztec • 1100-1522 AD • Government – Warriors • Military strength – Social structure • • • • Emperor Nobles Commoners Enslaved persons • Religion – Polytheistic – Their main god was the “sun god” – “fed” the god with human sacrifice • Quetzacoatl feathered serpent god – Legend -- left city and will return one day Aztec • Economy – Trade – obsidian – Tribute states – Pyramids, temples Aztec Civilization • Culture – A complex and rich society – A trade network – A mathematical system to keep up with the empire – Two different calendar systems – A Farming system – Used irrigation to keep their crops growing even during dry periods Chinampas floating gardens Aztec Civilization • They were known for their artwork … Aztec Civilization • and their architecture. • The pyramid temple was the center of this great city Aztec Civilization • Today, some of the art and buildings have been re-discovered. • A modern version of the Aztec language, Nahuatl, is still spoken by thousands of people in Mexico. Aztec Civilization • An important part of their culture was the sacrifice of animals and humans. • People who were conquered were required to pay large taxes. • They also had to provide people to offer as sacrifices to the Aztec gods. Aztec Sacrifice Montezuma Cortes Aztec Civilization • Arrival of Spanish led to the fall of the Aztec. • It ended in 1541 when conquered by the Spanish. • The Spanish destroyed much of the Aztec building and artwork. • They destroyed the city of Tenochtitlan and built Mexico City in its place. Aztecs Engineering an Empire: Aztec 5 The Inca Inca • Located in South America – 1400-1534 – Andes Mountains – Cuzco - capital – Peru Lost Cities of the Inca Inca • Government: – Theocracy – Strong central government – huge empire extending length of South America – Leader - descendent of sun god – Expanded empire – Powerful military – Bureaucracy Inca • Religion: – Religion ruled state – theocracy – Mummies – Animal sacrifice • Economy: – economic system – roads, – All roads lead to Cuzco Inca • Culture: – Ayulla - extended family - to do large tasks – Mita - required service to state Machu Picchu INCAS Machu Picchu • Built paved roads & suspension bridges used running messengers • Instead of writing system used knotted string to communicate messages & keep records - quipu Inca terraces Suspension bridge Quipu The Inca were conquered by the Spanish conquistador Pizarro. Atahualpa Pizarro Destruction of Culture • The Meso-American kingdoms were as advanced and sophisticated as the ancient Greeks and Romans • The European conquerors tried to destroy the evidence of this sophisticated culture