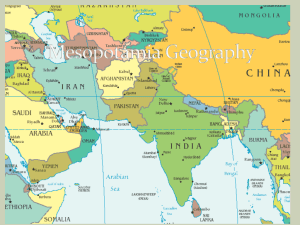
Ancient Mesopotamia
advertisement

Ancient Mesopotamia 0011 0010 1010 1101 0001 0100 1011 1 Stripes Team L. Nabulsi All information in this PowerPoint came from Banks, J. World Adventures in Time and Place. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2001. 2 4 Timeline 0011 0010 1010 1101 0001 0100 1011 • • • • • 4000 BC – Mesopotamia 3000 BC - Ur 2300 BC – Kish 1800 BC – Babylon 1250 BC - Canaan 1 2 4 Vocabulary 0011 0010 1010 1101 0001 0100 1011 • • • • • • Plateau Drought Fertile Crescent Tigris River Euphrates River Mesopotamia 1 2 4 Geography of the Fertile Crescent 0011 0010 1010 1101 0001 0100 1011 1 2 4 This is a direct quote so it needs quotation marks around it. The period goes outside the Parentheses which give the documentation information. If you used this quote in a paper, however, you would indent it because of its length, over 25 words. Read Aloud 0011 0010 1010 1101 0001 0100 1011 • “For six days and seven nights the wind blew, flood and tempest [storm] overwhelmed the land; when the seventh day arrived the tempest [and] flood…blew themselves out. The sea became calm, the …wind grew quieter, the flood held back….Silence reigned, for all mankind returned to clay” (Banks 104). 1 2 4 NOTE: clay” (Bank 104). The Big Picture 0011 0010 1010 1101 0001 0100 1011 • The Fertile Crescent was located northeast of Egypt and was developing at the same time as Egypt. • It is called a crescent because it is shaped “like a quarter moon” (Banks, 104). • Modern countries that are located in the Fertile Crescent are Lebanon, Israel, Syria and Iraq. 1 2 4 The land of two rivers 0011 0010 1010 1101 0001 0100 1011 • The Tigris River and the Euphrates River made the rocky, desert a fertile valley. • These rivers compare to the Nile in the way they affected the lives of the people near the river both positively and negatively (Banks, 104). 1 2 4 Between Two Rivers 0011 0010 1010 1101 0001 0100 1011 pp. 105-107 1 2 4 Between two rivers 0011 0010 1010 1101 0001 0100 1011 • The area between the two rivers was called Mesopotamia, which is its meaning in Greek. • Present day Iraq. 1 2 4 From Mountains to the Sea 0011 0010 1010 1101 0001 0100 1011 • Mountains – Taurus Mountains – the source of the two rivers in present-day Turkey • Flow from mountains through canyons to valleys below • Extend to a plateau in “present-day Iraq” (Banks 105). • Plateau – • Southern Iraq – land is lower where rivers eventually empty into the Persian Gulf 1 2 4 Flood • Mesopotamians “depended on river deposits of silt” (Banks 105). 0011 0010 1010 1101 0001 0100 1011 • Farmers challenged – Flooding not regular – Often at harvest time – Cost crops and lives – Farms needed protection – Crops needed watering – South Mesopotamia experienced droughts – Northern Mesopotamia had sufficient water but not large areas of fertile soil - Less silt in the North than in the South - South known for fertile fields 1 2 4 Maps that might help 0011 0010 1010 1101 0001 0100 1011 1 2 4 Assignment 0011 0010 1010 1101 0001 0100 1011 Take a piece of paper. Divide it in half horizontally. On the back of the paper, put your name, Social Studies, Fertile Crescent, date On the front which has a line halfway down the page horizontally, draw the map of the Nile on page 71 in the upper half of the page. Give an arrow to indicate the flow of the river. Determine from a world map the longitude and latitude. Mark these degrees on the map. Color the map and code the colors. On the lower half of that same page, draw a map of the Fertile Crescent as seen on p. 105. Indicate the longitude and latitude. Color code the map. 1 2 4 In Class Assignment: Can you compare the impact of the Nile River with the Tigris and Euphrates? 