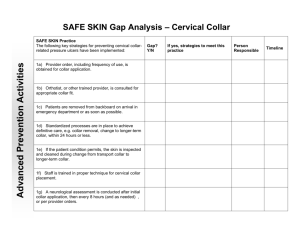
Goodbye 19th Century Math Courses
advertisement

Goodbye 19th Century Math Courses – Hello . . . Modern Accelerated Pathways Amy Getz Strategic Implementation Lead, Higher Education Team an initiative of the Charles A. Dana Center and the Texas Association of Community Colleges Other Countries’ Average Scale Score Math Performance on 8th Grade TIMSS Compared with the U.S. Number of Countries 60 50 9 40 30 14 20 7 10 5 6 6 8 11 Higher than the U.S. Same as the U.S. Lower than the U.S. 37 28 25 17 0 1999 2003 2007 2011 Source: Data taken from the Trends in International Mathematics and Science Study (TIMSS), accessed Jan 10, 2013 at http://nces.ed.gov/timss/index.asp. Computations of categories by the Charles A. Dana Center. 2 2 College Readiness Has Increased TSI Ready Students - All Texas Higher Ed. Institutions 100% 90% 2003 80% 2012 88% 80% 70% 60% 50% 40% 2003 37% 2012 45% 30% 20% 10% 0% Community College University Texas Higher Education Coordinating Board. (2004 & 2013). College Readiness Has Increased 90% TSI Readiness Increase By Race/Ethnicity- All Texas Higher Ed. Institutions 83% 80% 70% White 69% 66% 60% 56% 50% 40% 30% Hispanic/Latino 43% African American 31% African American Hispanic/Latino 20% White 10% 0% 2003 2012 Texas Higher Education Coordinating Board. (2004 & 2014). Source: Michael Marder, 2012. Source: Michael Marder, 2012. The Transition to College is Tough... Progression through Developmental Math Sequence Orange and Black: Percent out of original 100% at each step with duplication, i.e., students who continue are counted in multiple steps 41% Enroll 57% Pass 82% Enroll Referred to Lev. 3 100% 3 levels below Completed 16% 22% Enroll Not completed: 6% 29% Pass Not enrolled 7% 2 levels below Not completed: 12% Not enrolled 16% Not completed:25% Not enrolled 18% 1 level below Blue: Percent out of original 100% without duplication, i.e., each student is counted once Bailey, T. (2010). National Center for Postsecondary Research For What Purpose? Is the obstacle of the traditional algebra-based developmental math sequence justified? 8 Select Math Use All U.S. Workers 20% Algebra I 19% 18% 16% 14% 12% 10% Statistics 11% Algebra II 9% 8% 6% Calculus 5% 4% 2% 0% Handel, M.J. (2007). 35% Statistics Is Used More Than Algebra II 35% 30% 30% 25% 25% 20% 15% 10% 5% Upper Blue Upper Collar White 16% Collar 14% Lower Blue All Collar 9% Lower 8% White Collar Service 3% 2% 0% Upper White Collar 22% Upper Blue Collar 29% Lower Blue Collar 15% 20% 15% 10% All 11% Lower White Collar 5% 5% Service 2% 0% Algebra II Statistics Handel, M.J. (2007). A Dilemma... Encouraging more students to pursue STEM fields... Without institutionalizing inappropriate obstacles for students. 12 Source: David Bressoud - http://www.macalester.edu/~bressoud/talks/2011/portland-apcalc.pdf STATISTICS PATHWAY is designed for students seeking a college-level statistics course as part of their general education requirement for majors in fields including: • Nursing • Social Work • Criminal Justice QUANTITATIVE REASONING PATHWAY is designed for students pursuing a field of study in which general education math is a requirement. These fields include majors in: • Communications • Graphic Design • Paralegal STEM-PREP PATHWAY is designed for students seeking a STEM or mathematicsintensive major in fields including: • Petroleum Engineering • Computer Science • Chemistry 14 The New Mathways Project A systemic approach to improving student success by reforming developmental and gateway mathematics based on four fundamental principles: 1. Multiple pathways aligned to specific fields of study 2. Acceleration that allows students to complete a collegelevel math course more quickly 3. Intentional use of strategies to help students develop skills as learners 4. Curriculum design and pedagogy based on proven practice 15 What Does it Take? Changes in state policy Coordination with 4-year institutions on transfer Coordination with programs of study to set new math requirements Institutional changes to advising New curriculum to support changes in content and instructional strategies Modify student supports such as tutoring 16 What have we achieved? In first year: Project wide: 60% increase in students earned college credit in half the time In five colleges: 280% increase in students earning college credit in half the time In second year: 20 colleges implementing courses 14 colleges preparing to implement next year 17 The Faces Behind the Data 18 Want to know more about the NMP? Come to the breakout session at 3:15. Sign up to receive monthly updates about the NMP by contacting us at: mathways@austin.utexas.edu 19 Contact Information General information about the Dana Center: www.utdanacenter.org Higher Education work: www.utdanacenter.org/higher-education/ Amy Getz (general project issues): getz_a@austin.utexas.edu 20 About the Dana Center The Charles A. Dana Center at The University of Texas at Austin works with our nation’s education systems to ensure that every student leaves school prepared for success in postsecondary education and the contemporary workplace. Our work, based on research and two decades of experience, focuses on K–16 mathematics and science education with an emphasis on strategies for improving student engagement, motivation, persistence, and achievement. We develop innovative curricula, tools, protocols, and instructional supports and deliver powerful instructional and leadership development. 21