Parts of the tree - Industrial Techniques grade 8
advertisement

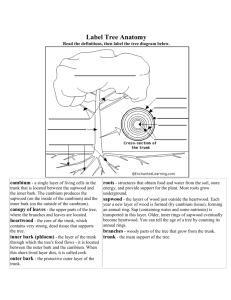
Parts of the tree Grade 8 Cross section of the tree trunk Parts of the tree The tree trunk consist of eight parts .They are: • Sapwood • Heartwood • Cambium • Pith • Annual rings • Medullary Ray • Bark • Inner Bark Label diagram 1. Sapwood • Sapwood is the outer part of the tree responsible for receiving the water and minerals from the roots and conducting them around the tree to the leaves as well as for food storage. It is located between the heartwood and the cambium. Location of the sapwood 2. Heartwood • Heartwood is the non-active part of the treeusually darker in colour than sapwood- and provides the tree with the rigidity often necessary to support the crown. The most durable wood for timber is from this part of the tree. It is located between the pith and the sapwood. Location of the heartwood 3. Medullary Rays • A ray consist of a strip of wood cells that allow sap to move transversely through the wood and provide for storage of surplus food and its movement when required . They may appear to radiate from the pith to the inner bark ,hence the name medullary ray is often used. Location of the medullary rays 4. Inner bark / bast • The inner bark distributes the food substances provided by the leaves through the whole of the tree. After one growing season it will become inactive as a mean of conducting food ; it takes on a new role as the outer bark. It is located between the cambium and the outer bark. Location of the inner bark / bast 5. Bark • The bark makes up the outer sheath of the whole tree. It serves to protect the inner parts of the tree from: • Fungal attack , Mechanical abrasion by animals and other agents , Extreme temperatures and Insect attack. Location of the bark 6. Pith • The pith is the center of the tree. The pith is the result of the tree’s earliest growth –a sapling –wood immediately surrounding it is called ‘juvenile wood’, which is not very desirable as timber. Location of the pith 7. Cambium • Cambium is the sleeves of cells located between the sapwood and the inner bark which covers the whole of the tree-that is its trunk, branches and twigs. These cells are responsible for growth of the tree both its girth[distance around the trunk] and height. As the cells formed during the growing season they become sub-divided in such a way that new cells are added to both the sapwood and the inner bark. Location of the cambium 8. Annual rings • This implies that the rings of wood cells ,which appear as bands ,are reproduced each year and by counting the number of rings we know how old the tree was when it was cut down. Location of the Annual Rings classwork • 1. Label the cross section of the tree trunk classwork • 2. Give function of each part identified