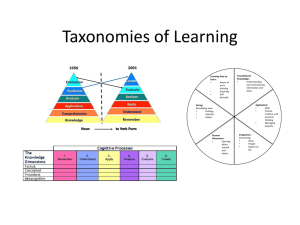
slides - DBWeb
advertisement
The Palm-tree Index Indexing with the crowd Ahmed R Mahmood* Eduard Dragut* Walid G. Aref* Saleh Basalamah** *Purdue University **Umm AlQura University Outline • • • • • • • Motivation Taxonomy for Crowd-based Indexing Problem Definition The Palm-tree Index Structure Traversal Algorithms Preliminary Experimental Results Conclusions and Future Work Motivation 500 1000 200 100 100 200 500 1000 Outline • • • • • • • Motivation Taxonomy for Crowd-based Indexing Problem Definition The Palm-tree Index Structure Traversal Algorithms Preliminary Experimental Results Conclusions and Future Work Taxonomy Outline • • • • • • • Motivation Taxonomy Problem Definition The Palm-tree Index Structure Traversal Algorithms Preliminary Experimental Results Conclusions and Future Work Problem Definition • Let S be a set of N keys (e.g., images or videos) and q be a query • B+-tree-like index is constructed over S • Study how to use human workers to search the index • Workers perform subjective comparisons between the query image and tree keys, and make subjective decisions, e.g., – Less than, greater than, almost the same – Better, worse, almost the same – Cheaper, more expensive, almost the same Outline • • • • • • • Motivation Taxonomy Problem Definition The Palm-tree Index Structure Traversal Algorithms Preliminary Experimental Results Conclusions and Future Work Index Structure Why B+-tree? What is tree order and height? How to construct tree? What are performance metrics? Index Structure • Why B+-tree? – To obtain predictive query cost – Cost reduction with more keys per node • How is the tree order and height determined? – Set by the ability of workers to process at once a specific number of keys Index height Fixed dataset size Error Fixed height Error Error Fixed order Index order Order increase Height decrease Index Construction: How to grow a palm tree? • Key associated with some “Quantitative Value” – Keys have a subjective property and an associated quantitative value – Index constructed based on the quantitative value – Example: Damaged car images with repair cost • Key car image • Subjective property car damage • Qualitative value repair cost 500 1000 200 100 100 200 500 1000 Index Construction: How to grow a palm tree? (Cont’d) • Key associated with some “Qualitative Property” • Keys have a subjective property only • Index constructed by successive insertions • e.g. images of butterflies to be ordered based on beauty Performance Metrics • What are performance metrics? – Error: Distance between ground truth and selected result Error – Cost: Total number of tasks to complete a job Cost Outline • • • • • • • Motivation Taxonomy Problem Definition The Palm-tree Index Structure Traversal Algorithms Preliminary Experimental Results Conclusions and Future Work Traversal Algorithms • How to descend the tree? – Leaf-only aggregation – All-level aggregation – All-level aggregation with backtracking Leaf-Only Aggregation Budget: 12 Tasks per worker w2 4 4 4 w3 w1 9 5 13 3 2 7 4 1 2 3 4 6 11 8 5 6 7 8 10 15 12 14 16 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 • Even budget distribution – Number of workers = Budget/Tree Height All-Levels Aggregation Budget: 12 w2 9 w1 w3 Tasks per level 3 3 3 3 5 w3 3 2 w2 7 4 1 2 3 4 6 13 w1 11 8 5 6 7 8 10 15 12 14 16 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 • Even budget distribution – Replication per level = Budget/Tree Height All-Levels Aggregation EDE Budget: 12 9 3 tasks per level 6 3 2 1 5 3 2 7 4 1 2 3 4 1.5 13 6 11 8 5 6 7 8 10 1 15 12 14 16 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 • Uneven budget distribution based on – Probability of distance d error at level l: Pdl – Expected Distance Error per level: EDE .5 Algorithms: Crowd-Search Backtracking All-Levels Aggregation Node A 9 Node C Node B 5 13 Node D 3 2 7 4 1 2 3 4 6 11 8 5 6 7 8 10 15 12 14 16 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Outline • • • • • • • Motivation Taxonomy Problem Definition The Palm-tree Index Structure Traversal Algorithms Preliminary Experimental Results Conclusions and Future Work Preliminary Experimental Results Experimental Setup • Squares dataset – Generated 200 images of squares with different sizes • Cars dataset – 1300 image of used cars associated with desired selling prices – Collected using a custom crawler from the Craigslist Website • Crowd: – Students in the DB Group at Purdue (and their spouses) – (IRB Approval) Preliminary Experimental Results Sample task Preliminary Experimental Results Sample task Preliminary Experimental Results • Mean Error while changing the tree fanout and the number of workers (replications) • Higher error on cars dataset • Error increases as fanout increases • Error decreases as number of replications increase • All-levels aggregation has less error than leafonly aggregation Preliminary Experimental Results • Mean Cost while changing the tree fanout and the number of workers (replications) Error • The taller the tree the higher the cost • Higher cost on the cars dataset (has more keys) • More replications involve higher cost Fixed dataset size Order increase Height decrease Outline • • • • • • • Motivation Taxonomy Problem Definition The Palm-tree Index Structure Traversal Algorithms Preliminary Experimental Results Conclusions and Future Work Conclusions and Future Work • Conclusions – The Palm-tree allows employing humans to perform index operations on keys that cannot be indexed by computer • Future Work – More extensive experimental evaluation – Mathematical analysis – Multi-dimensional indexing Questions?