0011 0010 1010 1101 0001 0100 1011 1 2 4 • I. Compare/contrast geography and effect of two rive cultures, the Nile River Valley and the Fertile Crescent – A. River Outline Information from VENN diagram • 1. Nile • 2. Tigris and Euphrates – B. Source 0011 0010 1101 0001 0100 1011 • 1.1010 Nile Source – mountains in Africa • 2. Fertile Crescent source – Taurus Mountains – C. Flow • 1. Nile – south to north • 2. T and E – north to south D. Empties 1. Nile – Mediterranean Sea 2. T and E – Persian Gulf – E. Carries silt – F. Effect on people • 1. Nile – predictable so they could plan where to live and when to harvest • 2. Fertile Crescent – unpredictable causing loss of life – g. Effect on land • 1. Nile – fertile land along the river which allowed for the development of land the length of the river • 2. Fertile Crescent – a. North as water but not much silt or land area – b. South had land area and silt but no water 1 2 4 From River to Field 0011 0010 1010 1101 0001 0100 1011 • • • • • PROBLEMS: Fall – Planting season in south; no water Spring – Harvest time, but floods came. SOLUTIONS Built “water-control and irrigation systems” (Banks 106). • See page 106 and http://www.mesopotamia.co.uk/geography/challen ge/cha_set.html 1 2 4 Farming in Ancient Mesopotamia 0011 0010 1010 1101 0001 0100 1011 • Crops grown in Mesopotamia – – – – – – – – – – Barley Wheat Beans Onions Lettuce Cucumbers Spice plants Date Palm Apple Pomegranate • Animals – Sheep • • – – 1 Goats Cattle • • • • • Milk Wool 2 Work animal Milk Leather Meat 4 Wild animals – – Jackals Lions Why it matters 0011 0010 1010 1101 0001 0100 1011 • Uninviting area of the world developed into one of the “earliest civilizations developed” (Banks 107). • Geography – the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers made the civilization • Farmers solving problems – 1 2 4 – managing the geography- made it work – Over producing lead to growth. Assignment- Cause/Effect Problem/solution 0011 0010 1010 1101 0001 0100 1011 • Journal Topic: You are a farmer in the North visiting in the South during the flooding season. Make a speech to the leaders of the south showing how the ability of man to handle the problems of the geography will result in prosperity for the farmers. Outline by listing each problem and then give the solution. Write • Greet your audience and tell the purpose of your speech. • Give the problems • Give the solution • End with a call for action 1 2 4 Research • Find information about devastating three floods along the Mississippi River. • What season the1011 year did they happen? 0011 0010 1010 1101 0001of 0100 • What was destroyed? • What are other effects? • What was learned from these floods? • What adjustments were made? • Did this culture handle the situation as well as the Egyptian and Mesopotamians did? • Place this information on a chart. • Write a five paragraph paper. Use MLA template. Document and have a works cited page. 1 2 4 Location When Effects Learned Adjustments 0011 0010 1010 1101 0001 0100 1011 Flood 1 Flood 2 Flood 3 1 2 4 Outline for paper • Introduction – Give historical background about Egypt and Mesopotamia – Floods still exist – Thesis: Modern man does/not learn and conquer nature the way ancient man did. • Development 0011 0010 1010 1101 0001 0100 1011 – Flood One – Topic sentence what/where and if anything learned simply stated • Where • When • Effects • Learned • Adjustments • Evaluate – Flood Two - Topic sentence what/where and if anything learned simply stated • – 1 • When • Effects • Learned • Adjustments • Evaluate Flood Three - Topic sentence what/where and if anything learned simply stated • • Where Where • When • Effects • Learned • Adjustments • Evaluate Conclusion – Who learned the most from nature and prospered 2 4 Grade for this unit • 1. Answer the questions on page 107. Answer in complete sentences. (10 points- in class) 0011 0010 1101 1011 • 2.1010 Draw the0001 maps0100 of the Nile and Fertile Crescent as indicated. (25 points – in class) • 3. Make a Venn diagram comparing/contrasting the Egypt and Mesopotamia. (10 points – in class) • 4. Write a journal entry (part of notebook grade) • 5. Make a chart for the research. ( 25 points – in class) • 6. Write the paper from the chart: MLA, Outline, five paragraph paper with documentation, work cited page. (100 points – in class) • 7. Ticket Outs – (10 points each) • 8. Test – (100 points) 1 2 4 Timeline 0011 0010 1010 1101 0001 0100 1011 • January 25 – Read pp. 104-107l do study questions on p. 107 • January 29 – Go over PP in class, TO 1, Venn Diagram. • February 2 – TO 2, Write journal (outline, write rough draft, peer evaluation, correct errors) • February 6 – TO 3 -Do research on floods, make charts • February 8 – TO 4 -Write outline for paper; fill in and document as you go (last para. #) or “Word in title” para. #). • February 12 – TO 5 – Test ; Read pp. 108- 115 and do questions p. 115. 1 2 4