Human Origins in Africa
advertisement

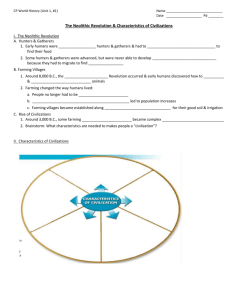
Chapter 1: Sec. 1 • Describe key scientific findings about human origins. • List human achievements during the Stone Age. • Trace emergence of modern humans. • State discoveries about early humans. Categorizing Forming and Supporting Opinions Making Inferences Drawing Conclusions Recognizing Effects Comparing Geography Environment Interaction Synthesizing ❑ Interact with History ❑ Discuss MAIN IDEA: Fossil evidence shows that the earliest humans originated in Africa and spread across the globe. ❑ Discuss WHY IT MATTERS NOW : The study of early human remains and artifacts helps in understanding our place in human history. Define the following Terms and Names ARTIFACT CULTURE HOMINID PALEOLITHIC AGE NEOLITHIC AGE TECHNOLOGY HOMO SAPIENS PAGE 11 QUESTIONS 3, 4 ,and 5 What were the earliest Humans like? Scientists use a variety of ways to research and learn more about how, when and where early humans developed. Archaeologists are specially trained scientists who work like detectives to uncover the story of prehistoric people. Since prehistoric human did not have written language It is necessary to learn from existing evidence left behind such as bones and artifacts. Artifacts are human made objects such as tools and jewelry …. These items might hint at how people lived, worked, dressed, and perhaps if they had a belief system Common Practices ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ What people eat, wear, jewelry, What sports or games they play Tools and Technology Social Customs Work Shared Understandings ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Language Symbols Religion Values Arts, music Political beliefs Social Organization ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Family Class and caste structure Relationships between individuals and community Government Economic systems View of authority Friends Religion Family Media Government You School 1970’s in East Africa footprints found resembling those of humans Found by Dr. Mary Leakey these prints belong to a hominid now know as australopithecines 1974 Ethiopia Africa The oldest human remains found A female hominid Lucy was only 1.1 m (3 ft. 7 in) tall, weighed 29 kg (64 lbs.) and looked somewhat like a Common Chimpanzee 2.5 million to 8000 BCE Invention of tools, mastery of Fire, development of Language Objectives: Students will • List technological and artistic achievements of the Paleolithic Age. • Describe the Neolithic Revolution. • Explain the growth of villages. Outlining Analyzing Primary Sources Making Inferences Skill builder: Map Summarizing Discuss MAIN IDEA: The development of agriculture caused an increase in population and the growth of a settled way of life. Discuss WHY IT MATTERS NOW: New methods for obtaining food and the development of technology laid the foundations for modern civilizations. Nomad Hunter-gatherer Neolithic revolution Slash and burn farming Domestication Page 19 Questions 3, 4, and 5 Making of tools Wolf Dog Objectives Students will • Explain how villages grew into cities. • List the characteristics of civilization. • Describe how the city of Ur exemplifies early civilizations Summarizing Drawing Conclusions Making Inferences Analyzing Causes Recognizing Effects Discuss MAIN IDEA: Prosperous farming villages, food surpluses, and new technology led to the rise of civilizations. Discuss WHY IT MATTERS NOW: Contemporary civilizations share the same characteristics typical of ancient civilizations. Civilization Specialization Artisan Institution Scribe Cuneiform Bronze Age Barter Ziggurat Questions Page 23 Numbers 1, 3, 4, and 5 How Civilization Develops 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Advanced Cities Specialized Workers Complex Institutions Record Keeping Advanced Technology Village or City is not determined by its size of population but rather its design. City center to foster trade and markets Centers for religious observance Site for retail and trade shops Persons that do a particular job or task artisan Merchants Soldiers Priests Scribes Farmers Weavers Government officials Metal workers Formal System of Government Priests with official political and religious authority; Religious ceremony Education to train those in a specific job such as scribes Need to learn established written language cuneiform Potters Wheel Metal work---Bronze ( 88% copper 12% tin ) How did the surplus of food help develop specialization of work? Why does a city such as Ur need a formal Government? Why did record keeping become important in Ur?