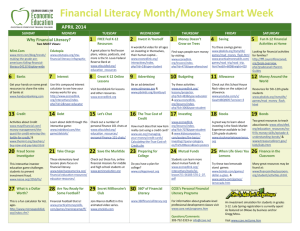
Economics and the Common Core
advertisement

The Common Core State Standards Initiative Who’s behind it? What’s it all about? www.corestandards.org CCSSI Mission and Goals Provide a clear, consistent understanding of what students are expected to learn Be robust and relevant to the real world Position US students to compete successfully in the global economy. Adapted from: The National Governors Association Center for Best Practices (NGA Center) and the Council of Chief State School Officers (CCSSO) Creating the Standards International Benchmarking Feedback and Review Evidence and Research Based International Benchmarking Used standards from high-performing countries and provinces to inform content, structure, rigor, coherence and language. Feedback and Review Postsecondary Faculty K-12 Faculty and staff State curriculum and assessments experts Researchers National organizations Evidence and Research Based Scholarly research on vocabulary, speaking, and listening Surveys on the skills students need to enter college and workforce training Assessment data on college and career readiness performance Common Core Adoptions Question: The Common Core Standards are about math and ELA. Why are they important to us? Robust and relevant to the real world Set expectations for what students should learn, but not how Focus on learning skills, not content Question: The Common Core Standards are about math and ELA. Why are they important to us? Teachers are struggling to figure out how to teach the Common Core Provides an opening to integrate economics and financial literacy into math and English classrooms ○ See: http://www.leginfo.ca.gov/pub/13-14/bill/asm/ab_0151- 0200/ab_166_bill_20130311_amended_asm_v98.html English Language Arts and Literacy in History/Social Studies Design and Organization Reading Writing Speaking and Listening Language Media requirements blended throughout Reading Comprehension (Standards 1−9) Range of reading and level of text complexity (Standard 10, Appx A and B) Key Advances Addresses reading and writing across the curriculum Balances literature and informational texts Focuses on text complexity and what students read Writing Writing types/purposes (Standards 1−3) Key Advances Emphasizes argument and informative/explanatory writing Uses source documents (evidence) Speaking and Listening Comprehension and collaboration (Standards 1−3) Key Advances Includes formal and informal talk Language Knowledge of language (Standards 1−3) Vocabulary (Standards 4−6) Key Advances Acquire general academic and domain-specific words and phrases Mathematics Standards Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them Reason abstractly and quantitatively. Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others Model with mathematics Use appropriate tools strategically Attend to precision Look for and make use of structure Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning Points of Intersection: ELA/Literacy Students use informational texts Students engage in research Students use academic language and domain specific language Points of Intersection: Mathematics Example: The Rule of 72 Show mathematically in general terms or by using graphs and examples that this rule is correct. Example: Becoming a Millionaire Assume that you are 18 years old and drink a latte a day. Show that under some reasonable set of assumptions that if you give that up and invest the money saved at historical interest rates you will be a millionaire by time you’re 60. Resources Council for Economic Education www.councilforeconed.org econedlink www.econedlink.org/ccss/ Council for Economic Education Council for Economic Education econedlink econedlink econedlink Lessons 7% 12% 67% 14% K-2 lessons 3-5 lessons 6-8 lessons 9-12 lessons econedlink Interactives 5% 50% 11% 33% K-2 interactives 3-5 interactives 6-8 interactives 9-12 interactives http://sdcee.org